Summary
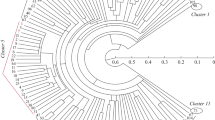
Hordeum spontaneum is the progenitor of cultivated barley (H. vulgare) and is an important source of genetic variation for barley breeding programs. The genetic diversity ofH. spontaneum in the Australian germplasm collection was investigated using the polymerase chain reaction with random and semi-random primers. This approach was found to be robust in respect of reaction conditions. Genetic dissimilarity values between genotypes were used to produce a phenogram of the relationships among the accessions using the unweighted pair group method with arithmetic mean. The largest divergence was observed among Israeli accessions, whereas the Turkish and Iranian samples clustered as distinct subsets, each apparently related to portion of the Israeli material. The results indicate that the genetic diversity of the wild barleys is broadly correlated with geographic distribution.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Brown, A.H.D., 1992. Genetic variation and resources in cultivated barley and wildHordeum. 6th International barley genetic symposium Barley genetics 6: Vol I (in press).
Brown, A.H.D., E. Nevo, D. Zohary & O. Dagan, 1978. Genetic variation in natural populations of wild barley (Hordeum spontaneum). Genetica 49:97–108.
Dawson, I.K., K.J. Chalmers, R. Waugh & W. Powell, 1993. Detection and analysis of genetic variation inHordeum spontaneum populations from Israel using RAPD markers. Mol. Ecol. 2:151–159.
Devos, K.M. & M.D. Gale, 1992. The use of randomly amplified polymorphic DNA markers in wheat. Theor. Appl. Genetics 84:567–572.
D'Ovidio, R., O.A. Tanzarella & E. Porceddu, 1990. Rapid and efficient detection of genetic polymorphism in wheat through amplification by polymerase chain reaction. Plant. Mol. Biol. 15:169–171.
Ellsworth, D.L., K.D. Rittenhouse & R.L. Honeycutt, 1993. Artifactual variation in randomly amplified polymorphic DNA banding patterns. BioTechniques 14:214–217.
Harlan, J. R. & D. Zohary, 1966. Distribution of wild wheats and barley. Science 153:1074–1080.
Nei, M. & W. Li, 1979. Mathematical model for studying genetic variation in terms of restriction endonucleases. Proc. Nat. Acad. Sci. USA 76:5269–5273.
Nevo, E., 1991. Origin, evolution, population genetics and resources for breeding of wild barley,Hordeum spontaneum, in the fertile crescent. In: P. Shewry (Ed.), Barley: genetics, biochemistry, molecular biology and biotechnology. Wallingford, UK: CAB Int; 19–43.
Nevo, E., A. Beiles & D. Zohary, 1986. Genetic resources of wild barley in the Near East: structure, evolution and application in breeding. Biol. J. Lin. Soc. 27:355–380.
Paterson, A.H., S.D. Tanksley & M.E. Sorrells, 1991. DNA markers in plant improvement. Advances in Agronomy 46:39–89.
Plucknett, D.L., N.J.H. Smith, J.T. Williams & N.M. Anishetty, 1983. Crop germplasm conservation and developing countries. Science 220:163–169.
Plucknett, D.L., N.J.H. Smith, J.T. Williams & N.M. Anishetty, 1987. Gene banks and the world's food. Princeton University Press, Princeton, NJ, USA.
Saiki, R.K. S. Scarf, F. Faloona, K.B. Mulliks, G.T. Horn, H.A. Erlich & N. Arnheim, 1985. Enzymatic amplification of betaglobin genomic sequences and restriction site analysis for diagnosis of sickly cell anemia. Science 230:1350–1354
Skolnick, M.H. & R.B. Wallace, 1988. Simultaneous analysis of multiply polymorphic loci using amplified sequence polymorphism (ASPS). Genomics 2:273–279.
Weining, S. & P. Langridge, 1991. Identification and mapping polymorphism in creases based on polymerase chain reaction. Theor, Appl. Genetics, 82:209–216.
Williams, J.G.K., A.R. Kubelik, K.J. Livak, J.A. Rafalski & S.V. Tingey, 1990. DNA polymorphisms amplified by arbitrary primers are useful as genetic markers. Nucleic Acids Res. 18:6531–6535.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Song, W., Henry, R.J. Molecular analysis of the DNA polymorphism of wild barley (Hordeum spontaneum) germplasm using the polymerase chain reaction. Genet Resour Crop Evol 42, 273–280 (1995). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02431262
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02431262