Abstract
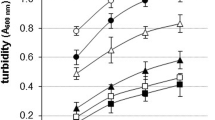
Research was carried out on the influence of heat treatment during isoelectric precipitation on the functionality of the resulting isolates prepared from “low-heated”, undenatured, defatted soy flour. The isoelectric dispersions were heated at 50°C, 60°C, 65°C or 70°C for 30 min and characterized for solubility, water absorption capacity, oil absorption capacity, viscosity and gel properties. The effect of heat treatment during isoelectric precipitation was reflected by all the functional properties. The soy isolated heated at 60°C showed remarkably different flow characteristics. It yielded the most viscous dispersions and the strongest gels and also the highest water absorption capacity value. Simple and multiple lineal regression models were used to provide a description of the relationship between the different properties studied. Significant correlations were found between gel viscosity and water absorption capacity. Gel characteristics also correlated significantly with viscosity of 20% dispersions. Viscosity of dispersions correlated to solubility or to water absorption capacity, depending on protein concentration. That dependence was quantified and a highly significant multiple correlation was found between viscosity and the independent variables of log solubility and water absorption capacity.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Kinsella, J.E., S. Damodaran and B. German, inNew Protein Foods, edited by A.M. Altschul and H.L. Wilcke, Academic Press, Orlando, FL, Vol. 5, 1985, p. 107.
Johnson, D.W.,J. Am. Oil Chem. Soc. 47:402 (1970).
Pour-El, A.,Am. Chem. Soc. Symp. Ser. 147:1 (1981).
A.A.C.C. Approved Methods, Vol. 1, American Association of Cereal Chemists, Inc., St. Paul, MN, 1976, Method 44-31.
A.O.A.C. Official Methods of Analysis of the Association of Official Analytical Chemists, Vol. 1, edited by William Horwitz, Association of Official Analytical Chemists, Washington, DC 20044, 1980, Method 2057.
AOCS Official and Tentative Methods, Vol. 1, edited by R.O. Walker, American Oil Chemists' Society, Champaign, IL, 1981, Method Ba 11–65.
Torgensen, H., and R. Toledo,J. Food Sci. 42:1615 (1977).
Kanterewicz, R.J., B.E. Elizalde, A.M.R. Pilosof, and G.B. Bartholomai, —Ibid. 52:1381 (1987).
Hermannsson, A.M., and M. Lucisano, —Ibid. 47:1955 (1982).
Hermansson, A.M.,J. Texture Studies 9:33 (1978).
López de Ogara, M.C., F. Bercovich, A.M.R. Pilosof and G.B. Bartholomai,J. Food Technol. 21:279 (1986).
Voutsinas, L.P., E. Cheung and S. Nakai,J. Food Sci. 48:26 (1983).
Urbanski, G.E., L.S. Wei, A.I. Nelson, and M.P. Steinberg, —Ibid. 48:691 (1983).
Schmidt, R.H., inProtein Functionality in Foods ACS Symposium Series 147, edited by J. Cherry, American Chemical Society, Washington, DC, 1981, p. 131.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
About this article
Cite this article
López de Ogara, M.C., Delgado de Layño, M., Pilosof, A.M. et al. Functional properties of soy protein isolates as affected by heat treatment during isoelectric precipitation. J Am Oil Chem Soc 69, 184–187 (1992). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02540573
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02540573