Summary
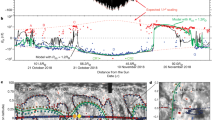
The cosmic-ray equatorial anisotropy inside broad high-speed solar-wind streams ejected by coronal holes,i.e. in quasi-stationary condition, is analysed over the years 1973–1974. From the beginning to the end of the stream the amplitudes of the first and second harmonics of the anisotropy are found to decrease remarkably by factors 2.5 and 2.0, respectively, while the phases do not show systematic variations. The development of the stream structure in the interplanetary space together with the Parker theory on the diurnal anisotropy in stationary condition give a plausible explaination for the large variation observed in the first harmonic of the anisotropy. The behaviour of the second harmonic is tentatively interpreted in the light of current theories.
Riassunto
Si analizza l'anisotropia equatoriale dei raggi cosmici galattici in condizioni quasi stazionarie all'interno di estesi flussi veloci di vento solare emessi da buchi coronali (RHSSs), durante gli anni 1973–1974. Si trova che le ampiezze della prima e della seconda armonica dell'anisotropia diminuiscono considerevolmente dall'inizio alla fine del RHSS, rispettivamente di 2.5 e di 2.0, mentre le fasi non mostrano variazioni sistematiche. L'evoluzione della struttura del RHSS nello spazio interplanetario insieme con la teoria di Parker sull'effetto diurno in condizioni stazionarie fornisce una possibile spiegazione della grande variazione osservata nella prima armonica dell'anisotropia equatoriale. Si tenta inoltre d'interpretare l'andamento della seconda armonica alla luce delle teorie correnti.
Резюме
Анализируется экваториальная анизотропия космических лучей, зарегистрированная в течение 1973–1974 г.г. внутри широких быстрых потоков солнечного ветра, испускаемых корональными дырами, т.е. при квазистационарном условии. Обнаружено, что от начала к концы потока амплитуда первой и второй гармоник анизотропии существенно уменьшается соответственно в 2.5 и 2 раза, тогда как фазы не обнаруживают систематических изменений. Анализ структуры потока в межпланетном пространстве вместе с теорией Паркера для суточной анизотропии при стационарном условии дает правдоподобное объяснение для больших изменений, наблюденных в первой гармоники анизотропии. Интерпретируется поведение второй гармоники в свете имеющихся теорий.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
M. A. Pomerantz andS. P. Duggal:Space Sci. Rev.,12, 75 (1971).
S. E. Forbush:J. Geophys. Res.,78, 7933 (1973).
A. G. Ananth, S. P. Agrawal andU. R. Rao:Pramana,3, 74 (1974).
E. N. Parker:Planet. Space Sci.,12, 735 (1964).
D. Stern:Planet. Space Sci.,12, 973 (1964).
U. R. Rao:Space Sci. Rev.,12, 719 (1972).
N. Iucci andM. Storini:Nuovo Cimento B,13, 361 (1973).
W. I. Axford:Planet. Space Sci.,13, 115 (1965).
J. B. Zirker, Editor:Coronal Holes and High Speed Wind Streams—A Monograph from Skylab Solar Workshop I (Boulder, Colo, 1977).
J. T. Gosling, J. R. Asbridge, S. J. Bame andW. C. Feldman:J. Geophys. Res.,83, 1401 (1978).
E. J. Smith andJ. H. Wolfe:Proceedings of COSPAR Symposium B, Tel-Aviv, June 1977, edited byM. A. Shea, D. F. Smart andS. T. Wu (Hanscom, Mass., 1977), p. 227.
N. Iucci, M. Parisi, M. Storini andG. Villoresi:Nuovo Cimento C,2, 421 (1979).
E. C. Roelof, R. E. Gold, A. S. Krieger, J. T. Nolte andD. Venkatesan:Proceedings of the XIV International Conference on Cosmic Rays, Vol.4 (Munich, 1975), p. 1138.
T. Murayama:Proceedings of the XIV International Conference on Cosmic Rays, Vol.4 (Munich, 1975), p. 1144.
N. R. Sheeley jr., J. W. Harvey andW. C. Feldman:Sol. Phys.,49, 271 (1976).
S. P. Agrawal:J. Geophys. Res.,86, 10115 (1981).
J. H. King:Interplanetary Medium Data Book, NSSDC/WDC-A-R & S 77-04 (Greenbelt, Md., 1977).
M. D. Wilson andM. Bercovitch:Cosmic Ray NM-64Neutron Monitor Data Reports, NRCL (Ottawa, Ont.).
H. S. Ahluwalia:Proceedings of the International Cosmic Ray Symposium on High Energy Cosmic Ray Modulation (Tokyo, 1976), p. 260.
H. Elliot:Proceedings of the XVI International Conference on Cosmic Rays, Vol.14 (Kyoto, 1979), p. 200.
J. J. Quenby andB. Lietti:Planet. Space Sci.,16, 1209 (1968).
K. Nagashima, K. Fujimoto, Z. Fujii, H. Ueno andI. Kondo:Rep. Ionos. Space Res. Jpn.,26, 31 (1972).
J. Kota:Proceedings of the XVI International Conference on Cosmic Rays, Vol.4 (Kyoto, 1979), p. 137.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
To speed up publication, the authors of this paper have agreed to not receive the proofs for correction.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Iucci, N., Parisi, M., Storini, M. et al. The behaviour of the cosmic-ray equatorial anisotropy inside fast solar-wind streams ejected by coronal holes. Il Nuovo Cimento C 6, 145–158 (1983). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02507930
Received:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02507930