Abstract
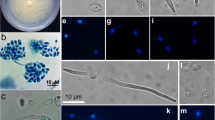
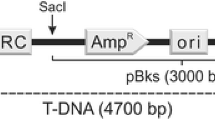
The barley leaf scald fungus,Rhynchosporium secalis, was transformed to hygromycin-B and phleomycin resistance using thehph gene fromE. coli and theble gene fromStreptoalloteichus hindustanus under the control ofAspergillus nidulans promoter and terminator sequences. Plasmid DNA was introduced into fungal protoplasts by PEG/CaCl2 treatment. Transformation frequencies varied from 59 to 493 transformants per 10 μg of DNA and 5x107 protoplasts. The antibiotic-resistant phenotype appeared to be stable under selective, as well as under nonselective, conditions for several generations. Co-transformation using theE. coli uidA gene under the control ofA. nidulans promoter and terminator sequences on a non-selectable plasmid occurred at frequencies of up to 66%.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Brückner B, Unkles SE, Weltring K, Kinghorn JR (1992) Transformation ofGibberella fujikuroi: effect of theAspergillus nidulans AMA1 sequence on frequency and integration. Curr Genet 22: 313–316
Cenis JL (1993) Rapid extraction of fungal DNA for PCR amplification. Nucleic Acids Res 20:2380
Cooley RN, Shaw RK, Franklin FCH, Caten CE (1988) Transformation of the phytopathogenic fungusSeptoria nodorum to hygromycin B resistance. Curr Genet 13:383–389
Flor HH (1971) Current status of the gene-for-gene concept. Annu Rev Phytopathol 9:275–296
Gritz L, Davies J (1983) Plasmid-encoded hygromycin B resistance: the sequence of the hygromycin B phosphotransferase gene and its expression inEscherichia coli andSaccharomyces cerevisiae. Gene 25:179–188
Hondel CAMJJ van den, Punt PJ (1991) Gene transfer systems and vector development for filamentous fungi. In: Peberdy JF, Caten CE, Ogden JE, Bennett JW (eds) Applied molecular genetics of fungi. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge, UK, pp 1–28
Knogge W, Gierlich A, Hermann H, Wernert P, Rohe M (1994) Molecular identification and characterization of thenip1 gene, an avirulence gene from the barley pathogenRhynchosporium secalis. In: Daniels MJ, Downie JA, Osbourn AE (eds) Advances in molecular genetics of plant-microbe interactions. Kluwer-Academic Publisher, Dordrecht, pp 207–214
Lehnackers H, Knogge W (1990) Cytological studies on the infection of barley cultivars with known resistance genotypes byRhynchosporium secalis. Can J Bot 68:1953–1961
Mattern IE, Punt PJ, Hondel CAMJJ van den (1988) A vector ofAspergillus transformation conferring phleomycin resistance. Fungal Genet Newslett 35:25
Newton AC (1988) Somatic recombination inRhynchosporium secalis. Plant Pathol 38:71–74
Punt PJ, Oliver RP, Dingemanse MA, Pouwels MA, Hondel CAMJJ van den (1987) Transformation ofAspergillus based on the hygromycin B resistance marker fromE. coli. Gene 56:117–124
Roberts IN, Oliver RP, Punt PJ, Hondel CAMJJ van den (1989) Expression of theEscherichia coli β-glucuronidase gene in industrial and phytopathogenic filamentous fungi. Curr Genet 15:177–180
Rohe M, Gierlich A, Hermann H, Hahn M, Schmidt B, Rosahl S, Knogge W (1995) The race-specific elicitor, NIP1, from the barley pathogen,Rhynchosporium secalis, determines avirulence on host plants of theRrs1 resistance genotype. EMBO J 14:4168–4177
Rozman D, Komel R (1994) Isolation of genomic DNA from filamentous fungi with high glucan level. Bio Technique 16:382–384
Sambrook J, Fritsch EF, Maniatis T (1989) Molecular cloning. Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory, Cold Spring Harbor, New York
Shipton WA, Boyd WJR, Ali SM (1974) Scald of barley. Rev Plant Pathol 53:839–861
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Communicated by R. Kahmann
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Rohe, M., Searle, J., Newton, A.C. et al. Transformation of the plant pathogenic fungus,Rhynchosporium secalis . Curr Genet 29, 587–590 (1996). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02426964
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02426964