Abstract
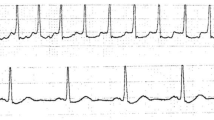
A consecutive series of 47 hospitalized cases of Guillain-Barré syndrome seen over a 10-year period was analysed with respect to: (1) age and sex; (2) antecedent events and seasonal distribution; (3) patterns of clinical presentation; (4) CSF and neurophysiological findings; (5) results of treatment with plasma exchange; and (6) outcome. Twenty-two were children, 20 middle-aged and 5 aged; 37 were male and 10 were female. The most frequent antecedent event was upper respiratory tract infections; a seasonal peak incidence was found in winter. Clinical, CSF and neurophysiological findings concurred with those in the Western literature; 79% of the cases were severe. Plasma exchange performed within the first 2 weeks of onset benefitted in the short-term outcome, i.e. improvement by 1 grade at 4 weeks, but the long-term benefit, i.e. the ability to regain independent locomotion, was questionable. Plasma exchange helped in curtailing the time to walking unaided but had no benefit on the duration of artificial ventilation. Factors associated with an adverse outcome were: age over 15 years, severity of motor electrodiagnostic findings (especially a decreased distal CMAP amplitude and EMG signs of acute denervation), requirement for ventilation and slow progression (>3 weeks) to maximum deficit. After a mean follow-up of 11 months, 55% of the patients regained independent locomotion, which is a comparatively low proportion.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abduljabbar MS (1991) Pattern of Guillain-Barré syndrome in Saudi Arabia. J Trop Geogr Neurol 1: 35–38
Arnason BGW (1993) Acute inflammatory demyelinating polyradiculoneuropathy. In: Dyck P. Thomas P, Lambert E (eds) Peripheral neuropathy. Saunders, Philadelphia, pp. 1437–1497.
Asbury AK, Arnason BG, Karp HR, McFarlin DE (1978) Criteria for the diagnosis of Guillain-Barré syndrome. Ann. Neurol 3: 565–566
Bahemuka M (1988) Guillain-Barré syndrome in Kenya: a clinical review of 54 patients. J Neurol 235: 418–421
Bosch E, Mitsumoto H (1989) Inflammatory demyelinating polyradiculoneuropathies. In: Bradley W, Daroff R, Fenichel G, Marsden C (eds) Neurology in clinical practice. vol. II. Butterworth-Heinemann. Boston, pp. 1747–1752.
Bradshaw D, Jones H (1992) Guillain-Barré syndrome in children: clinical course, electrodiagnosis, and prognosis. Muscle Nerve 15: 500–506
Brown WF, Feasby TE (1984) Conduction block and denervation in Guillain-Barré polyneuropathy. Brain 107: 219–239.
Cornblath D, Mellits E, Griffin J, McKhann G et al (1988) Motor conduction studies in Guillain-Barré syndrome: description and prognosite value. Ann Neurol 23: 354–359
Dyck P, Kurtzke J (1985) Plasma-pheresis in Guillain-Barré syndrome. Neurology 35: 1105–1107.
Eisen A, Humphreys P (1974) The Guillain-Barré syndrome. A clinical and electrodiagnostic study of 25 cases. Arch Neurol 30: 438–443
French Cooperative Group on Plasma Exchange in Guillain-Barré syndrome (1987) Efficiency of plasma exchange in Guillain-Barré syndrome: role of replacement fluids. Ann Neurol 22: 753–761
French Cooperative Group on Plasma Exchange in Guillain-Barré syndrome (1992) Plasma exchange in Guillain-Barré syndrome: one year follow-up. Ann Neurol 32: 94–97
Greenwood RJ, Newsom-Davis J, Hughes RAC, et al. (1984) Controlled trial of plasma exchange in acute inflammatory polyradiculoneuropathy. Lancet 1: 877–879.
Gross MLP, Legg NJ, Lockwood MC, Pallis C (1982) The treatment of inflammatory polyneuropathy by plasma exchange. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry 45: 675–679
Gruener G, Bosch E, Strauss R, et al (1987) Prediction of early beneficial response to plasma exchange in Guillain-Barré syndrome. Arch Neurol 44: 295–298
Guillain-Barré syndrome Study Group (1985) Plasmapheresis and acute Guillain-Barré syndrome. Neurology 35: 1096–1104
Halls J, Bredkjaer C, Friis ML (1988) Guillain-Barré syndrome: diagnostic criteria, epidemiology, clinical course and prognosis. Acta Neurol Scand 78: 118–122
Hughes RAC, Newsom-Davis JM, Perkins GD (1978) Controlled trial of Prednisolone in acute polyneuropathy. Lancet II: 1100
Kennard C, Newland AC, Ridley A (1982) Treatment of the Guillain-Barré syndrome by plasma exchange. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry 45: 847–850
Kleyweg RP, Van Der Meché FGA, Loonen MCB, De Jonge J, Knip B (1989) The natural history of the Guillain-Barré syndrome in 18 children and 50 adults. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry 52: 853–856
McKhann GM, Griffin JW, Cornblath DR, et al. (1988) Plasmapheresis and Guillain-Barré syndrome: analysis of prognostic factors and the effect of plasmapheresis. Ann Neurol 23: 347–353
Osterman P, Fagius J, Lundemo G et al. (1984) Beneficial effect of plasma exchange in acute inflammatory polyradiculoneuropathy. Lancet II: 1296–1298
Raphael JC, Chastang C (1984) Cooperative French Group. Cooperative randomised trial of plasma exchange (P.E.) in Guillain-Barré syndrome (GBS). Preliminary results. Ann Med Interne (Paris) 135: 32
Raphael JC, Masson C, Morice V, Brunel D, Gajdos P, Barois A, Goulon M (1986) Le syndrome de Landry-Guillain-Barré. Etude des facteurs pronostiques dans 223 cas. Rev Neurol (Paris) 142: 613–624
Ropper A, Wijdicks E, Shahani B (1990) Electrodiagnostic abnormalities in 113 consecutive patients with Guillain-Barré syndrome. Arch Neurol 47: 881–887
Smith GDP, Hughes RAC (1992) Plasma exchange treatment and prognosis of Guillain-Barré syndrome. Q J Med 306: 751–760
Winer JB, Hughes RAC, Greenwood RJ, Perkin GD (1985) Prognosis in Guillain-Barré Syndrome. Lancet I: 1202–1203
Winer JB, Hughes RAC, Osmond C (1988) A prospective study of acute idiopathic neuropathy. Clinical features and their prognostic value. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry 51: 605–612
Winer JB, Hughes RAC, Anderson MJ (1988) A prospective study of acute idiopathic neuropathy. Antecedent events. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry 51: 613–618
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Bahou, Y.G., Biary, N. & Al Deeb, S. Guillain-barré syndrome: A series observed at riyadh armed forces hospital january 1984–January 1994. J Neurol 243, 147–152 (1996). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02444006
Revised:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02444006