Abstract
The de novo creation of long, homogeneous, satellite DNA domains was postulated previously to occur by saltatory amplification. In this paper, pulsed field gel electrophoresis analysis of the α satellite DNA block organization of the human chromosome 21 supports this hypothesis.
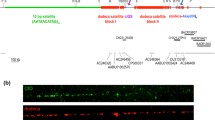
Double-dimension electrophoresis indicated that the variant copies of the basic α satellite repeat of chromosome 21 are organized in a single 3,150 Kblong domain. It was also established that the other satellite DNAs found in man (β, II, and III) are organized independently of the α satellite DNA block of the same chromosome.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Agresti A, Rainaldi G, Lobbiani A, Magnani I, Di Lernia R, Meneveri R, Siccardi AG, Ginelli E (1987) Chromosomal location by in situ hybridization of the human Sau3A family of DNA repeats. Hum Genet 75:326–332
Bellis M, Pagès M, Roizès G (1987) Electrophorèse de l'ADN en champ pulsé. Rev Inst Pasteur Lyon 20:45–55
Choo KH, Vissel B, Nagy A, Earle E, Kalitsis P (1991) A survey of genomic distribution of alpha satellite DNA on all the human chromosomes, and derivation of a new consensus sequence. Nucleic Acids Res 19:1179–1182
Chu G, Vollrath D, Davis RW (1986) Separation of large DNA molecules by contour-clamped homogenous electric fields. Science 234:1582–1585
Dod B, Mottez E, Desmarais E, Bonhomme F, Roizès G (1989) Concerted evolution of light satellite DNA in genusMus implies amplification and homogenization of large blocks of repeats. Mol Biol Evol 6:478–491
Dover G (1982) Molecular drive: a cohesive mode of species evolution. Nature 299:111–117
Drinkwater RD, Burgoyne LA, Skinner JD (1986) Two human repetitive DNA elements: a new interspersed repeat found in the factor IX gene, and a satellite 11 tandem repeat sequence. Nucleic Acids Res 14:9541
Feinberg AP, Vogelstein B (1983) A technique for radiolabeling DNA restriction endonuclease fragments to high specific activity. Anal Biochem 132:6–13
Fowler C, Drinkwater R, Skinner J, Burgoyne L (1988) Human satellite-III DNA: an example of a “macrosatellite” polymorphism. Hum Genet 79:265–272
Gosden JR, Mitchell AR, Buckland RA, Clayton RP, Evans HJ (1975) The location of four human satellite DNAs on human chromosomes. Exp Cell Res 92:148–158
Jorgensen AL, Bostock CJ, Bak AL (1987) Homologous subfamilies of human alphoid repetitive DNA on different nucleolus organizing chromosomes. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 84:1075–1079
Lohe AR, Brutlag DL (1987) Adjacent satellite DNA segments inDrosophila: structure of junctions. J Mol Biol 194:171–179
Manuelidis L (1978) Complex and simple sequences in human repeated DNAs. Chromosoma 66:1–21
Marçais B, Bellis M, Gérard A, Pagès M, Boublik Y, Roizès G (1991a) Structural organization and polymorphism of the alpha satellite DNA sequences of chromosomes 13 and 21 as revealed by pulse field gel electrophoresis. Hum Genet 86:311–316
Marçais B, Charlieu JP, Allain B, Brun E, Bellis M, Roizès G (1991b) On the mode of evolution of alpha satellite DNA in human populations. J Mol Evol 33:42–48
Marçais B, Gérard A, Bellis M, Roizès G (1991c) Taq I reveals two independent alphoid polymorphisms on human chromosomes 13 and 21. Hum Genet 86:307–310
Meneveri R, Agresti A, Marozzi A, Saccone S, Rocchi M, Archidiacono N, Corneo G, Della Valle G, Ginelli E (1993) Molecular organization and chromosomal location of human GC-rich heterochromatic blocks. Gene 123:227–234
Meneveri R, Agresti A, Della Valle G, Talarico D, Siccardi AG, Ginelli E (1985) Identification of a human clustered G + C-rich DNA family of repeats (Sau3A family). J Mol Biol 186:483–489
Oackey R, Tyler-Smith C (1990) Y Chromosome DNA haplotyping suggests that most European and Asian men are descended from one of two males. Genomics 7:325–330
Pech M, Streeck RE, Zachau HG (1979) Patchwork structure of a bovine satellite DNA. Cell 18:883–893
Singer MF (1982) Highly repeated sequences in mammalian genomes. Int Rev Cytol 76:67–112
Vissel B, Nagy A, Choo KHA (1992) A satellite III sequence shared by human chromosomes 13, 14, and 21 that is contiguous with α satellite DNA. Cytogenet Cell Genet 61:81–86
Vitek MP, Devine E, Dutkowski R, Blume A, Mullikin-Kilpatrick D, Miller DL, Brown WT, Wray W (1985) Isolation of specific chromosomes and their DNA. Gene Anal Tech 2:16–21
Warburton PE, Willard HF (1990) Genomic analysis of sequence variation in tandemly repeated DNA. Evidence for localized homogeneous sequence domains within arrays of α-satellite DNA. J Mol Biol 216:3–16
Waye JS, Willard HF (1989) Human β satellite DNA: genomic organization and sequence definition of a class of highly repetitive tandem DNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 86:6250–6254
Willard HF, Waye JS (1987) Hierarchical order in chromosome-specific human alpha-satellite DNA. Trends Genet 3:192–198
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Marçais, B., Laurent, AM., Charlieu, JP. et al. Organization of the variant domains of α satellite DNA on human chromosome 21. J Mol Evol 37, 171–178 (1993). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02407353
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02407353