Abstract
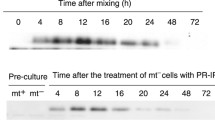
When mating-type minus (mt−) and plus (mt+) cells of theClosterium peracerosum-strigosum-littorale complex were mixed together in a nitrogen-deficient mating medium, cells of both types released protoplasts, this release being the first step in the process of conjugation. Release of protoplasts by mt− cells also proceeded without pairing in a medium in which mt− and mt+ cells had previously been cultured together. A protein with the ability to induce the release of protoplasts was purified from this medium by sequential column-chromatographic steps, and named PR-IP (protoplast-release-inducing protein). The PR-IP had an apparent molecular mass (Mr) of 95000 on gel filtration and could be separated into several isoforms by anion-exchange chromatography. Each isoform consisted of two glycopolypeptides of Mrs 42000 and 19000, while the deglycosylated polypeptides had Mrs of 34000 and 18000, respectively. From an analysis of dose-response curves, the numbers of PR-IP molecules required for the release of a protoplast by a single cell was calculated as 1.5·109 and the concentration required for 50% of the maximum response (ED50) as 4.1·10−9M. We suggest that the PR-IP is a biologically active glycoprotein which induces the release of gametic protoplasts from mt− cells of thisClosterium complex.
Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- kDa:
-
kilodalton
- MI medium:
-
nitrogen-deficient mating medium
- Mr :
-
apparent molecular mass
- PI:
-
protoplastrelease-inducing
- PR-IP:
-
protoplast-release-inducing protein
- SDS-PAGE:
-
sodium dodecyl sulfate-polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis
References
Bradford, M.M. (1976) A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal. Biochem.72, 248–254
Buchanan, M.J., Snell, W.J. (1988) Biochemical studies on lysin, a cell wall degrading enzyme released during fertilization inChlamydomonas. Exp. Cell Res.179, 181–193
Edge, A.S.B., Faltynek, C.R., Hof, L., Reichert, L.E., Weber, P. (1981) Deglycosylation of glycoproteins by trifluoromethanesulfonic acid. Anal. Biochem.118, 131–137
Hogetsu, T., Yokoyama, M. (1979) Light, a nitrogen-depleted medium and cell-cell interaction in the conjugation process ofClosterium ehrenbergii Meneghini. Plant Cell Physiol.20, 811–817
Ichimura, T. (1971) Sexual cell division and conjugation-papilla formation in sexual reproduction ofClosterium strigosum. Proc. 7th Int. Seaweed Symp., pp. 208–214, Nishizawa, K., ed. University of Tokyo Press, Tokyo
Jaenicke, L., Kuhne, W., Spessert, R., Wahle, U., Waffenschmidt, S. (1987) Cell-wall lytic enzymes (autolysins) ofChlamydomonas reinhardtii are (hydroxy)proline-specific proteases. Eur. J. Biochem.170, 485–491
Kato, A., Sasaki, K. (1983) Effect of tunicamycin on sexual reproduction in heterothallic strains ofClosterium. J. Fac. Sci. Hokkaido Univ. Ser. V13, 1–6
Kato, A., Sasaki, K. (1985) Sexual interaction in heterothallic strains ofClosterium peracerosum-strigosum-littorale. Plant Physiol.77, 556–559
Kato, A., Obokata, J., Sasaki, K. (1981) Mating type interaction inClosterium peracerosum-strigosum-littorale: mating induced protoplast release. Plant Cell Physiol.22, 1215–1222
Konat, G., Offner, H., Mellah, J. (1984) Improved sensitivity for detection and quantitation of glycoproteins on polyacrylamide gels. Experientia40, 303–304
Laemmli, U.K. (1970) Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature227, 680–685
Matsuda, Y., Tamaki, S., Tsubo, Y. (1978) Mating type specific induction of gametes inChlamydomonas reinhardtii. Plant Cell Physiol.19, 1253–1261
Matsuda, Y., Saito, T., Yamaguchi, T., Kawase, H. (1985) Cell wall lytic enzyme released by mating gametes ofChlamydomonas reinhardtii is a metalloprotease and digests the sodium perchlorate-insoluble component of cell wall. J. Biol. Chem.260, 6373–6377
Snell, W.J., Eskue, W.A., Buchanan, M.J. (1989) Regulated secretion of a serine protease that activates an extracellular matrixdegrading metalloprotease during fertilization inChlamydomonas. J. Cell. Biol.109, 1689–1694
Tamaki, S., Matsuda, Y., Tsubo, Y. (1981) The isolation and properties of the lytic enzyme of the cell wall released by mating gametes ofchlamydomonas reinhardtii. Plant Cell Physiol.22, 127–133
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sekimoto, H., Satoh, S. & Fujii, T. Biochemical and physiological properties of a protein inducing protoplast release during conjugation in theClosterium peracerosum-strigosum-littorale complex. Planta 182, 348–354 (1990). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02411384
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02411384