Abstract
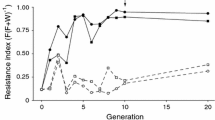
The evolution of resistance to malathion byLucilia cuprina initially results in an increase in fluctuating asymmetry. Resistant flies are at a selective disadvantage, relative to susceptibles, in the absence of the insecticide. A fitness/asymmetry modifier of diazinon-resistant phenotypes ameliorates these effects resulting in malathion-resistant phenotypes of relative fitness and asymmetry similar to susceptibles. For the nine genotypic combinations of the modifier and malathion-resistance alleles, developmental time increases linearly with increasing asymmetry. Percentage egg hatch decreases linearly with increasing asymmetry. The initially disruptive effect of the malathion-resistant allele was partially dominant, the effect of the modifier dominant. The results are discussed in terms of developmental perturbation, asymmetry estimation and relative fitness to consider whether it is adequate to use changes in fluctuating asymmetry alone as measures of developmental instability. It is suggested that in some circumstances antisymmetry may indicate developmental instability and that the diazinon/malathion-resistance systems inL. cuprina may allow the relative importance of genetical and/or environmental developmental perturbations to be ascertained.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Artavanis-Tsakonas, S., 1988. The molecular biology of the Notch locus and the fine tuning of differentiation in Drosophila. Trends in Genetics 4: 95–101.
Clarke, G. M. & J. A. McKenzie, 1987. Developmental stability of insecticide resistant phenotypes in blowfly; a result of canalizing natural selection. Nature 325: 345–346.
Clarke, G. M. & J. A. McKenzie, 1992. Coadaptation, developmental stability, and fitness of insecticide resistance genotypes in the Australian sheep blowfly, Lucilia cuprina: a review. Acta. Zool. Fennica 191: 107–110.
Clarke, G. M. & L. J. McKenzie, 1992a. Fluctuating asymmetry as a quality control indicator for insect mass rearing processes. J. Econ. Entomol. (In Press).
Clarke, G. M. & T. J. Ridsdill-Smith, 1990. The effect of avermectin B1, on developmental stability in the bush fly, Musca vetustissima, as measured by fluctuating asymmetry. Entomol. exp. appl. 54: 265–269.
Clarke, G. M., B. P. Oldroyd & P. Hunt, 1992. The genetic basis of developmental stability in Apis mellifera: heterozygosity versus genic balance. Evolution 46: 753–762.
Graham, J. H., 1992. Genomic coadaptation and developmental stability in hybrid zones. Acta Zool. Fennica 191: 121–131.
Graham, J. H., D. C. Freeman & J. M. Emlen, 1993. Antisymmetry, directional asymmetry and dynamic morphogenesis. Genetica (This Volume).
Hoffmann, A. A. & P. A. Parsons, 1991. Evolutionary genetics and environmental stress. Oxford University Press, Oxford.
Hortsch, M. & C. S. Goodman, 1991. Cell and substrate adhesion molecules in Drosophila. Ann. Rev. Cell. Biol. 7: 505–557.
Hughes, P. B. & A. L. Devonshire, 1982. The biochemical basis of resistance to organophosphorus insecticides in the sheep blowfly, Lucilia cuprina. Pestic. Biochem. Physiol. 18: 289–297.
Hughes, P. B. & J. A. McKenzie, 1987. Insecticide resistance in the Australian sheep blowfly, Lucilia cuprina: speculation, science and strategies, pp. 162–177 in: Combating resistance to Xenobiotics. Biological and chemical approaches, edited by M. G. Ford, D. W. Hollowman, B. P. S. Khambay and R. M. Sawicki, Ellis Horwood, Chichester.
Hughes, P. B., P. E. Green & K. G. Reichmann, 1984. Specific resistance to malathion in laboratory and field populations of the Australian sheep blowfly Lucilia cuprina (Diptera: Calliphoridae). J. Econ. Entomol. 77: 1400–1404.
Leary, R. F. & F. W. Allendorf, 1989. Fluctuating asymmetry as an indicator of stress: implications for conservation biology. Trends Ecol. Evol. 4: 214–217.
Leary, R. F., F. W. Allendorf & K. L. Knudsen, 1992. Genetic, environmental and developmental causes of meristic variation in rainbow trout. Acta Zool. Fennica 191: 79–95.
Markow, T. A. & J. P. Ricker, 1991. Developmental stability in hybrids between the sibling species pair, Drosophila melanogaster and Drosophila simulans. Genetica 84: 115–121.
Maynard Smith, J., R. Burian, S. Kauffman, P. Alberch, J. Campbell, B. Goodwin, R. Lande, D. Raup & L. Wolpert, 1985. Developmental constraints and evolution Quart. Rev. Biol. 60: 266–287.
Møller, A. P. & J. Höglund, 1992. Patterns of fluctuating asymmetry in avian feather ornaments: implications for models of sexual selection. Proc. Roy. Soc. Lond. B. 245: 1–5.
McKenzie, J. A., 1987. Insecticide resistance in the Australian sheep blowfly - messages for pesticide usage. Chem. Ind. 8: 266–269.
McKenzie, J. A., 1990. Selection at the dieldrin resistance locus in overwintering populations of Lucilia cuprina (Wiedemann). Aust. J. Zool. 38: 493–501.
McKenzie, J. A., 1993. Measuring fitness and intergenic interactions: The evolution of resistance to diazinon in Lucilia cuprina. Genetica (In Press).
McKenzie, J. A. & G. M. Clarke, 1988. Diazinon resistance, fluctuating asymmetry and fitness in the Australian sheep blowfly, Lucilia cuprina. Genetics 120: 213–220.
McKenzie, J. A. & A. Y. Game, 1987. Diazinon resistance in Lucilia cuprina; mapping of a fitness modifier. Heredity 59: 381–391.
McKenzie, J. A., P. Batterham & L. Baker, 1990. Fitness and asymmetry modification as an evolutionary process. A study in the Australian sheep blowfly, Lucilia cuprina and Drosophila melanogaster, pp. 57–73. In: Ecological and evolutionary genetics of Drosophila, edited by J. S. F. Baker, W. T. Starmer and R. J. MacIntyre, Plenum Press, New York.
McKenzie, J. A., J. M. Dearn & M. J. Whitten, 1980. Genetic basis of resistance to diazinon in Victorian populations of the Australian sheep blowfly, Lucilia cuprina. Aust. J. Biol. Sci. 33: 85–95.
McKenzie, J. A., J. M. Whitten & M. A. Adena, 1982. The effect of genetic background on the fitness of diazinon resistance genotypes of the Australian sheep blowfly, Lucilia cuprina. Heredity 49: 1–9.
Palmer, A. R. & C. Strobeck, 1986. Fluctuating asymmetry: measurement, analysis, patterns. Ann. Rev. Ecol. System. 17: 391–421.
Palmer, A. R. & C. Strobeck, 1992. Fluctuating asymmetry as a measure of developmental stability: Implications of non-normal distributions and the power of statistical tests. Acta Zool. Fennica 191: 57–72.
Parker, A. G., R. J. Russell, A. C. Delves & J. G. Oakeshott, 1991. Biochemistry and physiology of esterases in organo-phosphate-susceptible and -resistant strains of the Australian sheep blowfly, Lucilia cuprina. Pest. Biochem. Physiol. 41: 305–318.
Parsons, P. A., 1990. Fluctuating asymmetry: an epigenetic measure of stress. Biol. Rev. 65: 131–145.
Parsons, P. A., 1991. Evolutionary rates: stress and species boundaries. Ann. Rev. Ecol. System. 22: 1–18.
Parsons, P. A., 1992. Fluctuating asymmetry: a biological monitor of environmental and genomic stress. Heredity 68: 361–364.
Raftos, D. A., 1986. The biochemical basis of malathion resistance in the Australian sheep blowfly, Lucilia cuprina. Pestic. Biochem. Physiol. 26: 302–309.
Raftos, D. A. & P. B. Hughes, 1986. Genetic basis of a specific resistance to malathion in the Australian sheep blowfly, Lucilia cuprina (Diptera: Calliphoridae). J. Econ. Ent. 79: 553–557.
Roush, R. T. & J. A. McKenzie, 1987. Ecological genetics of insecticide and acaricide resistance. Ann. Rev. Ent. 32: 361–380.
Russell, R. J., M. M. Dumancic, G. G. Foster, G. L. Weller, M. J. Healy & J. G. Oakeshott, 1990. Insecticide resistance as a model system for studying molecular evolution, pp. 293–314. In: Ecological and evolutionary genetics of Drosophila, edited by J. S. F. Barker, W. T. Starmer and R. J. MacIntyre, Plenum Press, New York.
Scharloo, W., 1991. Canalization: genetic and developmental aspects. Ann. Rev. Ecol. System. 22: 65–93.
Sokal, R. R. & F. J. Rohlf, 1981. Biometry, 2nd edn., W. H. Freeman, San Francisco.
Templeton, A. R., H. Hollocher, S. Lawler & J. S. Johnston, 1990. The ecological genetics of abnormal abdomen in Drosophila mercatorum, pp. 17–35. In: Ecological and evolutionary genetics of Drosophila, edited by J. S. F. Barker, W. T. Starmer and R. J. MacIntyre, Plenum Press, New York.
Thornhill, R., 1992. Fluctuating asymmetry, interspecific agression and male mating tactics in two species of Japanese scorpion flies. Behav. Ecol. Sociobiol. 30: 357–363.
Van Valen, L., 1962. A study of fluctuating asymmetry. Evolution 16: 125–142.
Whitten, M. J., J. M. Dearn & J. A. McKenzie, 1980. Field studies on insecticide resistance in the Australian sheep blowfly, Lucilia cuprina. Aust. J. Biol. Sci. 33: 725–735.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
McKenzie, J.A., O'Farrell, K. Modification of developmental instability and fitness: Malathion-resistance in the Australian sheep blowfly,Lucilia cuprina . Genetica 89, 67–76 (1993). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02424506
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02424506