Summary
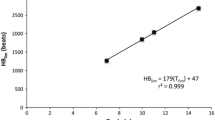
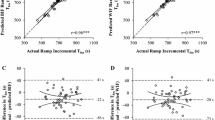
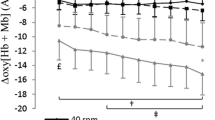
Recent studies have demonstrated there is a definitive deflection in the heart rate response to incremental velocity work that coincides with the anaerobic threshold. These studies were conducted with elite athletes who performed the specific activities in which they were trained. The purpose of this study was to determine if the same relationship in heart rate and ventilatory response to increasing velocity was evident in nine untrained healthy subjects aged 22 to 36 years performing leg ergometry under controlled laboratory conditions. All subjects began pedaling at 50 rpm with an initial power output of 100 W. Pedaling rates were increased by 5 rpm every 30 s. This increment was equivalent to a power increase of 11.1 W. The subjects cycled to the point of exhaustion or until they could no longer maintain the pedaling speed at the higher velocities. Heart rate and expiration gases were collected at 30-s intervals. The results indicated that the heart rate and ventilatory response to increasing velocity as previously reported under field conditions does not exist under laboratory conditions. While there was a definitive and statistically significant inflection in the ventilatory response to increasing velocity, heart rate remained linear. Therefore, caution should be used when determining the anaerobic threshold from the single measure of heart rate response.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Cellini M, Vitiello P, Nagliati A, Ziglis PG, Martinelli S, Ballarin E, Conconi F (1986) Noninvasive determination of the anaerobic threshold in swimming. Int J Sports Med 7:347–351
Conconi F, Ferrari M, Ziglio P, Droghetti P, Codeca L (1982) Determination of the anaerobic threshold by a noninvasive field test in runners. J Appl Physiol 52:869–873
Droghetti P, Borsetto C, Casoni I, Cellini M, Ferrari M, Paolini AR, Ziglio PG, Conconi F (1985) Noninvasive determination of the anaerobic threshold in canoeing, cross-country skiing, cycling, roller, and iceskating, rowing, and walking. Eur J Appl Physiol 53:299–303
Dwyer J, Bybee R (1983) Heart rate indices of the anaerobic threshold. Med Sci Sports Exerc 15:72–76
Francis KT (1989) Anaerobic threshold. Comput Biol Med 19:1–6
Hansen D, Francis KT (1988) Anaerobic threshold in arm ergometry with increasing resistance. J Ala Acad Sci 59:193
Hughson RL (1984) Methodologies for measurement of the anaerobic threshold. Physiologist 27:304–311
Jones RH, Molitoris BA (1984) A statistical method for determining the breakpoint of two lines. Anal Biochem 141:287–290
Kremser CB, Rajfer S (1986) The normal cardiovascular response to exercise. In: Leff A (ed) Cardiopulmonary exercise testing. Grune and Stratton, Orlando, pp 107–121
Lundberg MA, Hughson RL, Weisiger KH, Jones RH, Swanson GD (1986) Computerized estimation of lactate threshold. Comput Biomed Res 19:481–486
Palka MJ, Rogozinski A (1986) Standards and predicted values of anaerobic threshold. Eur J Appl Physiol 54:643–646
Reybrouck T, Heigenhauser GF, Faulkner JA (1975) Limitations to maximum oxygen uptake in arm, leg, and combined arm-leg ergometry. J Appl Physiol 38:774–778
Sumsion B, Francis KT (1988) Anaerobic threshold in arm ergometry with increasing velocity. J Ala Acad Sci 59:186
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Francis, K.T., McClatchey, P.R., Sumsion, J.R. et al. The relationship between anaerobic threshold and heart rate linearity during cycle ergometry. Europ. J. Appl. Physiol. 59, 273–277 (1989). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02388328
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02388328