Abstract
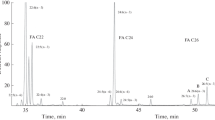
The fatty acid methyl esters obtained by the esterification of total lipids extracted from 24 species of fin fish and 4 species of invertebrates caught in the rivers and coastal waters of southern Australia were analyzed by gas chromatography. The lipids of most species contained significant levels of arachidonic acid (0.7–15.8%) as well as the more common marine polyunsaturate, eicosapentaenoic acid (0.7–15.9%). The major ω6 fatty acid present in most species was 20∶4; however, other fatty acids of this series, including 18∶2, 22∶4 and 22∶5, were present. The level of total ω6 fatty acids ranged from 3.9 to 22.3% of the total lipid. In general, the level of total ω3 polyunsaturates was higher than the total ω6 fatty acids with levels of ω3 fatty acids ranging from 9.6 to 48.2%. Only 2 fish (barramundi and gurnard perch) had ω6/ω3 ratios greater than 1.0. Most of the Australian species examined contained low levels of fat (0.5–7.8% of fresh weight). Two species examined, callop (freshwater) and blue groper (marine) contained sufficient quantities of both fat (7.7 and 7.8%) and arachidonic acid (4.8 and 9.3%) to warrant consideration for commercial exploitation.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bang, H.O., Dyerberg, J., and Hjøne, N. (1976) Acta Med. Scand. 200, 69–73.
Bang, H.O., Dyerberg J., and Sinclair, H.M. (1980) Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 33, 2657–2661.
Ackman, R.G. (1967) Comp. Biochem. Physiol. 22, 907–922.
Budowski, P. (1981) Isr. J. Med. Sci. 17, 223–231.
Bronsgeest-Schoute, H.C., van Gent, C.M., Luten, J.B., and Ruiter, A. (1981) Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 34, 1752–1757.
Goodnight, S.H., Harris, W.S., Connor, W.E., and Illingworth, D.J. (1982) Arteriosclerosis 2, 87–113.
Needleman, P., and Raz, A., Minkes, M.S., Ferrendelli, J.A., and Sprecher, H. (1979) Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 76, 944–948.
Dyerberg, J., Bang, H.O., Saffersen, E., Moncada, S., and Vane, J.R. (1978) Lancet ii, 117–119.
Siess, W., Scherer, B., Bohlig, B., Roth, P., Kurzmann, I., and Weber, P.C. (1980) Lancet i, 441–444.
Dyerberg, J., and Bang, H.O. (1979) Lancet ii, 433–435.
Von Lossonczy, T.O., Ruiter, A., Bronsgeest-Schoute, H.C., van Gent, C.M., and Hermus, R.J.J. (1978) Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 31, 1340–1346.
Saynor, R., and Verel, D. (1982) Lancet ii, 272.
Jones, D.B., and Davies, T.M.E. (1982) Lancet ii, 221.
Toyomizu, M., Nakamura, T., and Shono, T. (1976) Bull. Jpn. Soc. Sci. Fish. 42, 101–108.
Bligh, E.G., and Dyer, W.J. (1959) Can. J. Biochem. Physiol. 37, 911–917.
Gibson, R.A., and Kneebone, G.M. (1981) Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 34, 252–257.
Charnock, J.S., Gibson, R.A., McMurchie, E.J., and Raison, J.K. (1980) Molec. Pharmacol. 18, 476–482.
Stansby, M.E. (1969) World Rev. Nutr. Dietet. 11, 46–195.
Kinsella, J.E., Shimp, J.L., Mai, J., and Weihrauch, J. (1977) J. Am. Oil Chem. Soc. 54, 424–429.
Gunstone, F.D., Wijesundera, R.C., and Scrimgeour, C.M. (1978) J. Sci. Fd. Agric. 29, 539–550.
O'Dea, K., and Sinclair, A.J. (1982) Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 36, 868–872.
Johns, R.B., Nichols, P.D., and Perry, G.J. (1979) Phytochemistry 18, 799–802.
Nichols, P.D., Klumpp, D.W., and Johns, R.B. (1982) Phytochemistry 21, 1613–1621.
Smith, M.W., and Miller, N.G.A. (1980) in Animals and Environmental Fitness (Gilles, R., ed.) pp. 521–540, Pergamon Press, Oxford.
Iritani, N., and Fujikawa, S. (1982) J. Nutr. Sci. Vitaminol. 28, 621–620.
Scholkens, B.A., Gehrink, D., Scholette, V., and Neithmann, U. (1982) Prost. Leuk. Med. 8, 273–285.
Horrobin, D.F. (1980) Med. Hypoth. 6, 469–486.
Ackman, R.G., Eaton, C.A., and Dyerberg, J. (1980) Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 33, 1814–1817.
Hay, C.R.M., Durber, A.P., and Saynor, R. (1978) Lancet i, 1269–1272.
Hornstra, G., Christ-Hazelhof, E., Haddeman, E., Ten Hoor, F., and Nugtern, D.J. (1981) Prostaglandins 21, 727–738.
Moncada, S., and Vane, J.R. (1978) Br. Med. Bull. 34, 129–135.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
About this article
Cite this article
Gibson, R.A. Australian fish—An excellent source of both arachidonic acid and ω-3 polyunsaturated fatty acids. Lipids 18, 743–752 (1983). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02534631
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02534631