Abstract
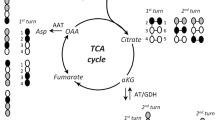
Cerebral pentose phosphate pathway (PPP) plays a role in the biosynthesis of macromolecules, antioxidant defense and neurotransmitter metabolism. Studies on this potentially important pathway have been hampered by the inability to easily quantitate its activity, particularly in vivo. In this study we review the use of [1,6-13C2,6,6-2H2]glucose for measuring the relative activities of the PPP and glycolysis in a single incubation in cultured neurons and in vivo, when combined with microdialysis techniques. PPP activity in primary cerebrocortical cultures and in the caudate putamem of the rat in vivo was quantitated from data obtained by GC/MS analysis of released labeled lactate following metabolic degradation of [1,6-13C2,6,6-2H2]glucose. Exposure of cultures to H2O2 resulted in stimulation of PPP activity in a concentration-dependent fashion and subsequent cell death. Chelation of iron during H2O2 exposure exerted a protective effect thus implicating the participation of the Fenton reaction in mediating damage caused by the oxidative insult. Partial inhibition of glutathione peroxidase, but not catalase, was extremely toxic to the cultures reflecting the pivotal role of GPx in H2O2 detoxification. These results demonstrate the ability to dynamically monitor PPP activity and its response to oxidative challenges and should assist in facilitating our understanding of antioxidant pathways in the CNS.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Baquer, N. Z., Hothersall, J. S., and McLean, P. 1988. Funotion and regulation of the pentose phosphate pathway in brain. Vol. 29, pages 265–289,in Horecker, B. L. and Stadtman, E. R. (eds), Current Topics in Cellular Regulation.
Baquer, N. Z., Hothersall, J. S., McLean, P., and Greenbaum, A. L. 1977. Aspects of carbohydrate metabolism in developing brain. Develop. Med. Child Neurol. 19:81–104.
Zubairu, S., Hothersall, J. S., El-Hassan, A., McLean, P., and Greenbaum, L. 1983. Alternative pathways of glucose utilization in brain: Changes in the pattern of glucose utilization and of the response of the pentose phosphate pathway to 5-hydroxytryptamine. J. Neurochem. 41:76–83.
Coleman, M. Y., and Allen, N. 1978. The hexose monophosphate pathway in ethylnitrosourea induced tumors of the nervous system. J. Neurochem. 30:83–90.
Hothersall, J. S., Baquer, N. Z., Greenbaum, A. L., and McLean, P. 1979. Alternative pathways of glucose utilization in brain. Changes in the pattern of glucose utilization in brain during development and the effect of phenazine methosulfate on the integration of metabolic routes. Arch. Biochem. Biophys. 198:478–492.
Loreck, D. J., Galarraga, J., Van der Feen, J., Phang, J. M., Smith, B. H., and Cummins, C. J. 1987. Regulation of the pentose phosphate pathway in human astrocytes and gliomas. Metab. Brain Disease 2:31–46.
Appel, S. H., and Parrot, B. L. 1970. Hexosemonophosphate pathway in synapses. J. Neurochem. 17:1619–1626.
Tabakoff, B., Groskopt, W., Anderson, R., and Alivisatos, S. G. A. 1974. Biogenic aldehyde metabolism, relation to pentose shunt in brain. Biochem. Pharmacol. 23:1710–1719.
Baquer, N. Z., McLean, P., and Greenbaum, A. L. 1975. Systems relationships and the control of metabolism pathways in developing brain. Pages 109–132,in Hommes, F. A., and Van den Berg, C. J., (eds), Normal and Pathological Development of Energy Metabolism, Academic Press, London.
Hothersall, J. S., Greenbaum, A. L., and McLean, P. 1982. The functional significance of the pentose phosphate pathway in synaptosomes: Protection against peroxidative damage by catecolamines and oxidants. J. Neurochem. 39:1325–1332.
Brin, M. 1966. Erythrocyte as a biopsy tissue for functional evaluation of thiamine adequacy, J. Am. Med. Assoc. 187:762–766.
Herken, H., Lange, K., and Kolbe, H. 1969. Brain disorders induced by pharmacological blockade of the pentose phosphate pathway. Biochim. Biophys. Res. Commun. 36:93–100.
Gaitonde, M. K., Evison, E., and Evans, G. M. 1983. The rate of utilization of glucosevia hexosemonophosphate shunt in brain. J. Neurochem. 41:1253–1260.
Embree, L. J., and Dreyfus, P. M. 1963. Blood transketolase determinations in nutritional disorders of the nervous system. Trans. Am. Neurol. Assoc. 88:36–42.
Hawkins, R. A., Mans, A. M., Davis, D. W., Vina, J. R., and Hibbard, L. S. 1985. Cerebral glucose use measured with [14C]glucose labeled in the 1,2 or 6 position. Am. J. Physiol. 248: C170-C176.
Duncan, G. E., Stumpf, W. E., Brustle, O., Givens, B. S., Breese, G. R., and Pilgrim, C. 1988. Topography of basal glucose utilization in the hippocampus determined with [1-14C]glucose and [6-14C]glucose. Neuroscience 24:877–883.
Dienel, G. A., Cruz, N. F., Nakanishi, H., Melzer, P., Moulis, P., and Sokoloff, L. 1992. Comparison of rates of local cerebral glucose utilization determined with deoxy[1-14C]glucose and deoxy[6-14C]glucose. J. Neurochem. 59:1430–1436.
Ross, B. D., Kingsley, P. B., and Ben-Yoseph, O. 1994. Measurement of pentose phosphate pathway activity in a single incubation with (1,6-13C2,6,6-2H2) glucose. Biochem. J. 302:31–38.
Ben-Yoseph, O., Kingsley, P. B., Camp, D. M., Robinson, T. E., and Ross, B. D. 1994. Measurement of pentose phosphate pathway activity by microdialysis in vivo and in a single incubation in vitro. Neurosci. Protocols. 94-060-02-01-13.
Ben-Yoseph, O., Ross, B. D., Camp, D. M., and Robinson, T. E. 1995. Dynamic measurements of cerebral pentose phosphate pathway activity in vivo. J. Neurochem. 64:1336–1342.
Rose, K., Goldberg, M. P., and Choi, D. W. 1993. Cytotoxicity in murine cortical culture. Pages 46–60,in Tyson, C. A., and Frazier, J. M. (eds.), In Vitro Biological Methods, Academic Press, San Diego, California.
Koh, J. Y., and Choi, D. W. 1987. Quantitative determination of glutamate mediated cortical neuronal injury in cell culture by lactate dehydrogenase efflux assay. J. Neurosci. Meth. 149:279–293.
Boxer, P. A., Ben-Yoseph, O., Levy, J., and Ross, B. D. 1995. Role of the glutathione pathway in the detoxification of hydrogen peroxide in culture neurons. Soc. Neurosci. Abstr. 21:99.20.
Coyle, J. and, Puttfarcken, P. 1993. Oxidative stress, glutamate and neurodegenerative disorders. Science 262:689–695.
Chaudiere, J., Wilhelmsen, E. C., and Tappel, A. L. 1984. Mechanism of selenium-glutathione peroxidase and its inhibition by mercaptocarboxylic acids and other mercaptants. J. Biol. Chem. 259:1043–1050.
Bondy, S. G., and Lebel, C. P. 1993. The relationship between excitotoxicity and oxidative stress in the central nervous system. Free Rad. Biol. Med. 14:633–642.
Hostetler, K. Y., and Landau, B. R. 1967. Estimation of the pentose cycle contribution to glucose metabolism in tissue in vivo. Biochemistry 6:2961–2964.
Ben-Yoseph, O., Boxer, P. A., and Ross, B. D. 1994. Oxidative stress in the CNS: Monitoring the metabolic response using the pentose phosphate pathway. Dev. Neurosci. 16:328–336.
Dykens, J. A. 1994. Isolated cerebral and cerebellar mitochondria produce free radicals when exposed to elevated Ca2+ and Na+: Implication for neurodegeneration. J. Neurochem. 63:584–591.
Kish, S. J., Morito, C., and Hornykiewicz, O. 1985. Glutathione peroxidase in Parkinson's disease brain. Neurosci. Lett. 58:343–346.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Special issue dedicated to Dr. Herman Bachelard.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ben-Yoseph, O., Boxer, P.A. & Ross, B.D. Noninvasive assessment of the relative roles of cerebral antioxidant enzymes by quantitation of pentose phosphate pathway activity. Neurochem Res 21, 1005–1012 (1996). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02532410
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02532410