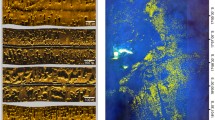
Summary
A correlation between skeletal growth of recent bryozoans and external environmental factors (e.g. abrasion, suspended sediment load) exists in ahermatypic tropical shallow water associations of the Philippines. Yet, the spatial zonation pattern of bryozoan species in a modern Philippine reef exhibits an amazingly high level of stability and order which cannot be readily correlated with external environmental factors. This is due to the observation that zonation correlates with the bryozoan taxa but not with their growth form categories (e.g. flexible-erect). Bryozoans are closely linked with their reef (micro)environment and reef microbiota by feedback control: Interacting biofilms, microbial mats, bryozoans and bryozoan larvae illustrate how such internal functions in a Philippine reef may stabilize the biotope structure as a whole
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bijma, J. &Boekschoten, G. J. (1985): Recent Bryozoan Reefs and Stromatolite Development in Brackish Inland Lakes, SW Netherlands.—Senckenbergiana marit.17/1–33, 163–185, Frankfurt
Bishop, J.D.D. (1988): Disarticulated bivalve shells as substrates for encrustation by the bryozoanCribrilaria puncturata in the Plio-Pleistocene Red Crag of Eastern England.—Paleontology31, 237–253
Bishop, J.D.D. (1989): Colony form and the exploitation of spatial refuges by encrusting Bryozoa.—Biol. Rev.64, 197–218.
Briggs, J. &Peat, F.D. (1990): Die Entdeckung des Chaos. Eine Reise durch die Chaos-Theorie.—German Edition, 330 pp. München (Hanser)
Chafetz, H.S. &Buczynski, C. (1992): Bacterially Induced Lithification of Microbial Mats.—Palaios7/3, 277–293
Cramer, F. (1989): Chaos und Ordnung: Die komplexe Struktur des Lebendigen.—3. Edition, 320 pp., Stuttgart (DVA)
Crisp, D.J. &Ryland, J.S. (1960): Influence of filming and of surface texture on the settlement of marine organisms.—Nature185, p. 119
Cuffey, R.J. (1970): Bryozoan Environment Interrelationships An Overview of Bryozoan Paleoecology and Ecology.—Earth and Mineral Sciences39/6, 41–48
Dick, M.H. &Ross, J.R.P. (1988): Intertidal Bryozoa (Cheilostomata) of the Kodiak Vicinity, Alaska.—133 pp., Bellingham (Center for Pacific Northwest Studies, Western Washington University)
Erben, H.K. (1990): Evolution. Eine Übersicht sieben Jahrzehnte nach Ernst Haeckel.—179 pp., Stuttgart (Enke)
Flügel, E. &Flügel-Kahler, E. (1992): Phanerozoic Reef Evolution: Basic Questions and Data Base.—Facies26, 167–278
Freiwald, A. (1993): Subarktische Kalkalgenriffe im Spiegel hochfrequenter Meeresspiegelschwankungen und interner biologischer Steuerungsprozesse.—Ph. thesis, Christian-Albrecht Universität zu Kiel, 207 pp.
Freiwald, A. (1993): Coralline algal frameworks-Islands within the phaeophytic kelp belt.—Facies29, this volume
Freiwald, A., Henrich, R., Schäfer, P. &H. Willkomm (1991): The significance of High Boreal to Subarctic Maerl Deposits in Northern Norway to Reconstruct Holocene Climatic Changes and Sea Level Oscillations.—Facies25, 315–340
Gall, J. C. &Krumbein, W.E. (1992): Weichkörperfossilien.—Fossilien1/92, 35–49
Geister, J. (1983): Holozäne westindische Korallenriffe: Geomorphologie, Ökologie und Fazies.—Facies9, 173–284
Gordon, D.P. &Mawatari, S.F. (1992): Atlas of Marine Fouling Bryozoa of New Zealand Ports and Harbours.—Miscellaneous Publications, N.Z. Oceanographic Institute107, 1–52
Grobe, H., Willkom, H. &G. Wefer (1985): Internal Structure and Origin of the Double Reefs of North Bohol and the Olango Reef Flat (Philippines).—The Philippine Scientist22, 83–94
Harmelin, J.G. (1990): Deep water crisiids (Bryozoa: Cyclostomata) from the northeast Atlantic ocean.—J. Natur Hist.24, 1597–1616
Henrich, R., Hartmann, M., Reitner, J., Schäfer, P., Freiwald, A., Steinmetz, S., Dietrich, P. &J. Thiede (1992): Facies Belts and Communities of the Arctic Vesterisbanken Seamount (Central Greenland Sea).—Facies27, 71–104
Hillmer, G. (1979): Two abundant species of Recent Reteporidae (Bryoz. Cheil.) in Cebu Island, Philippines.—The Philippine Scientist16, 84–93
Hillmer, G. &Scholz, J. (1991): Artificial Reefs and Bryozoen.—Die Geowissenschaften9/12, 371–377
Howse, P.E. (1979): The Uniqueness of Insect Societies: Aspects of Defense and Integration.—In:Larwood, G. &Rosen, B.R. (eds.): Biology and Systematics of Colonial Organisms: 345–374. London, New York, San Francisco (Academic Press)
Jackson, J. B. C. (1979): Morphological Strategies of Sessile Animals.—In:Larwood, G. &Rosen, B. R. (eds.): Biology and Systematics of Colonial Organisms.—499–555, London (Academic Press)
Jantsch, E. (1992): Die Selbstorganisation des Universums. Vom Urknall zum menschlichen Geist.—2nd. ed. 464 pp., München (Hanser)
Jurgan, H. (1989): Observations on Recent sedimentary environments in the bank belt northwest of Bohol Philippines.—Geol. Jb.B70, 407–428
Krumbein, W. E. (1983): Biogene Lamination-Stromatolith und Biostrom.—Weltenburger Akademie, Erwin Rutte Festschrift, 133–141, Kehlheim/Weltenburg
Krumbein, W. E. &Stal, L. J. (1991): The geophysiology of marine cyanobacterial mats and biofilms.—Kieler Meeresforsch., Sonderh.8, 137–145
Lagaau, R. &Gautier, Y. V. (1965): Bryozoan assemblages from marine sediments of the Rhone Delta, France.—Micropaleontology11, 37–58
Lovelock, J. (1990): The Ages of Gaia. A Biography of Our Living Planet.—252 pp., New York (Bantam)
— (1991): Gaia. The Practical Science of Planetary Medicine.—192 pp., North Sydney (Allen & Unwin)
Martindale, W. (1992): Calcified epibionts as palaeoecological tools: examples from the Recent and Pleistocene reefs of Barbados.—Coral Reefs11/3, 167–177.
McKinney, F. K. & McKinney, N. (1993): Larval behaviour and choice of settlement site: correlation with environmental distribution pattern in an erect bryozoan.—Facies, 29, this volume
McKinney, F.K. &Jackson, J. B. C. (1989): Bryozoan Evolution. —Special Topics in Paleontology 2, 1–238, Boston, (Unwin Hyman)
Mergner, H. &Schuhmacher, H. (1974): Morphologie, Ökologie und Zonierung von Korallenriffen bei Aqaba (Golf von Aqaba, Rotes Meer).—Helgoländer wiss. Meeresunters.26, 238–358
Milliman, J.D. (1990): River Discharge of Water and Sediment to the Oceans.—In:Ittekkot, V., Kempe, S., Michaelis, W. &A. Spitzy (eds.): Facets of Modern Geochemistry.—Festschrift forE. T. Degens: 83–90. Berlin (Springer)
Poluzzi, A. & Coppa, M. G. (1991): Zoarial Strategies to Win Substratum Space inCalpensia nobilis (Esper).—In:Bigey, F. P. (ed.): Bryozoaires Actuels et Fossiles.—Bull. Soc. Sci. Nat. Quest Fr. Mem. HS1, 337–360, Nantes
Rau, N. (1980): Hydrographical and biological properties, and the fishery in the harbor area of Cebu City, Philippines.—Dissertation an der Christian-Albrecht-Universität zu Kiel. 98 pp
Reitner, J. (1993): Modern pacific cryptic microbial crusts linked with bacteria bearing sponges—a model for fossil ‘sponge/crusts reefs’.—Facies29, this volume
Reitner, J. &R. Henrich (1991): Benthos-Gemeinschaften des Vesterisbanken Seamount in der NE-Grönland See (Fs ‘Polarstern’expedition ark VII/1, 1990).—Verh. Deutsch. Zool. Ges, 84. Jahresvers Tübingen, 20. bis 25. Mai 1991.—p. 507. Stuttgart (Fischer)
Riedl, R. &Forstner, H. (1968): Wasserbewegung im Mikrobereich des Benthos.—Sarsia34, 163–188
Ristedt, H. (1985):Cribrilaria Arten (Bryozoa) des Indopazifiks (Rotes Meer, Seychellen, Philippinen).—Mitt. Geol. Paläont. Inst. Univ. Hamburg59, 15–38
Ristedt, H. &Hillmer, G. (1985): The Cheilostomate Bryozoan Fauna from Shallow Waters of the Hilutangan Channel, Cebu, Philippines: Part I.—The Philippine Scientist22, 133–143.
Ryland, J.S. (1970): Bryozoans.—London (Hutchinson). 175 pp
Ryland, J.S. &Hayward, P.J. (1977): British Anascan Bryozoans. Keys and notes for the identification of species.—Linnean Society Synopses of the British Fauna10, 188 pp., London (Academic Press)
Sander, L.M. (1989): Fraktales Wachstum.—In: Chaos und Fraktale.—120–127. Heidelberg (Spektrum)
Schäfer, W. (1962): Aktuo Paläontologie nach Studien in der Nordsee.—666 pp., Frankfurt a. M. (Kramer)
Scheer, B.T. (1945): The development of marine fouling communities.—Biol. Bull. (Woods Hole, Mass.)89, 102–121
Scholz, J. (1990): The significance of Philippine reef and harbor Bryozoa as indicators of environmental stress.—The Philippine Scientist27, 19–26
Scholz, J. (1991a): Monsoon related Settlement Patterns in Reef and Harbor Bryozoans, Philippines.—In:Bigey, F.P. (ed.): Bryozoaires Actuels et Fossiles.—Bull. Soc. Sci. Nat. Quest Fr. Mem. HS1, 409–416
— (1991b): Bryozoanresponse to ‘pollution events’.—N. Jb. Geol. Paläont. Mh.1991, 543–548
— (1991c): Die Bryozoenfauna der philippinischen Riffregion Cebu.—Mitt. Geol. Paläont. Inst. Univ. Hamburg70, 253–403
Scholz, J. &Cusi, M. A. (1991): Paleoecologic implications of modern coral and bryozoan communities from southern Leyte Philippines.—Mitt. Geol. Paläont. Inst. Univ. Hamburg70, 405–431
Scholz, J. & Krumbein, W.E. (in press): Riffentwicklung und Mikroorganismen.—Biologie in unserer Zeit.—Weinheim (VCH)
Schopf, T. J. m. (1969): Paleoecology of Ectoprocts (Bryozoans).—J. Paleont., 43/2, 234–244
Silen, L. (1977): Structure of Adnate Colony Portions in Crisiidae (Bryozoa Cyclostomata).—Acta zool. (Stockh.) D, 227–244
Silen, L. (1980): Colony Substratum Relations in Scrupocellariidae (Bryozoa, Cheilostomata).—Zoologica Scripta9, 211–217
Soule, J. D. &Soule, D. F. (1977): Fouling and Bioadhesion: Life Strategies of Bryozoans.—In:Woollacott, R. M. &Zimmer, R. L. (eds.): Biology of Bryozoans.—437–457, New York (Academic Press)
Sy, J.C. & Herrera, F. S. (1981): Coral Community Structure of a Fringing Reef at Mactan Island, Cebu, Philippines.—In: Proceedings of the 4th Int. Coral Reef Symposium, 2, 263–280. Manila
Taylor, P. D. (1990): Encrusters.—In:Briggs, D. E. G. &Crowther, P. R. (eds.): Paleobiology: A Synthesis.—346–351, Oxford (Blackwell)
Voigt, E. (1988): Wachstums- und Knospungsstrategie vonGrammothoa filiferaVoigt & Hillmer (Bryozoa, Cheilostomata, Ob. Kreide).—Paläont. Z.62/3–4, 193–203
Walch, M., Hamilton, W. A., Handley, P. S., Holm, N. C., Kuenen, J. G., Revsbech, N. P. Rubio, M. A., Stahl, D. A., Wanner, O., Ward, D. M., Wilderer, P. A. &J. W. T. Wimpenny (1989): Group Report: Spatial Distribution of Biotic and Abiotic Components in the Biofilm.—In:Characklis, W. G. &P. A. Wilderer (eds.): Structure and Functions of Biofilms.—Report on the Dahlem Workshop, Berlin: 165–191, Chichester (Wiley)
Winston, J. E. (1988): Life Histories of Free-living Bryozoans.—National Geographic Research4/4, 528–539
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Scholz, J. Indications for microbial clues for bryozoans when settling. Facies 29, 107–118 (1993). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02536923
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02536923