Summary
Octacalcium phosphate (Ca8H2(PO4)6·5H2O) is considered to be a precursor in the formation of apatite in bones and teeth; a crucial step for incorporation of impurities appears to occur during its hydrolysis. The present study examines the role that octacalcium phosphate plays in the process of incorporation of carbonate into apatite. Chemical, X-ray diffraction, and infrared techniques were used.
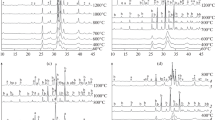
When octacalcium phosphate is hydrolyzed in the presence of sodium and carbonate ions in aqueous media, approximately one sodium and one carbonate ion seem to substitute for a calcium and phosphate ion, respectively, in forming apatite, and thea axis is shortened. The infrared spectrum of the product indicates that the carbonate is in the type B site, which is presumed to be a phosphate site. This mechanism is of particular importance since the presence of carbonate in human enamel appears to be related to caries susceptibility. A structural mechanism for the incorporation of impurities during hydrolysis of octacalcium phosphate is presented.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Young, R.A.: Some aspects of crystal structural modeling of biological apatites, Collogues Int. C.N.R.S. (Paris), 1973
LeGeros, R.Z., LeGeros, J.P., Trauz, O.R., Shirra, W.P.: Conversion of monetite, CaHPO4, to apatites, Adv. X-ray Anal.14:57, 1971
Suzuki, M.: Studies on the physicochemical nature of hard tissue, Collogues Int. C.N.R.S. (Paris), 1973
Elliott, J.C.: The crystallographic stucture of dental enamel and related apatities, Ph.D. Thesis, University of London, 1964
Bonel, G., Montel, G.: Synthetic carbonated apatite, C.R. Acad. Sci. [D] (Paris)258:923, 1964
LeGeros, R.Z.: Effect of carbonate on the lattice parameters of apatite, Nature206:403, 1965
LeGeros, R.Z., LeGeros, J.P., Trautz, O.R., Klein, E.: Spectral properties of carbonate in carbonate containing apatites, J. Dent. Res.43:751, 1964 (abst.)
Hayek, E.: Die Mineralsubstanz der Knochen, Klin. Wochenschr.45:857–863, 1967
Blitz, R.M., Pellegrino, E.D.: The nature of bone carbonate, Clin. Orthop.129:279, 1977
Pellegrino, E.D., Blitz, R.M.: Calcium phosphate carbonate transformations in renal calculi, Calcif. Tissue Res.26:191, 1978
Brown, W.E.: Crystal growth of bone mineral, Clin. Orthop.44:205, 1966
Sobel, A.E.: Interrelationship of tooth composition, body fluids, diet, and caries susceptibility, Ann. N.Y. Acad. Sci.85:96–109, 1960
Willis, J.B.: The determinations of metals in blood serum by atomic absorption spectroscopy—I. Calcium, Spectrochim. Acta16:259–272, 1960
Brabson, J.S., Dunn, R.L., Epps, E.Z., Jr., Hoffman, W.M., Jacob, K.D.: Report on phosphorus in fertilizers: photometric determination of total phosphorus, J. Assoc. Off. Anal. Chem.41:517, 1958
LeGeros, R.Z.: Crystallographic studies on the carbonate substitution in the apatite, Thesis, New York University, 1967
Bonel, G., Labarthe, J.C., Vignoles, C.: Sur la physicochimie et la cristallographie des apatites d'interest biologique, C.R. Coll. Int. 117–125, Paris, September, 1973
Brown, W.E., Chow, L.C.: Chemical properties of bone mineral, Annu. Rev. Mater. Sci.6:213–236, 1976
Brown, W.E., Schroeder, L.W., Ferris, J.S.: Interlayering of crystalline octacalcium phosphate and hydroxyapatite, J. Phys. Chem. (in press)
Brown, W.E., Smith, J.P., Lehr, J.R., Frazier, A.W.: Crystallographic and chemical relations between octacalcium phosphate and hydroxyapatite, Nature196:1050–1055, 1962
Brown, W.E., Nylen, M.U.: Role of octacalcium phosphate in formation of hard tissues, J. Dent. Res.43:5, 1964 (abst. 18)
Schroeder, L.W., Mathew, M.: Cation ordering in Ca2La8(SiO4)6O2, J. Solid State Chem.26:383–387, 1978
Glas, J.-E.: Studies on the ultrastructure of dental enamel VI crystal chemistry of shark's teeth, Odontologisk Revy.13:315–316, 1962
Blumenthal, N.C., Betts, F., Posner, A.S.: Effect of carbonate and biological macromolecules on formation and properties of hydroxyapatite, Calcif. Tissue Res.18:81–90, 1975
Despotovic, R., Filipovic-Vincekovic, N., Füredi-Milhofer, H.: Precipitation of calcium phosphates from electrolyte solutions. III, Calcif. Tissue Res.18:13–26, 1975
Eanes, E.D., Meyer, J.L.: The maturation of crystalline calcium phosphates in aqueous suspensions at physiological pH, Calcif. Tissue Res.23:259–260, 1977
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Chickerur, N.S., Tung, M.S. & Brown, W.E. A mechanism for incorporation of carbonate into apatite. Calcif Tissue Int 32, 55–62 (1980). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02408521
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02408521