Abstract
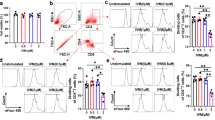
Immune response to liver-specific lipoprotein (LSP) is involved in the pathogenesis of chronic active hepatitis. Experimental hepatitis could thus be prepared in C57BL/6 mice by injection of liver-specific protein in a syngeneic liver homogenate with Freund's complete adjuvant. In hepatitic mice treated with maitake (Grifola frondosa) fruit bodies, the values of glutamic oxaloacetic transaminase (GOT) and glutamic pyruvic transaminase (GPT) values increased temporarily by 2.24–2.79 times and decreased rapidly thereafter. However, in the mice given normal feed, both values increased constantly. Thus, we examined T cell activities both in the exacerbation and remission stages of hepatitis. We suggest that the activation of CD8+ cells is more potentiated than that of CD4+ cells by administration of maitake or the D-Fraction-glucan (β-1,6 glucan having β-1,3 branches), which can enhance immuno-competent cells at the exacerbation stage. However, at the remission stage, marked potentiation of CD8+ cell activity was not observed. These results suggest that depressed suppressor T cell activity is revived by the X-Fraction-glucan (β-1,6 glucan having α-1,4 branched glucan), while the cytotoxic T cell activity, which is activated by the D-Fraction, is restricted, thereby creating a smooth shift from the exacerbation stage to the remission stage.
Similar content being viewed by others
Literature cited
Adachi, K., Nanba, H. and Kuroda, H. 1987. Potentiation of host-mediated antitumor activity in mice by β-glucan obtained fromGrifola frondosa (Maitake). Chem. Pharm. Bull.35: 262–270.
Hakomori, S. 1964. A rapid permethylation of glycolipid, and polysaccharide catalyzed by methylsulfinyl carbanion in dimethyl sulfoxide. J. Biochem.55: 205–208.
Hishida, I., Nanaba, H. and Kuroda, H. 1988. Antitumor activity exhibited by orally administered extract from fruit body ofGrifola frondosa (Maitake). Chem. Pharm. Bull.36: 1819–1827.
Hodgson, H. J. F., Wands, J. R. and Isselbacher, K. J. 1978. Alteration in suppressor cell activity in chronic active hepatitis. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA75: 1549–1553.
Kakumu, S., Hara, T., Goji, H. and Sakamoto, N. 1978. Lymphocyte cytotoxicity against chang liver cells in chronic active hepatitis. Cell Immunol.36: 46–53.
Meyer zum Buschenfelde, K. H. and Miescher, P. A. 1972. Liver specific antigens purification and characterization. Clin. Exp. Immunol.10: 89–102.
Meyer zum Buschenfelde, K. H., Kossling, F. K. and Miescher, P. A. 1972. Experimental chronic active hepatitis in rabbits following immunization with human liver proteins. Clin. Exp. Immunol.11: 99–108.
Mizoguchi, Y., Monna, T., Yamamoto, S. and Morisawa, S. 1982. Studies on the mechanism of liver injury by antibody-dependent cell-mediated cytotoxicity (ADCC): partial purification of cytotoxic factor detected in the culture supernatant of ADCC reaction. Gastroenterogia Japonica17: 360–367.
Mori, T., Mori, Y., Ogawa, M., Ueda, S., Yoshida, H., Iesato, K., Kato, I., Wakashin, Y. and Wakashin, M. 1986. Cytotoxic activities of sensitized spleen cells from hepatitis mice against hepatocyte: characterization of immune mechanisms responsible for hepatocellular damages in microcytotoxicity assay. Kanzo27: 425–430.
Mori, Y., Mori, T., Ueda, S., Yoshida, H., Iesato, K., Wakashin, Y., Wakashin, M. and Okuda, K. 1985. Study of cellular immunity in experimental autoimmune hepatitis in mice: transfer of spleen cells sensitized with liver proteins. Clin. Exp. Immunol.61: 577–584.
Nanba, H., Hamaguchi, A. and Kuroda, H. 1987. The chemical structure of an antitumor polysaccharide in fruit bodies ofGrifola frondosa (Maitake). Chem. Pharm. Bull.35: 1162–1168.
Peavy, D. and Pierce, C. W. 1974. Cell-mediated immune responses in vitro. I. Suppression of the generation of cytotoxic lymphocytes by concanavalin A and concanavalin A-activated spleen cells. J. Exp. Med.140: 356–369.
Thomson, A. D., Cochran, A. M. G., McFarlane, I. G., Eddleston, A. L. W. F. and Williams, R. 1974. Lymphocyte cytotoxicity to isolated hepatocyte in chronic active hepatitis. Nature252: 721–722.
Vergani, G. M., Vergani, D., Jenkins, P. J., Portmann, B., Mowat, A. P., Eddleston, A. L. W. F. and Williams, R. 1979. Lymphocyte cytotoxicity to autologous hepatocytes in HBsAg-negative chronic active hepatitis. Clin. Exp. Immunol.38: 16–21.
Wands, J. R., Perroto, J. L., Alpert, E. and Isselbacher, K. J. 1975. Cell-mediated immunity in acute and chronic hepatitis. J. Clin. Invest.55: 921–929.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
About this article
Cite this article
Kubo, K., Nanba, H. Modification of cellular immune responses in experimental autoimmune hepatitis in mice by maitake (Grifola frondosa). Mycoscience 39, 351–360 (1998). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02460895
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02460895