Abstract
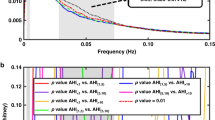
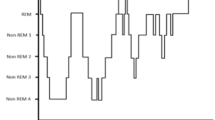
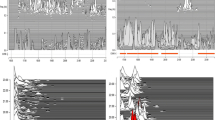
The sleep apnoea/hypopnoea syndrome (SAHS) elicits a unique heart rate rhythm that may provide the basis for an effective screening tool. The study uses the receiver operator characteristic (ROC) to assess the diagnostic potential of spectral analysis of heart rate variability (HRV) using two methods, the discrete Fourier transform (DFT) and the discrete harmonic wavelet transform (DHWT). These two methods are compared over different sleep stages and spectral frequency bands. The HRV results are subsequently compared with those of the current screening method of oximetry. For both the DFT and the DHWT, the most diagnostically accurate frequency range for HRV spectral power calculations is found to be 0.019–0.036 Hz (denoted by AB2). Using AB2, 15 min sections of non-REM sleep data in 40 subjects produce ROC areas, for the DFT, DHWT and oximetry, of 0.94, 0.97 and 0.67, respectively. In REM sleep, ROC areas are 0.78, 0.79 and 0.71, respectively. In non-REM sleep, spectral analysis of HRV appears to be a significantly better indicator of the SAHS than the current screening method of oximetry, and, in REM sleep, it is comparable with oximetry. The advantage of the DHWT over the DFT is that it produces a greater time resolution and is computationally more efficient. The DHWT does not require the precondition of stationarity or interpolation of raw HRV data.
Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- AB1 :
-
apnoea band 1 (0.019–0.071 Hz)
- AB2 :
-
apnoea band 2 (0.019–0.036 Hz)
- AHI:
-
apnoea/hypopnoea index, h−1
- HF:
-
high-frequency band (0.15–0.4 Hz)
References
Atlas Task Force (1992): ‘EEG arousals: scoring rules and examples’,Sleep,15, pp. 173–184
Bates, R. A., Hilton, M. F., Godfrey, K. R., andChappell, M. J. (1998): ‘Comparison of methods for harmonic wavelet analysis of heart rate variability’,IEEE Proc. Sci. Meas. Technol.,145, pp. 291–300
Bonsignore, M. R., Marrone, O., Insalaco, G., andBonsignore, G. (1994): ‘The cardiovascular effects of obstructive sleep apnoeas: analysis of pathogenic mechanisms’,Eur. Respir. J.,7, pp. 786–805
Burgess, H. J., Trindler, J., Kim, Y., andLuke, D. (1997): ‘Sleep and circadian influences on cardiac autonomic nervous system activity’,J. Physiol.,273, pp. H1761-H1768
Coleman, R. M., Pollack, C. P., andWeitzman, E. D. (1980): ‘Periodic movements in sleep (nocturnal myoclonus): relation to sleep disorders’,Ann. Neurol.,8, pp. 416–421
Cooper, B. G., Veale, D., Griffiths, C. J., andGibson, G. J. (1991): ‘Value of nocturnal oxygen saturation as a screening test for sleep apnoea’,Thorax,46, pp. 586–588
Daniels, J. E., Chappell, M. J., Tjahjadi, T., andCayton, R. M. (1997): ‘CADOSA: A fuzzy expert system for differential diagnosis of obstructive sleep apnoea and related conditions’,Exp. Syst. Appl.,12, pp. 163–177
Deegan, P. C., andMcNicholas, W. T. (1995): ‘Pathophysiology of obstructive sleep apnoea’,Eur. Respir. J.,8, pp. 1161–1178
Duglas, N. J., Calverley, P. M. A., Catterall, J. R., Johnson, A. J., Prowse, K., andStradling, J. R. (1990): ‘Facilities for the diagnosis and treatment of abnormal breathing during sleep including nocturnal hypoventilation’,BTS News,5, pp. 7–10
Douglas, N. J., Thomas, S., andJan, M. A. (1992): ‘Clinical value of polysomnography’,Lancet,339, pp. 347–350
Dutt, A., andRokhlin, V. (1993): ‘Fast Fourier transforms for nonequispaced data’,SIAM J. Sci. Stat. Comp.,14, pp. 1368–1393
Flemons, W. W., Remmers, J. E., andGillis, A. M. (1993): ‘Sleep apnea and cardiac arrhythmias. Is there a relationship?’,Am. Rev. Respir. Dis.,148, pp. 618–621
Gould, G. A., Whyte, K. F., Rhind, G. B., Airlie, M. A., Catterall, J. R., Shapiro, C. M., andDouglas, N. J. (1988): ‘The sleep hypopnoea syndrome’,Am. Rev. Respir. Dis.,137, pp. 895–898
Guilleminault, C., Tilkian, A., andDement, W. C. (1976): ‘The sleep apnoean syndromes’,Ann. Rev. Med.,27, pp. 465–484
Guilleminault, C., Winkle, R., Connolly, S., Melvin, K., andTilkian, A. (1984): ‘Cyclical variation of the heart rate in sleep apnoea syndrome. Mechanisms and usefulness of 24 hr electrocardiography as a screening technique’,Lancet,1, pp. 126–131
Guilleminault, C., Stochs, R., Clerk, A., Cetel, A., andMaistros, P. (1993): ‘A cause of excessive daytime sleepiness: the upper airways resistance syndrome’,Chest,104, pp. 781–787
Gyulay, S., Olson, L. G., Hensley, M. J., King, M. T., Allen, K. M., andSaunders, N. A. (1993): ‘A comparison of clincial assessment and home oximetry in the diagnosis of obstructive sleep apnea’,Am. Rev. Respir. Dis.,147, pp. 50–53
Hanley, J. A., andMcNeil, B. J. (1982): ‘The meaning and use of the area under a receiver operating characteristic (ROC) curve’,Radiology,143, pp. 29–36
Hanley, J. A., andMcNeil, B. J. (1983): ‘A method of comparing the areas under receiver operating characteristic curves derived from the same cases’,Radiology,148, pp. 839–843
Hartikainen, J., Tarkiainen, I., Tahvanainen, K., Mantysaari, M., Länsimies, E., andPyörälä, K. (1993): ‘Circadian variation of cardiac autonomic regulation during 24-h bed rest’,Clin. Physiol.,13, pp. 185–196
Hayano, J., Skakibara, Y., Yamada, A., Yamada, M., Mukai, S., Fujinami, T., Yokoyama, K., Watanabe, Y., andTakata, K. (1991): ‘Accuracy of assessment of cardiac vagal tone by heart rate variability in normal subjects’,Am. J. Cardiol.,67, pp. 199–204
He, J., Kryger, M. H., Zorick, F. J., Conway, W., andRoth, T. (1988): ‘Mortality and apnea index in obstructive sleep apnea. Experience in 385 male patients’,Chest,94, pp. 9–14
Hedner, J., Ejnell, H., Sellgren, J., Hedner, T., andWallin, G. (1988): ‘Is high and fluctuating muscle sympathetic nerve activity in the sleep apnoea syndrome of pathogenic importance for the development of hypertension?’,J. Hypertens.,6, pp. 529–531
Hla, K. M., Young, T. B., Bidwell, T., Palta, M., Skatrud, J. B., andDempsey, J. (1994): ‘Sleep apnea and hypertension. A population-based study’,Ann. Intern. Med.,120, pp. 382–388
Huikuri, H. V., Valkama, J. O., Airaksinen, K. E., Seppanen, T., Kessler, K. M., Takkunen, J. T., andMyerburg, R. J. (1993): ‘Frequency domain measures of heart rate variability before the onset of non-sustained and sustained ventricular tachycardia in patients with coronary artery disease’,Circulation,87, pp. 1220–1228
Keyl, C., Lemberger, P., Pfeifer, M., Hochmuth, K., andGeisler, P. (1997): ‘Heart rate variability in patients with daytime sleepiness suspected of having sleep apnoea syndrome: a receiver-operating characteristic andlysis’,Clin. Sci.,92, pp. 335–343
Levy, P., Pepin, J. L., Deschaux-Blanc, C., Paramelle, B., andBrambilla, C. (1996): ‘Accuracy of oximetry for detection of respiratory disturbances in sleep apnea syndrome’,Chest,109, pp. 395–399
Mansier, P., Clairambault, J., Charlotte, N., Medigue, C., Vermeiren, C., Lepape, G., Carre, F., Gounaropoulou, A., andSwynghedauw, B. (1996): ‘Linear and non-linear analyses of heart rate variability: a minireview’,Cardiovasc. Res.,31, pp. 371–379
Newland, D. E. (1995): ‘Discrete wavelet analysis’in ‘Random vibrations, spectral and wavelet analysis, 3rd edn.’ (Longman, Singapore), pp. 295–370
Penzel, T. (1993): ‘Spectral analysis of blood pressure in patients with sleep-related breathing disorders during NREM and REM sleep’,Sleep,16, pp. S150-S151
Rechtschaffen, A., andKales, A. (1968): ‘A manual of standardised terminology, techniques and scoring system for sleep stages of human subjects’ (Brain Information service/Brain Research Institute, UCLA, Los Angeles)
Ryan, P. J., Hilton, M. F., Boldy, D. A. R., Evans, A., Bradbury, S., Sapiano, S., Prowse, K., andCayton, R. M. (1995): ‘Validation of the British Thoracic Society guidelines for the diagnosis of the sleep apnoea/hypopnoea syndrome: can polysomnography be avoided?’,Thorax,50, pp. 972–975
Shiomi, T., Guilleminault, C., Sasanabe, R., Hirota, I., Maekawa, M., andKobayashi, T. (1996): ‘Augmented very low frequency component of heart rate variability during obstructive sleep apnea’,Sleep,19, pp. 370–377
Sullivan, C. E., Issa, F. G., Berthon-Jones, M., andEves, L. (1981): ‘Reversal of obstructive sleep apnoea by continuous positive airway pressure applied through the nares’,Lancet,1, pp. 862–865
Task Force of the European Society of Cardiology and the North American Society of Pacing and Electrophysiology (1996): ‘Heart rate variability: standards of measurement, physiological interpretation, and clinical use’,Eur. Heart J.,17, pp. 354–381
Tilkian, A. G., Guilleminault, C., Schroeder, J. S., Lehrman, K. L., Simmons, F. B., andDement, W. C. (1976): ‘Hemodynamics in sleep-induced apnea: studies during wakefulness and sleep’,Ann. Intern. Med.,85, pp. 714–719
Tilkian, A. G., Guilleminault, C., Schroeder, J. S., Lehrman, K. L., Simmons, F. B., andDement, W. C. (1977): ‘Sleep-induced apnea syndrome. Prevalence of cardiac arrhythmias and their reversal after tracheostomy’,Am. J. Med.,63, pp. 348–358
Varoneckas, G., Dauksys, R., Podilpskyte, A., andZemaityte, D. (1999): ‘Sleep structure and restoration of autonomic heart rate control during sleep’,Sleep,22, pp. S309
Welch, P. D. (1967): ‘The use of fast Fourier transformation for the estimation of power spectra: a method based on time averaging over short, modified periodograms’,IEEE Trans. Audio Electroacoust.,AU-15, pp. 70–73
Young, T., Palta, M., Dempsey, J., Skatrud, J., Weber, S., andBard, S. (1993): ‘The occurrence of sleep-disordered breathing among middle aged adults’,N. Eng. J. Med.,328, pp. 1230–1235
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hilton, M.F., Bates, R.A., Godfrey, K.R. et al. Evaluation of frequency and time-frequency spectral analysis of heart rate variability as a diagnostic marker of the sleep apnoea syndrome. Med. Biol. Eng. Comput. 37, 760–769 (1999). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02513379
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02513379