Summary
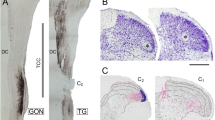
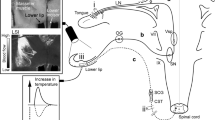
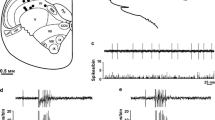
Extracellular recordings were made in the thalamus of cats anaesthetized with chloralose and urethane following electrical, mechanical and chemical stimulation of the superior sagittal sinus or middle meningeal artery. Facial receptive fields were looked for using electrical and mechanical stimuli. The locations of fifty-six cells were verified histologically. Twenty six cells were located in the ventroposteromedial nucleus (VPM) and six in its ventral periphery (VPMvp). All units in VPM had facial receptive fields, usually involving the first trigeminal division. Cells with nociceptive receptive fields or responding to the craniovascular application of bradykinin were often found in the periphery or “shell” region of VPM. Other craniovascular nociceptive cells were found in VPMvp, in the posterior group and in the intralaminar complex. This study shows that craniovascular afferents in the cat project to several thalamic nuclei and implicate VPM especially in craniovascular nociception.
Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- CeM:
-
Central medial nucleus
- CM:
-
Centre médian nucleus
- eml:
-
external medullary lamina
- HT:
-
Habenulopeduncular tract
- LGN:
-
Lateral geniculate complex
- LP:
-
Lateral posterior complex
- OT:
-
Optic tract
- POm:
-
Posterior complex, medial nucleus
- PP:
-
Pes pedunculi
- R:
-
Reticular nucleus
- VMb:
-
Basal ventral medial nucleus
- VPL:
-
Ventroposterolateral nucleus
- VPM:
-
Ventroposteromedial nucleus
- VPMvp:
-
Ventroposteromedial nucleus (ventral periphery)
- ZI:
-
Zona incerta
- Other: SSS:
-
superior sagittal sinus
- MMA:
-
middle meningeal artery
- RF:
-
receptive field
- NS:
-
nociceptive specific
- WDR:
-
wide dynamic range
- LTM:
-
low threshold mechanoreceptor
- INH:
-
inhibitory
- UNC:
-
uncertain
- BK:
-
bradykinin
- PeST:
-
peristimulus
- PoST:
-
poststimulus
References
Albe-Fessard D, Berkley KJ, Kruger L, Ralston HJ III, Willis WD Jr (1985) Diencephalic mechanisms of pain sensation. Brain Res Rev 9:217–296
Andres KH, von During M, Muszynski K, Schmidt RF (1987) Nerve fibres and their terminals of the dura mater encephali of the rat. Anat Embryol 175:289–301
Berkley KJ (1980) Spatial relationships between the terminations of somatic sensory and motor pathways in the rostral brainstem of cats and monkeys. I. Ascending somatic sensory inputs to lateral diencephalon. J Comp Neurol 193:283–317
Berman AL, Jones EG (1982) The thalamus and basal telencephalon of the cat: a cytoarchitectonic atlas with stereotaxic coordinates. University of Wisconsin Press, Madison
Burton H (1986) Second somatosensory cortex and related areas. In: Peters A, Jones EG (eds) Cerebral cortex, Vol. 50. Sensory-motor areas and aspects of cortical connectivity. Plenum Press, New York, pp 31–89
Burton H, Craig AD, Poulos DA, Molt JT (1979) Efferent projections from temperature sensitive recording loci within the marginal zone of the nucleus caudalis of the spinal trigeminal complex in the cat. J Comp Neurol 183:753–778
Bushnell MC, Duncan GH (1987) Mechanical response properties of ventroposterior medial thalamic neurons in the alert monkey. Exp Brain Res 67:603–614
Carstens E, Leah J, Lechner J, Zimmerman M (1988) Brainstem projections to thalamus and hypothalamus. Soc Neurosci Abstr 14:125
Craig AD Jr (1987) Medial thalamus and nociception: the nucleus submedius. In: Besson J-M, Guilbaud G, Peschanski M (eds) Thalamus and pain. Elsevier, Amsterdam, pp 227–243
Craig AD Jr, Burton H (1981) Spinal and medullary lamina 1 projections to nucleus submedius in medial thalamus: a possible pain center. J Neurophysiol 45:443–466
Curry MJ (1972) The exteroceptive properties of neurones in the somatic part of the posterior group (PO). Brain Res 44:439–462
Darian-Smith I (1964) Cortical projections of thalamic neurones excited by mechanical stimulation of the face of the cat. J Physiol 171:339–369
Davis KD, Dostrovsky JO (1986) Activation of trigeminal brainstem nociceptive neurons by dural artery stimulation. Pain 25:395–401
Davis KD, Dostrovsky JO (1987) Thalamic neurons excited by stimulation of the sagittal sinus and middle meningeal artery. Pain Suppl 4:S264
Davis KD, Dostrovsky JO (1988a) Responses of feline trigeminal spinal tract nucleus neurons to stimulation of the middle meningeal artery and sagittal sinus. J Neurophysiol 59:648–666
Davis KD, Dostrovsky JO (1988b) Cerebrovascular application of bradykinin excites central sensory neurons. Brain Res 446:401–406
Davis KD, Dostrovsky JO (1988c) Properties of feline thalamic neurons activated by stimulation of the middle meningeal artery and sagittal sinus. Brain Res 454:89–100
Dong WK, Ryu H, Wagman IH (1978) Nociceptive responses of neurons in medial thalamus and their relationship to spinothalamic pathways. J Neurophysiol 41:1592–1613
Dostrovsky JO, Broton JG, Warma NK (1987) Functional properties of subnucleus caudalis lamina I neurons projecting to nucleus submedius. In: Schmidt RF, Schaible H-G, Vahle-Hinz C (eds) Fine afferent nerve fibres and pain. VCH, Weinheim, pp 357–366
Feindel W, Penfield W, McNaughton F (1960) The tentorial nerves and localization of intracranial pain in man. Neurology 10:555–563
Furness JB, Papka RE, Della NG, Costa M, Eskay RL (1982) Substance P-like immunoreactivity in nerves associated with the vascular system of guinea-pigs. Neuroscience 7:447–459
Ganchrow D (1978) Intratrigeminal and thalamic projections of nucleus caudalis in the squirrel monkey (Saimiri sciureus): a degeneration and autoradiographic study. J Comp Neurol 178:281–312
Guilbaud G, Caille D, Besson JM, Benelli G (1977) Single units activities in ventral posterior and posterior group thalamic nuclei during nociceptive and non nociceptive stimulations in the cat. Archs Ital Biol 115:38–56
Guilbaud G, Peschanski M, Gautron M, Binder D (1980) Neurones responding to noxious stimulation in VB complex and caudal adjacent regions in the thalamus of the rat. Pain 8:303–318
Helme RD, Fletcher JL (1982) Substance P in the trigeminal system at postmortem: evidence for a role in pain pathways in man. Clin Exp Neurol 19:37–44
Herron P, Dykes R (1986) The ventroposterior inferior nucleus in the thalamus of cats: a relay nucleus in the pacinian pathway to somatosensory cortex. J Neurophysiol 56:1475–1497
Honda CN, Mense S, Perl ER (1983) Neurons in ventrobasal thalamus selectively responsive to noxious mechanical stimulation. J Neurophysiol 49:662–673
Hu JW, Dostrovsky JO, Sessle BJ (1981) Functional properties of neurons in cat trigeminal subnucleus caudalis (medullary dorsal horn). I. Responses to oral-facial noxious and nonnoxious stimuli and projections to thalamus and subnucleus oralis. J Neurophysiol 45:173–191
Itakura T (1986) Aminergic innervation of the cerebral veins shown by catecholamine histofluorescence, DBH immunohistochemistry, and electron microscopy. In: Owman C, Hardebo JE (eds) Neural regulation of brain circulation. Elsevier, Amsterdam, pp 451–463
Jones EG (1985) The thalamus. Plenum Press, New York
Kaelber WW, Smith TB (1979) Projections of the zona incerta in the cat, with stimulation controls. Exp Neurol 63:177–200
Kniffki K-D, Craig AD (1985) The distribution of nociceptive neurons in the cat's lateral thalamus: the dorsal and ventral periphery of VPL. In: Rowe M, Willis WD (eds) Development, organization, and processing in somatosensory pathways. Alan R Liss, New York, pp 375–382
Kniffki K-D, Mizumura K (1983) Responses of neurons in VPL and VPL-VL region of the cat to algesic stimulation of muscle and tendon. J Neurophysiol 49:649–661
Kniffki K-D, Vahle-Hinz C (1987) The periphery of the cat's ventroposteromedial nucleus (VPMp): nociceptive neurones. In: Besson J-M, Guilbaud G, Peschanski M (eds) Thalamus and pain. Elsevier, Amsterdam, pp 245–257
Lambert GA, Bogduk N, Duckworth JW, Lance JW (1979) Trigeminal correlates of cranio-vascular sensation. Proc Aust Physiol Pharmacol Soc 10/2:231P
Lambert GA, Goadsby PJ, Zagami AS, Duckworth JW (1988) Comparative effects of stimulation of the trigeminal ganglion and the superior sagittal sinus on cerebral blood flow and evoked potentials in the cat. Brain Res 453:143–149
Lambert GA, Zagami A, Lance JW (1986) Physiology and pharmacology of cervical spinal cord elements activated by stimulation of the dura mater. Soc Neurosci Abstr 12:230
Liu-Chen L-Y, Gillespie SA, Norregaard TV, Moskowitz MA (1984) Co-localization of retrogradely transported wheat germ agglutinin and the putative neurotransmitter substance P within trigeminal ganglion cells projecting to cat middle cerebral artery. J Comb Neurol 225:187–192
Liu-Chen L-Y, Mayberg MA, Moskowitz MA (1983) Immunohistochemical evidence for a substance P-containing trigeminovascular pathway to pial arteries in cats. Brain Res 168:162–166
Matsumoto N, Sato T, Sawano H, Tochinai A, Suzuki TA (1988) Characteristics of tooth pulp-driven neurons in the posterior group of the cat thalamus. Neurosci Lett 93:253–258
Mayberg MR, Langer R, Zervas N, Moskowitz MA (1981) Perivascular meningeal projections from cat trigeminal ganglia: possible pathway for vascular headaches in man. Science 213:228–230
Mayberg MR, Zervas NT, Moskowitz MA (1984) Trigeminal projections to supratentorial pial and dural blood vessels in cats demonstrated by horseradish peroxidase histochemistry. J Comp Neurol 223:46–56
Moskowitz MA (1984) The neurobiology of vascular head pain. Ann Neurol 16:157–168
Northfield DWC (1938) Some observations on headache. Brain 61:133–162
O'Connor TP, van der Kooy D (1986) Pattern of intracranial and extracranial projections of trigeminal ganglion cells. J Neurosci 6:2200–2207
Olausson B (1989) Thalamo-cortical mechanisms in nociception. Thesis. University of Göteborg, Göteborg, pp 115–131
Pandya DN, Yeterian EH (1985) Architecture and connections of cortical association areas. In: Peters A, Jones EG (eds) Cerebral cortex, Vol. 4. Association and auditory cortices. Plenum Press, New York, pp 3–55
Penfield W, McNaughton F (1940) Dural headache and innervation of the dura mater. Arch Neurol Psychiat 44:43–75
Perl ER, Whitlock DG (1961) Somatic stimuli exciting spinothalamic projections to thalamic neurons in cat and monky. Exp Neurol 3:256–296
Poggio GF, Mountcastle VB (1960) A study of the functional contributions of the lemniscal and spinothalamic systems to somatic sensibility. Bull Johns Hopk Hosp 106:266–316
Ray BS, Wolff HG (1940) Experimental studies on headache: Pain-sensitive structures of the head and their significance in headache. Arch Surg 41:813–856
Rinvik E (1968) A re-evaluation of the cytoarchitecture of the ventral nuclear complex of the cat's thalamus on the basis of corticothalamic connections. Brain Res 8:237–254
Rydenhag B, Roos A (1986) Projections of tooth pulp afferents to the thalamus of the cat. II. Distribution and characteristics of single units. Exp Brain Res 64:49–58
Shammah-Lagnado SJ, Negrao N, Ricardo JA (1985) Afferent connections of the zona incerta: a horseradish peroxidase study in the rat. Neuroscience 15:109–134
Shigenaga Y, Nakatani Z, Nishimori T, Suemune S, Kuroda R, Matano S (1983) The cells of origin of cat trigeminothalamic projections: especially in the caudal medulla. Brain Res 277:201–222
Shigenaga Y, Takabatake M, Sugimoto T, Sakai A (1979) Neurons in marginal layer of trigeminal nucleus caudalis projecting to ventrobasal complex (VB) and posterior nuclear group (PO) demonstrated by retrograde labeling with horseradish peroxidase. Brain Res 166:391–396
Siegel S (1956) Nonparametric statistics for the behavioural sciences. McGraw-Hill Kogakusha, Tokyo
Steiger HJ, Meakin CJ (1984) The meningeal representation in the trigeminal ganglion-an experimental study in the cat. Headache 24:305–309
Stewart WA, King RB (1963) Fiber projections from the nucleus caudalis of the spinal trigeminal nucleus. J Comp Neurol 121:271–286
Strassman A, Mason P, Moskowitz M, Maciewicz R (1986) Response of brainstem trigeminal neurons to electrical stimulation of the dura. Brain Res 379:242–250
Tiwari RK, King RB (1974) Fiber projections from trigeminal nucleus caudalis in primate (squirrel monkey and baboon). J Comp Neurol 158:191–206
Vahle-Hinz C, Bruggemann J, Kniffki K-D (1987) “Inhibitory” responses to noxious stimuli of neurons located in the periphery of the ventroposteromedial nucleus (VPMp) of the cat. Soc Neurosci Abstr 13:581
Vogt BA (1985) Cingulate cortex. In: Peters A, Jones EG (eds) Cerebral cortex, Vol. 4. Association and auditory cortices. Plenum Press, New York, pp 89–150
Willis WD Jr (1985) Nociceptive transmission in the primate spinal cord. In: Rowe M, Willis WD Jr (eds) Development, organization and processing in somatosensory pathways. Alan R Liss Inc, New York, pp 333–345
Wirth FP Jr, Van Buren JM (1971) Referral of pain from dural stimulation in man. J Neurosurg 34:630–642
Woda A, Azerad J, Guilbaud G, Besson JM (1975) Etude microphysiologique des projections thalamiques de la pulpe dentaire chez le chat. Brain Res 89:193–213
Yasui Y, Itoh K, Kamiya H, Ino T, Mizuno N (1988) Cingulate gyrus of the cat receives projection fibers from the thalamic region ventral to the ventral border of the ventrobasal complex. J Comp Neurol 274:91–100
Yokota T (1988) Anatomy and physiology of intra- and extracranial nociceptive afferents and their central projections. In: Olesen J, Edvinsson L (eds) Basic mechanisms of headache. Elsevier, Amsterdam, pp 117–126
Yokota T, Asato F, Koyama N, Masuda T, Taguchi H (1988) Nociceptive body representation in nucleus ventralis posterolateralis of cat thalamus. J Neurophysiol 60:1714–1727
Yokota T, Koyama N, Matsumoto N (1985) Somatotopic distribution of trigeminal nociceptive neurons in ventrobasal complex of cat thalamus. J Neurophysiol 53:1387–1400
Yokota T, Matsumoto N (1983a) Somatotopic distribution of trigeminal nociceptive specific neurons within the caudal somatosensory thalamus of the cat. Neurosci Lett 39:125–130
Yokota T, Matsumoto N (1983b) Location and functional organization of trigeminal wide dynamic range neurons within the nucleus ventralis posteromedialis of the cat. Neurosci Lett 39:231–236
Yokota T, Nishikawa Y, Koyama N (1986) Tooth pulp input to the shell region of nucleus ventralis posteromedialis of the cat thalamus. J Neurophysiol 56:80–98
Zagami AS, Lambert GA, Lance JW (1987) Studies in the cat on the pathway for vascular head pain. Cephalalgia Suppl 6:7–9
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zagami, A.S., Lambert, G.A. Stimulation of cranial vessels excites nociceptive neurones in several thalamic nuclei of the cat. Exp Brain Res 81, 552–566 (1990). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02423504
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02423504