Abstract
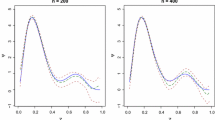
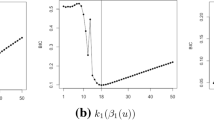
We consider the use ofB-spline nonparametric regression models estimated by the maximum penalized likelihood method for extracting information from data with complex nonlinear structure. Crucial points inB-spline smoothing are the choices of a smoothing parameter and the number of basis functions, for which several selectors have been proposed based on cross-validation and Akaike information criterion known as AIC. It might be however noticed that AIC is a criterion for evaluating models estimated by the maximum likelihood method, and it was derived under the assumption that the ture distribution belongs to the specified parametric model. In this paper we derive information criteria for evaluatingB-spline nonparametric regression models estimated by the maximum penalized likelihood method in the context of generalized linear models under model misspecification. We use Monte Carlo experiments and real data examples to examine the properties of our criteria including various selectors proposed previously.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Akaike, H. (1973). Information theory and an extension of the maximum likelihood principle,2nd International Symposium on Information Theory (eds. B. N. Petrov and F. Csaki), 267–281, Akademiai Kiado, Budapest (Reproduced inBreakthroughs in Statistics, Volume 1 (eds. S. Kotz and N. L. Johnson), Springer Verlag, New York (1992)).
Akaike, H. (1974). A new look at the statistical model identification.IEEE Trans. Automat. Control,AC-19, 716–723.
Akaike, H. (1980a). On the use of predictive likelihood of a Gaussian model,Ann. Inst. Statist. Math.,32, 311–324.
Akaike, H. (1980b). Likelihood and the Bayes procedure,Bayesian Statistic (eds. J. M. Bernardo, M. H. DeGroot, D. V. Lindley and A. F. M. Smith), University Press, Valencia, Spain.
Bozdogan, H. (ed.) (1994).Proceedings of the First US/Japan Conference on the Frontiers of Statistical Modeling: An Informational Approach, Kluwer, Dordrecht.
Craven, P. and Wahba, G. (1979). Smoothing noisy data with spline functions,Numer. Math.,31, 377–403.
De Boor, C. (1978),A Practical Guide to Splines, Springer, Berlin.
Dierckx, P. (1993).Curve and Surface Fitting with Splines, Oxford University Press, Oxford.
Efron, B. (1979). Bootstrap methods: Another look at the jacknife,Ann. Statist.,7, 1–26.
Eilers, P. H. C. and Marx, B. D. (1996). Flexible smoothing withB-splines and penalties (with discussion),Statist. Sci.,11, 89–121.
Eubank, R. L. (1988)Spline Smoothing and Nonparametric Regression, Marcel Dekker, New York.
Good, I. J. (1965).The Estimation of Probabilities, M. I. T. Press, Cambridge, Massachusetts.
Good, I. J. and Gaskins, R. A. (1971). Nonparametric roughness penalties for probability densities,Biometrika,58, 255–277.
Green, P. J. (1987). Penalized likelihood for general semi-parametric regression models,International Statistical Review,55, 245–259.
Green, P. J. and Silverman, B. W. (1994).Nonparametric Regression and Generalized Linear Models, Chapman and Hall, London.
Hampel, F. R., Rousseeuw, P. J., Ronchetti, E. M. and Stahel, W. A. (1986).Robust Statistics. The Approach on Influence, Wiley, New York.
Härdle, W. (1990).Applied Nonparametric Regression, Cambridge University Press, Cambridge.
Hastie, T. and Tibshirani, R. (1990). Generalized Additive Models, Chapman and Hall, London.
Hurvich, C. M. and Tsai, C.-L. (1989). Regression and time series model selection in small samples,Biometrika,76, 297–307.
Hurvich, C. M., Simonoff, J. S. and Tsai, C.-L. (1998). Smoothing parameter selection in nonparametric regression using an improved Akaike information criterion,J. Roy. Statist. Soc. Ser. B,60, 271–293.
Ishiguro, M. and Arahata, E. (1982). A Bayesian spline regression (in Japanese),Proc. Inst. Statist. Math.,30, 30–36.
Ishiguro, M., Sakamoto, Y. and Kitagawa, G. (1997). Bootstrapping log likelihood and EIC, an extension of AIC,Ann. Inst. Statist. Math.,49, 411–434.
Kitagawa, G. and Gersch, W. (1996).Smoothness Priors Analysis of Time Series, Springer, New York.
Konishi, S. (1999). Statistical model evaluation and information criteria.Multivariate Analysis, Design of Experiments and Surrey Sampling (ed. S. Ghosh), 369–399, Marcel Dekker, New York.
Konishi, S. and Kitagawa, G. (1996). Generalised information criteria in model selection,Biometrika,83, 875–890.
Kullback, S. and Leibler, R. A. (1951). On information and sufficiency,Ann. Math. Statist.,22, 79–86.
McCullagh, P. and Nelder, J. A. (1989).Generalized Linear Models, 2nd ed., Chapman and Hall, London.
Nelder, J. A. and Wedderburn, R. W. M. (1972). Generalized linear models.J. Roy. Statist. Soc. Ser. A,135, 370–384.
Silverman, B. W. (1985). Some aspects of the spline smoothing approach to nonparametric regression curve fitting (with discussion),J. Roy. Statist. Soc. Ser. B,47, 1–52.
Silverman, B. W. (1986).Density Estimation for Statistics and Data Analysis, Chapman and Hall, London.
Simonoff, J. S. (1996).Smoothing Methods in Statistics, Springer, New York.
Stone, C. J. (1974). Cross-validatory choice and assessment of statistical predictions (with discussion),J. Roy. Statist. Soc. Ser. B,36, 111–147.
Sugiura, N. (1978). Further analysis of the data by Akaike's information criterion and finite corrections,Comm. Statist. Theory Methods,A7, 13–26.
Tanabe, K. and Tanaka, T. (1983). Fitting curves and surfaces to data by using Bayes model (in Japanese),Chikyu,5, 179–186.
Wahba, G. (1978). Improper priors, spline smoothing and the probrem of guarding against model errors in regression,J. Roy. Statist. Soc. Ser. B,40, 364–372.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
About this article
Cite this article
Imoto, S., Konishi, S. Selection of smoothing parameters inB-spline nonparametric regression models using information criteria. Ann Inst Stat Math 55, 671–687 (2003). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02523388
Received:
Revised:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02523388