Abstract
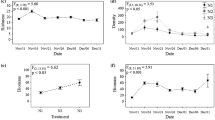
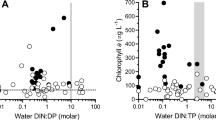
The results of long-term, full-scale experiments in biomanipulation (in the closer sense of top-down control of the food web) in water bodies having extremely different phosphorus loads reveal that there is a close connection between the efficiency of food web manipulation and the nutrient situation in the particular water body. Top-down control provides a high probability of improving water quality with respect to Secchi depth and algal biomass only if it is connected with a decrease in the in-lake phosphorus. If that decrease in phosphorus is not achieved for different reasons, the high probability of an efficient top-down control is limited to zooplankton and to structural changes in the phytoplankton. A lake-specific ‘biomanipulation-efficiency threshold’ of the phosphorus load should not be exceeded. The results show that integrated water quality control, i.e. a combination of the strategy of load reduction with the strategy of ‘ectotechnology’, seems to be a very promising way.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Andersson, G.: The role of fish in lake ecosystems—and in limnology. In: Bosheim, S., and Nicholls, M. (ed.): Interactions between trophic levels in freshwaters, Oslo 1984, p. 189–197 (1984).
Andersson, G., Berggren, H., Cronberg, G., and Gelin, C.: Effects of planktivorous and benthivorous fish on organisms and water chemistry in eutrophic lakes. Hydrobiologia59, 9–15 (1978).
Andersson, G., and Cronberg, G.:Aphanizomenon flos-aquae and largeDaphnia—An interesting plankton association in hypertrophic lakes. In: Bosheim, S., and Nicholls, M. (ed.): Interactions between trophic levels in freshwaters, Oslo 1984, 63–76 (1974).
Benndorf, J.: Kausalanalyse, theoretische Synthese und Simulation des Europhierungsprozesses in stehenden und gestauten Gewässern, p. 1–165. Dissertation B, Technische Univ. Dresden, Fakultät für Bau-, Wasserund Forstwesen (1979).
Benndorf, J:: Objectives and unsolved problems in ecotechnology and biomanipulation: A preface. Limnologica19 (1) (1987 in press).
Benndorf, J., Kneschke, H., Kossatz, K., and Penz, E.: Manipulation of the pelagic food web by stocking with predacious fishes. Int. Revue ges. Hydrobiol.69, 407–428 (1984).
Benndorf, J., Schultz, H., Benndorf, A., Unger, R., Penz, E., Kneschke, H., Kossatz, K., Dumke, R., Hornig, U., Kruspe, R., and reichel, S.: Food-web manipulation by enhancement of piscivorous fish stocks: Long-term effects in the hypertrophic Bautzen reservoir. Limnologica19 (1) (1987, in press).
Benndorf, J., Uhlmann, D., and Pütz, K. (1981): Strategies for water quality management in reservoirs in the German Democratic Republic.—Water Quality Bull.6 (3), 68–73 and 90.
Björk, S.: Restoration of degraded lake ecosystems. Proceedings of the MAB Project 5 Regional Workshop ‘Land use impacts on lake and reservoir ecosystems’, Warsaw, 26 may to 2 June 1978, p. 196–219 (1978).
Böttger, A. and Köhler, J.: Langzeiteffekte der Biomanipulation im Steinbruch-Restgewässer Gräfenhain, p. 1–31. Technische Univ. Dresden, Sektion Wasserwesen, Bereich Hydrobiologie, Jahresarbeit (1986 unpublished).
Edmondson, W.T., and Litt, A.H.:Daphnia in Lake Washington. Limnol. Oceanogr.,27, 272–293 (1982).
Edmondson, W.T., and Litt, A.H.: Mt. St. Helens ash in lakes in the lower Grand Coulee, Washington State. Verh. int. Verein. Limnol.22, 510–512 (1984).
Edmondson, W.T., and Abella, S.: Unplanned biomanipulation in Lake Washington. Limnologica19 (1) (1987, in press).
Goad, J.A.: A biomanipulation experiment in Green Lake, Seattle, Washington. Arch. Hydrobiol.102 (2), 137–153 (1984).
Henrikson, L., Nyman, H.G., Oscarson, H.G., and Stenson, J.A.: Trophic changes, without changes in the external nutrient loading. Hydrobiologia68, 257–263 (1980).
Hrbaček, J., Dvorakova, M., Kořinek, V., and Prochazkova, L.: Demonstration of the effect of fish stock on the species composition and the intensity of metabolism of the whole plankton association. Verh. int. Verein. Limnol.14, 192–195 (1961).
Hrbâcek, J., Desortova, B., and Popovsky, J.: The influence of the fishstock on the phosphorus-chlorophyll ratio. Verh. internat. Verein. Limnol.20, 1624–1628 (1978).
Kasprzak, P., Benndorf, J., Koschel, R., and Recknagel, F.: Applicability of food-web manipulation in the restoration program of a hypertrophic stratified lake: Model studies for Lake Haussee (Feldberg, GDR). Limnologica19 (1) (1987, in press).
Lammens, E.H.R.R.: Trophic interactions in the hypertrophic lake Tjeukemeer: top-down and bottom-up effects in relation to hydrology, predation and bioturbation during the period 1974–1985. Limnologica19 (1) (1987, in press).
Lynch, M.: Predation, competition and zooplankton community structure: An experimental study. Limnol. Oceanogr.24, 253–272 (1979).
Lynch, M., and Shapiro, J.: Predation, enrichment, and phytoplankton community structure. Limnol. Oceanogr.26, 86–102 (1981).
Lynch, M., and Shapiro, J.: Manipulations of planktivorous fish—Effects on zooplankton and phytoplankton. In: Shapiro, J., Forsberg, B., Lamarra, V., Lindmark, G., Lynch, M., Smeltzer, E., and Zoto, G.: Experiments and Experiences in Biomanipulation, p. 158–188. Interim Report No. 19, Limnological Research Center, Univ. of Minnesota, Minneapolis, Minnesota 1982.
Reinertsen, H., and Olsen, Y.: Effects of fish elimination on the phytoplankton community of a eutrophic lake. Verh. int. Verein. Limnol.22, 649–657 (1984).
Schultz, H.: Untersuchungen über die Grösse und Struktur des Fischbestandes sowie den Nahrungskonsum ausgewählter Fischarten in zwei Staussen unterschiedlichen Trophiegrades, p. 1–141. Dissertation A, Technische Univ. Dresden, Fakultät für Bau-, Wasser- und Forstwesen (1983).
Schultz, H.: An acoustic fish-stock assessment in the Bautzen reservoir Limnologica19 (1) (1987, in press).
Shapiro, J.: Effects of rotenone in Wirth Lake. In: Shapiro, J., Forsberg, B., Lamarra, V., Lindmark, G.; Lynch, M.; Smeltzer, E., and Zoto, G.: Experiments and experiences in biomanipulation, p. 195–207. Interim report No. 19 of the Limnological Research Center, Univ. of Minnesota, Minneapolis 1982.
Shapiro, J., Forsberg, B., Lamarra, V., Lindmark, G., Lynch, M., Smeltzer, E., and Zoto, G.: Experiments and experiences in biomanipulation, p. 1–251. Interim report No. 19 of the Limnological Research Center, Univ. of Minnesota, Minneapolis 1982.
Shapiro, J., Lamarra, V., and Lynch, M.: Biomanipulation: an ecosystem approach to lake restoration. In: Brezonik, P.L., and Fox, J.L. (ed.): Water Quality Management through Biological Control, p. 85–96. Report No. ENN-07-75-1, University of Florida, Gainesville 1975.
Shapiro, J., and Wright, D.I.: Lake restoration by biomanipulation: Round Lake, Minnesota, the first two years. Freshwater Biol.,14, 371–383 (1984).
Stenson, J.A.E., Bohlin, T., Henrikson, L., Nilsson, B.I., Nyman, H.G., Oscarson, H.G., and Larsson, P.: Effects of fish removal from a small lake. Verh. int. Verein. Limnol.20, 794–801 (1978).
Vollenweider, R.A.: Advances in defining critical loading levels for phosphorus in lake eutrophication. Mem. Ist. ital. Idrobiol.33, 53–83 (1976).
Wright, D.I., and Shapiro, J.: Nutrient reduction by biomanipulation: an unexpected phenomenon, and its possible cause. Verh. int. Verein. Limnol.22 (1), 518–524 (1984).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Benndorf, J. Food web manipulation without nutrient control: A useful strategy in lake restoration?. Schweiz. Z. Hydrol 49, 237–248 (1987). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02538505
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02538505