Summary
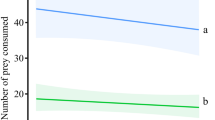
WhenPhytoseiulus persimilis was reared withTetranychus urticae, infesting roses propagated in a greenhouse at controlled daily temperatures of 24°C (12 hrs) and 18°C (12 hrs), prey numbers fluctuated with peaks of increasing amplitude. Differential dispersal of prey and predator species was one factor contributing to the inability of the natural enemy to control the pest population.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Amano, H. andD. A. Chant (1977) Life history and reproduction of two species of predactious mites,Phytoseiulus persimilis Athias-Henriot andAmblyseius andersoni (Chant) (Acarina: Phytoseiidae).Can. Jour. Zool.55: 1978–1983.
Amano, H. andD. A. Chant (1978) Some factors affecting reproduction and sex-ratios in two species of predactious mites,Phytoseiulus persimilisAthias-Henriot andAmblyseius andersonii (Chant) (Acarina: Phytoseiidae).Can. Jour. Zool.56: 1593–1607.
Binns, E. S. (1971) The toxicity of some soil-applied systemic insecticides toAphis gossypei (Hom: Aphidea) andPhytoseiulus persimilis (Acarina: Phytoseiidae) on cucumbers.Ann. Appl. Biol.67: 211–222.
Binns, E. S., P. Bocion andH. J. Gould (1971) The integration of chemical control of the melon applied with predatory control of glasshouse red spider mite on cucumbers.Ann. Appl. Biol.68: 1–9.
Bravenboer, L. (1971) Chemical and biological control of the common spotted spider mite of greenhouse crops.Acta Horticulturae17: 181–186.
Bravenboer, L. (1971) Chemical and biological control of the common spotted spider mite of greenhouse crops.Acta Horticulturae17: 181–186.
Bravenboer, L. (1975) Developments in biological pest control in greenhouses Teitschrift fuer Angewandte.Entomologie77: 390–391.
Bravenboer, L. andG. Dosse (1962)Phytoseiulus riegeli Dosse as a predator of red spider mite of theTetranychus urticae group.Ent. Exp. et Appl.5: 291–304.
Bravenboer, L. andD. Theune (1960) A new predator of the red spiderTetrancychus urticae. Proefstation v. d. Groenten en Fruittellt onder Gas to Naaldivyk p. 139.
Burges, H. D. (1974) Modern pest control in glasshouses.International Pest Control May/June 18–21.
Burnett, T. (1970) Effect of temperature on a greenhouse acarine predator-prey population.Can. Jour. Zool.48: 555–562.
Chant, D. A. (1961) An experiment in biological control ofTetranychus telarius (L.) (Acarina: Tetranychidae) in a greenhouse using the predacious mitePhytoseiulus persimilisAthias-Henriot (Phytoseiidae).Can. Ent.93: 437–443.
Coulon, J. andP. Barres (1976) Etudede laboratoire concernant la taxicite des produits phytosanitaires pourPhytoseiulus persimilis. Progress in Integrated Control in GlasshousesW.P.R.S. Bulletin, pp. 45–63.
Dixon, G. M. (1973) Observations on the use ofPhytoseiulus persimilisAthias-Henriot to controlTetranychus urticae (Koch) on tomatoes.Plant Pathology22: 134–139.
Force, D. C. (1967) Effect of temperature on biological control of two-spotted spider mites byPhytoseiulus persimilis.Jour. Econ. Ent.60: 1308.
Gould, H. J. (1971) Large-scale trials of an integrated control program for cucumber pests on commercial nurseries.Plant Pathology20: 149–156.
Gould, H. J. (1976) The development of biological control on cucumbers and tomatoes in the United Kingdom. Progress in Integrated Control in Glasshouses.W. P. R. S. Bulletin pp. 5–8.
Herne, D. C. andD. A. Chant (1965) Relative toxicity of Parathion and Kelthane to the predacious mitePhytoseiulus persimilisAthias-Henriot and its prey,Tetranychus urticaeKoch, (Acarina: Phytoseiidae, Tetranychidae) in the laboratory.Can. Ent.97: 172–176.
Hussey, N. W. andW. J. Parr (1965) Observations on the control ofTetranychus urticaeKoch on cucumbers by the predatory mitePhytoseiulus riegeliDosse.Ent. Exp. et Appl.8: 271–281.
Laing, J. E. andC. B. Huffaker (1960) Comparative studies of predation byPhytoseiulus persimilisAthias-Henriot andMetaseiulus occidentalis (Nesbitt) (Acarina: Phytoseiidae) on populations ofTetranychus urticaeKoch (Acarina: Tetranychidae).Res. Popul. Ecol.11: 105–126.
Legowski, T. J. (1966) Experiments on predator control of the glasshouse red spider mite on cucumbers.Plant Pathology15: 34.
Kowalska, T. andS. Pruszynski (1976) Biological and integrated control in Glasshouses in Poland. Progress in Integrated Control in Glasshouses.W. P. R. S. Bulletin pp. 30–33.
Maukkula, M. (1976) Studies and experiences on the biological control of the most important prests on glasshouse cultures in Finland. Progress in Integrated Control in GlasshousesW.P.R.S. Bulletin pp. 19–24.
McMurtry, J.A. andG.T. Scriven (1975) Population increase ofPhytoseiulus persimilis on different insectary feeding programs.Jour. Econ. Ent.68: 319–321.
Mori, H. andD. A. Chant (1966) The influence of prey density, relative humidity and starvation on the predacious behavior ofPhytoseiulus persimilis.Can. Jour. Zool.44: 483–491.
Parr, W. J. (1972) Biological control of glasshouse pests.Journal of the R. A. S. E.133 48–54.
Pralavorio, M. (1976) Essai de mise au point d'une methode de lutte integree en serre de rosiers. Progress in Integrated Control in Glasshouses.W.P.R.S. Bulletin pp. 170–176.
Pruszynski, S. (1976) Observations on the predacious behaviour ofPhytoseiulus persimilis. Progress in Integrated Control in Glasshouses.W.P.R.S. Bulletin pp. 39–44.
Simmons, S.P. (1972) Observations on the control ofTetranychus urticae on roses byPhytoseiulus persimilis.Plant Pathology21: 163–165.
Stensth, C. (1976) Progress of integrated control of pests under glass in Norway. Progress in Integrated Control in Glasshouses.W.P.R.S. Bulletin pp. 9–17.
Takafuji, A. (1977) The effect of the rate of successful dispersal of a phytoseiid mite,Phytoseiulus persimilis (Acarina: Phytoseiidae) on the persistence in the intercting system between the predator and its prey.Res. Popul. Ecol.18: 210–222.
Takafuji, A. andD. A. Chant (1976) Comparative studies of two species of predacious phytoseiid mites (Acarina: Phytoseiidae) with special reference to their responses to the density of their prey.Res. Popul. Ecol.17: 255–310.
Tanigoshi, L.K. andJ.A. McMurtry (1977) The dynamics of predation ofStethories picipes (Coleoptera: Coccinellidae) andTyphlodromus floridans on the preyOligoxychus punicae (Acarina: Phytoseiidae, Tetranychidae).Hilgardia45: 237–288.
Unwin, B. (1971) Biology and control of the two-spotted miteTetranychus urticae.Jour. Aust. Institute Agr. Sci.37: 192–211.
Woets, J. (1976) Progress report on the integrated pest control in glasshouses in Holland. Progress in Integrated Control in Glasshouses.W.P.R.S. Bulletin pp. 34–37.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Burnett, T. An acarine predator-prey population infesting roses. Res Popul Ecol 20, 227–234 (1979). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02512628
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02512628