Abstract
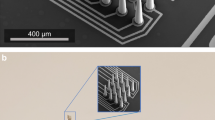
Photofabrication techniques have been used to produce a nickel-iron microelectrode array on Kapton film specifically designed for biological implantation. The probe is 2·5 mm×2 mm and carries four tissue terminals, each 2 μm in width. Both spontaneous and evoked potentials have been recorded from frog sciatic nerve. Developmental possibilities for the probe are fully discussed.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Blum, B. andFeldman, B. (1965) A micro-drive for the independent manipulation of four microelectrodes.IEEE Trans. BME-12, 121–122.
Breitweiser, G. (1974) Surface profile measurements—a survey of applications in the area of vacuum deposition.J. Vac. Sci & Technol. 11, 101–105.
Clark, G. M. andHallworth, R. J. (1976) Multiple electrode array for cochlear implant.J. Laryngol. & Otol. 90, 623–627.
Davidse, P. D. (1969) RF sputter etching—a universal etch.J. Electrochem. Soc. 116, 100.
Donaldson, P. E. K. (1973) Experimental visual prosthesis.Proc. IEEE 120, 281–298.
Dymond, A. M. (1976) Characteristics of the metaltissue interface of stimulation electrodes.IEEE Trans. BME-23, 274–280.
Erlanger, J. andGasser, H. D. (1937)Electrical signs of nervous activity, University Pennsylvania Press, Philadelphia.
Frank, K. andBecker, M. C. (1964) Microelectrodes for recording and stimulating. InNastuk, W. L. (Ed.)Physiological techniques in biological research, Chap. 2, Academic Press, New York.
Fryer, T. B. andSandler, H. (1974) A review of implant telemetry systems.Biotelemetry 1, 351–374.
Hanna, G. R. andJohnson, R. N. (1968) A rapid and simple method for the fabrication of arrays of recording electrodes.Electroenceph. Clin. Neurophysiol. 25, 284–286.
Hatzakis, M. (1969) Electron resists for microcircuit and mask production.J. Electrochem. Soc. 116, 1033–1037.
Kater, S. B. andNicholson, C. (1973),Intracellular staining in neurobiology. Springer-Verlag, Berlin.
Kohllöffel, L. U. E. (1971) Studies of the distribution of cochlear potentials along the basilar membrane.Acta Ota-Laryngol. Suppl. 288, 67.
Llinas, R., Nicholson, C. andJohnson, K. (1973) Implantable monolithic wafer recording electrodes for neurophysiology.In Phillips, M. I. (Ed.),Brain unit activity during behaviour, C. C. Thomas, Illinois.
Loeb, G. E., Marks, W. B. andBeatty, P. G. (1977) Analysis and microelectronic design of tubular electrode arrays intended for chronic, multiple singleunit recording from captured nerve fibres.Med. & Biol. Eng. 15, 195–201.
Mannard, A., Stein, R. B. andCharles, D. (1974) Regeneration electrode units: implants for recording from single peripheral nerve fibres in freely moving animals,Science 183, 547–549.
McCaffery, E. L. (1970)Laboratory preparation for macromolecular chemistry, McGraw Hill Book Co., New York.
Michelson, R. P. (1971) The results of electrical stimulation of the cochlea in human sensory deafness.Ann. Otol. Rh. & Laryngol. 80, 914–919.
Pickard, R. S. (in press) Printed circuit microelectrodes.In Donaldson, P. E. K. (Ed.),Electronics for biological research, Butterworths, London.
Pickard, R. S. andMill, P. J. (1975) Ventilatory muscle activity in restrained and free-swimming dragonfly larvae (Odonata: Anisoptera).J. comp. Physiol. 96, 37–52.
Pickard, R. S. andWelberry, T. R. (1976) Printed circuit microelectrodes and their application to honeybee brain.J. Exp. Biol. 64, 39–44.
Robinson, D. (1968) The electrical properties of metal microelectrodes.Proc. IEEE 56, 1065–1071.
Sard, R. andMaydan, R. (1971) A structural investigation of the laser machining of thin bismuth films.J. Appl. Phys. 42, 5084–5094.
Sato, K., Harada, S. Saiki, A., Kimura, T., Okubo, T. andMukai, K. (1973) A novel planar multilevel interconnection technology utilising polyimide. 23rd Electronics Components Conference, 15–20.
Skrzypek, J. andKeller, E. (1975) Manufacture of metal microelectrodes with the scanning electron microscope.IEEE Trans. BME-22, 435–437.
Sonn, M. andFeist, W. M. (1974) A prototype flexible microelectrode array for implant-prosthesis applications.Med. & Biol. Eng. 12, 778–791.
Stämpfli, R. andHille, B. (1976) Electrophysiology of the peripheral myelinated nerve.In R. Llinás andW. Precht,Frog neurobiology, Springer-Verlag, New York.
Starr, A., Wise, K. D. andCsongradi, J. (1973) An evaluation of photoengraved microelectrodes for extracellular single-unit recording.IEEE Trans. BME-20, 291–293.
Thomas, C. A., Springer, P. A., Loeb, G. E., Berwald-Netter, Y. andOkun, L. M. (1972) A miniature microelectrode array to monitor the bioelectric activity of cultured cells.Exp. Cell Res. 74, 61–66.
Vossen, J. L. andO'Neil, J. J. (1968) RF sputtering processes.RCA Rev. 29, 149–179, Princeton, New Jersey.
Wise, K. D. andAngell, J. B. (1975) A low-capacitance multielectrode probe for use in extracellular neurophysiology.IEEE Trans. BME-22, 212–219.
Wise, K. D., Angell, J. B. andStarr, A. (1970) An integrated circuit approach to extracellular microelectrodes.IEEE Trans. BME-17, 238–246.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Pickard, R.S., Joseph, P.L., Collins, A.J. et al. Flexible printed-circuit probe for electrophysiology. Med. Biol. Eng. Comput. 17, 261–267 (1979). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02440939
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02440939