Abstract
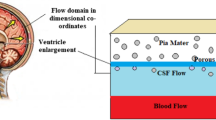
Coughing produces pulses of pressure in the cerebrospinal fluid. A mathematical model is proposed for the examination of the propagation of waves through the cerebrospinal-fluid pathways. The effects due to differing degrees of obstruction of the spinal-fluid pathway (blockage) on the attenuation factors and wave speeds are discussed as are the effects due to vibrations of the elastic dura.
Sommaire
La toux produit des impulsions de pression dans le liquide cérébrospinal. Cet article suggère un modèle mathématique pour l'examen de la propagation des ondes à travers les voies de passage du liquide cérébrospinal, et il examine les effets de différents degrés d'obstruction des voies de passage du liquide spinal (blocage) sur les facteurs d'affaiblissement et les vitesses de propagation des ondes, ainsi que les effets des vibrations sur la dura élastique.
Zusammenfassung
Durch Husten werden Druckimpulse in der zerebrospinalen Flüssigkeit erzeugt. Zur Untersuchung der Fortpflanzung von Wellen durch die zerebrospinalen Flüssigkeitskanäle wird ein mathematisches Modell vorgeschlagen. Die auf die verschiedenen Behinderungsstärken für die Spinalflüssigkeitskanäle (Blockierungen) zurückzuführenden Auswirkungen auf die Dämpfungsfaktoren und Wellengeschwindigkeiten werden besprochen, ebenso die Auswirkungen von Schwingungen der elastischen Dura.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ayer, J. B. (1921) Spinal subarachnoid block as determined by combined cisternal and lumbar puncture: with special reference to the early diagnosis of cord tumour.Arch. Neurol. Psychiat. (Chic.) 4, 529–541.
Gilland, O. (1966)CSF dynamic diagnosis of spinal block. Almquist & Wiksell, Stockholm.
Lakke, J. P. W. F. (1969) Queckenstedt's test.Exerpta. Med. Amsterdam.
Lamb, H. (1898) On the velocity of sound in a tube, as affected by the elasticity of the walls.Manchester Memoirs xlii, 1–16.
Landau, L. D. andLifshitz, E. M. (1959) InFluid Mechanics, Course of theoretical physics 6. Pergamon Press.
Queckenstedt, H. H. G. (1916) Zur Diagnose der Ruckenmarkskompression.Dtsch. Z. Nervenheilk 55, 325–333.
Williams, B. (1972) Combined cisternal and lumbar pressure recordings in the sitting position using differential manometry.J. Neurol. Neurosurg. Psychiat. 35, 142–143.
Womersley, J. R. (1955) Oscillatory motion of a viscous liquid in a thin-walled elastic tube 1: the linear approximation.Phil. Mag. 46, 199–221.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lockey, M.P., Poots, G. & Williams, B. Theoretical aspects of the attenuation of pressure pulses within cerebrospinal-fluid pathways. Med. & biol. Engng. 13, 861–869 (1975). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02478090
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02478090