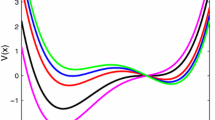
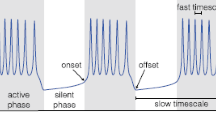
Abstract
A general mechanism underlying bursting is proposed and described. It consists of two coupled nonlinear oscillators with different frequencies, where the slower oscillator alternatively switches the faster one on and off. This mechanism is shown to work in an extended Bonhoefer-van der Pol oscillator as well as in a modified version of the Hodgkin-Huxley equations.
Similar content being viewed by others
Literature
Benettin, G., C. Froeschl and J. P. Scheide, 1979. Dynamical system with an increasing number of degrees of freedom,Phys. Rev. A 19, (6) 2454–2460.
Best, E. N., 1979. Null space in the Hodgkin-Huxley equations.Biophys. J. 27, 87–104.
Chay, T. R. and J. Keizer, 1983. Minimal model for membrane oscillations in the pancreatic beta-cell,Biophys. J. 42, 181–190.
FitzHugh, R., 1961. Impulses and physiological states in theoretical models of nerve membrane,Biophys. J.,1, 445–466.
Game, C. J. A., 1982. BVP Models: An adjustment to express a mechanism of inactivation,Biol. Cybern. 44, 223–229.
Hodgkin, A. L. and A. F. Huxley, 1952. A quantitative description of membrane current and its application to conduction and excitation in nerve,J. Physiol. (Lond.) 117, 500–544.
Holden, A. V. and M. Yoda, 1981. Ionic channel density of excitable membranes can act as bifurcation parameter,Biol. Cybern. 42, 29–38.
— and S. M. Ramadan, 1981. The response of a molluscan neuron to a cycle input: Entrainment and phaselocking,Biol. Cybern. 41, 157–163.
Jalife, J. and C. Antzelevitch, 1979. Phase resetting and annihilation of pacemaker activity in cardiac tissue,Science 206, 695–697.
Pavlidis, T., 1973.Biological Oscillators: Their Mathematical Analysis. Academic Press, New York, London.
Pinsker, H. M., 1977.Aplysia. Bursting neurons as endogeneous oscillators I. Phase-response curves for pulsed inhibitory synaptic input.J. Neurophys. 40, 527–556.
Plant, R. E., 1978. The effects of Ca2+ on bursting neurons: A modelling study,Biophys. J.,21, 217–237.
—, 1981. Bifurcation and resonance in a model for bursting nerve cells.J. Math. Biol. 11, 15–32.
— and M. Kim, 1975. On the mechanism underlying bursting in theAplysia abdominal ganglion R15 cell.Math. Biosci. 26, 357–375.
— and —, 1976. Mathematical description of a bursting pacemaker neuron by a modification of the Hodgkin-Huxley equations,Biophys. J.,16, 227–244.
Shimada, I. and T. Nagashima. 1979. A numerical approach to ergodic problems of dissipative dynamic systems,Prog. Theor. Phys. 61, 1605–1616.
Stoer, J. and R. Bulirsch, 1978.Einführung in die numerische Mathematik 2. Springer, Berlin.
Winfree, A. T. 1980.The Geometry of Biological Time. Springer, Berlin.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Honerkamp, J., Mutschler, G. & Seitz, R. Coupling of a slow and a fast oscillator can generate bursting. Bltn Mathcal Biology 47, 1–21 (1985). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02459643
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02459643