Abstract
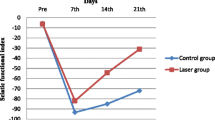
The effects of electromagnetic irradiation (EMI) of wavelength 5.6 mm (frequency 53.57 GHz) and power density 4 mW/cm2 on the recovery of function in damaged rat sciatic nerve were studied; damage was produced by nerve section followed by microsuturing. Irradiation was applied to the skin of the thigh in the area of suturing. Total action potential (TAP) recording from the nerve was used to study the functional properties of regenerating nerve fibers five months after lesioning. These experiments demonstrated that EMI had a stimulatory effect on regenerative processes in the nerve, in terms of 25–30% increases in the rate of action potential conduction along nerve fibers, with increases in TAP amplitude.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
G. N. Akoev, V. D. Avelev, and P. G. Semen'kov, “Perception of low-intensity millimeter-range electromagnetic irradiation by electroreceptors in skates,” Dokl. Akad. Nauk,322, No. 4, 791–794 (1992).
G. N. Akoev, V. D. Avelev, M. I. Chalisova, and M. I. Lyubyno, “Studies of the effect of millimeter-range electromagnetic irradiation on cultures of sensory neurons of chick embryos,” Neirofiziol.,1, No. 3, 175–179 (1993).
G. N. Akoev, O. B. Il'inskii, L. I. Kolosova, et al., “The effect of the opioid peptide dalargin on the regeneration of the sciatic nerve in the rat,” Fiziol. Zh. SSSR,75, No. 1, 33–37 (1989).
O. B. Betskii, “Millimeter waves in biology and medicine,” Radiotekh. Élektron.,38 No. 10, 1760–1782 (1993).
P. Ya Gaponyuk, A. E. Stolbikov, and T. Yu. Sherkovina, “The role of the reflex mechanism in the actions of millimeter-range electromagnetic irradiation on the human body,” in: The Use of Low-Intensity UHF Irradiation in Biology and Medicine [in Russian], Proceedings of the VII All-Union Seminar, Moscow (1989).
K. A. Grigorovich, The Surgical Treatment of Damaged Nerves [in Russian], Moscow (1981).
N. D. Devyatkov, M. B. Golant, and O. V. Betskii, Millimeter Waves and Their Role in Life Processes [in Russian], Moscow (1991).
V. S. Zemskov, N. N. Korpan, et al., “UHF electromagnetic irradiation in the treatment of purulent complications of acute inflammatory processes of the extrahepatic bile ducts,” in: The Use of Low-Intensity UHF Irradiation in Biology and Medicine [in Russian], Proceedings of the VII All-Union Seminar, Moscow (1989).
L. I. Kolosova, G. N. Akoev, V. D. Avelev, et al., “The effect of low-intensity millimeter-range electromagnetic irradiation on regeneration of the sciatic nerve in the rat,” Neirofiziologiya,1, No. 1, 27–31 (1993).
A. G. Pakhomov, “The nonthermic actions of microwaves on the functions of nerve fibers,” Biofizika,38, No. 2, 367–371 (1993).
M. V. Poslavskii, O. F. Zdanovich, A. V. Zhukotskii, et al., “The basic mechanisms of the clinical efficacy of UHF therapy,” in: The Use of Low-Intensity UHF Irradiation in Biology and Medicine [in Russian], Proceedings of the VII All-Union Seminar Moscow (1989).
L. V. Ryzhkova, “A new direction in the medical use of ultra-high frequency fields,” Izv. SPb Élektrotekhn. Instituta, No. 488, 80–86 (1992).
A. A. Simakova, T.S. Tammbaeva, and M. V. Kungurtseva, “The use of millimeter electromagnetic waves in orthopedics and traumatology,” in: The Use of Low-Intensity UHF Irradiation in Biology and Medicine [in Russian], Proceedings of the VII All-Union Seminar, Moscow (1989).
E. I. Chumasov, G. N. Akoev, L. I. Kolosova, and O. G. Trofimova, “Regeneration of the innervation of the rat limb after uniting the ends of the damaged nerve with microsurgical sutures,” Arkh. Anat., Gistol. Émbriol.,94, No. 2, 6–13 (1988).
B. G. Gold and W. C. Modley, “Regulation of axonal caliber, neurofilament content and nuclear localization in mature sensory neurons by nerve growth factor,” J. Neurosci.,11, No. 4, 943–955 (1991).
C. D. McCaig and A. M. Rajnicek, “Electrical fields, nerve growth and nerve regeneration,” Exp. Physiol.,76, 473–494 (1991).
B. F. Sisken, M. Kanje, G. Lundborg, and W. Kurtz, “Pulsed electromagnetic fields stimulate nerve regenerationin vitro andin vivo,” Restor. Neurol. Neurosci.,1, No. 3-4, 303–309 (1990).
Additional information
Laboratory for Reception Physiology, I. P. Pavlov Institute of Physiology, Russian Academy of Sciences, 199034 St. Petersburg. Translated from Fiziologicheskii Zhurnal imeni I. M. Sechenova, Vol. 82, No. 2, pp. 85–90, February, 1996.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kolosova, L.I., Akoev, G.N., Ryabchikova, O.V. et al. Effect of low-intensity millimeter-range electromagnetic irradiation on the recovery of function in lesioned sciatic nerves in rats. Neurosci Behav Physiol 28, 26–30 (1998). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02461908
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02461908