Abstract
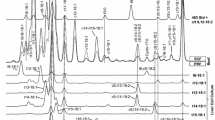
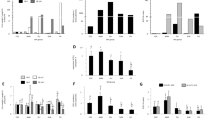
The percentage distribution of the geometrical and positional isomers in the hexadecenoates and octadecenoates isolated from triglycerides, phosphatidylcholines, and phosphatidylethanolamines of brain, heart, kidney, liver, lung, muscle, spleen, and adipose tissues from rats maintained four weeks on a semipurified diet supplemented with 15% partially hydrogenated safflower fatty acids, has been determined. Except for brain, octadecenoate percentages were increased in each of the lipid classes of all the tissues by the dietary fat. Although the diet did not contain detectable hexadecenoates, the 16∶1 fraction from the lipid classes of all the tissues was composed of 10–70% of thetrans isomers, indicating chain shortening of the dietary octadecenotes. Distribution ofcis andtrans positional isomers in triglyceride hexadecenoates was approximately the same in all tissues. Relatively high percentages of the Δ9, Δ10, and Δ11 isomers were observed, but the Δ8 was the predominatingtrans hexadecenoate isomer, indicating preferential chain shortening of thetrans δ10 octadecenoate.Trans octadecenoates were found in all tissues, but concentrations were dependent on tissue and lipid class. The distribution of thecis andtrans octadecenoate isomers was similar in all the tissue triglycerides, with the distribution of thetrans isomers resembling the diet. In contrast, the percentage distribution of thetrans octadecenoates in the phospholipid classes differed dramatically from the diet, and the distribution was dependent on both the tissue and lipid class. The Δ12, Δ13, and Δ14trans octadiet, suggesting an accumulation of these isomers. Although thecis Δ10 octadecenoate was a significant dietary component, this isomer was not incorporated significantly into any lipid class of any tissue. The metabolic fate of this isomer remains unknown.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Wood, R., in “Geometrical and Positional Fatty Acids Isomers,” Edited by E.A. Emken and H.J. Dutton, AOCS Press, Champaign, IL, Chapter 9, 1979, pp 213–281.
Wood, R., F. Chumbler, and R. Wiegand, J. Biol. Chem. 252:1965 (1977).
Wood, R., and F. Chumbler, Lipids 13:75 (1978).
Wood, R., and F. Chumbler, Fed. Proc. 37:1831 (1978).
Blight, E.G., and W.J. Dyer, Can. J. Biochem. Physiol. 37:911 (1959).
Wood, R., J. Falch, and R.D. Wiegand, Lipids 10:202 (1975).
Wood, R., Lipids 10:736 (1975).
Wood, R., and J. Falch, Lipids 9:979 (1974).
Wood, R., J. Falch, and R.D. Wiegand, Lipids 9:987 (1974).
Beroza, M., and B.A. Bierl, Anal. Chem. 39:1131 (1967).
Wood, R., F. Chumbler, M. Matocha, and A. Zoeller, Lipids 14:789 (1979).
Shrock, C.G., and W.E. Connor, Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 28:1020 (1975).
Schlenk, H., D.M. Sand, and J.L. Gellerman, Biochim. Biophys. Acta 187:201 (1969).
Kunau, W.H., in “Polyunsaturated Fatty Acids,” Edited by W.H. Kunau and R.T. Holman, AOCS Press, Champaign, IL, Chapter 4, 1977, pp. 51–67.
Chang, H.C., and R.T. Holman, Biochim. Biophys. Acta 280:17 (1972).
Fiecchi, A., M. Galli-Kienle, A. Scala, G. Galli, and R. Paoletti, Eur. J. Biochem. 38:516 (1973).
Greville, G.D., and P.K. Tubbs, in “Essays in Biochemistry,” Vol. 4, Edited by P.N. Campbell and G.D. Greville, Academic Press, 1968, pp. 155–212.
Stoffel, W., and H.G. Schiefer, Hoppe-Seyler’s Z. Physiol. Chem. 341:84 (1965).
Lippel, K., F.D. Gunstone, and J.A. Barve, Lipids 8:119 (1973).
Lippel, K., D. Carpenter, F.D. Gunstone, and I.A. Ismail, Lipids 8:124 (1973).
Reitz, R.D., M. El-Sheikh, W.E.M. Lands, I.A. Ismail, and F.D. Gunstone, Biochim. Biophys. Acta 176:480 (1969).
Okuyama, H., W.E.M. Lands, R.D. Gunstone, and J.A. Barve, Biochemistry 11:4392 (1972).
Tamai, Y., W.E.M. Lands, J.A. Barve, and F.D. Gunstone, Biochim. Biophys. Acta 296:563 (1973).
Goller, H.J., D.S. Sgoutas, I.A. Ismail and F.D. Gunstone, Biochemistry 9:3072 (1970).
Sgoutas, D.S., Biochim. Biophys. Acta 164:317 (1968).
Takatori, T., F.C. Phillips, H. Shimasaki, and O.S. Privett, Lipids 11:272 (1976).
Jensen, B., Lipids 11:179 (1976).
Mounts, T.L., Lipids 11:676 (1976).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
About this article
Cite this article
Wood, R. Incorporation of dietarycis andtrans octadecenoate isomers in the lipid classes of various rat tissues. Lipids 14, 975–982 (1979). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02533433
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02533433