Abstract
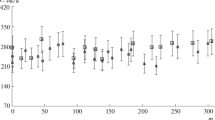
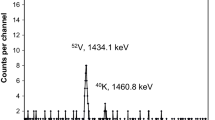
Arsenic is toxic to humans with the lethal dose being approximately 1 mg/kg/day. At much lower long-term exposures, arsenic is hypothesized to increase the risk of certain cancers. We have developed an irradiation position for the neutron activation analysis (NAA) of nail specimens for arsenic, in support of a case-control study involving New Hampshire residents consuming well water above the EPA Safe Drinking Water Standard of 0.050 ppm. Arsenic is bound to nail keratin through sulfhydryl groups proportional to intake providing a convenient means of integrating arsenic intake in population-based studies. Our objective was to develop the necessary facilities and procedures by which relatively small samples (i.e. 20 to 100 mg) could be accurately analyzed for arsenic, so that affordable nutritional epidemiology investigations, requiring large numbers of samples (>1000 in this case), could be undertaken. A high-flux reflector position, with minimal axial variation throughout the fuel cycle, suitable for pneumatic-tube irradiations, was characterized by measurement of the neutron flux distribution (thermal and epithermal) within the irradiation capsule over time. Results from application of the method to a case-control study of basal and squamous cell skin cancer will be presented.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Toxicological Profile for Arsenic (ATSDR/TP-88/02), Washington, D.C., Agency for-Toxic Substances and Disease Registry, 1989.
M. R. Karagas, J. S. Morris, J. E. Weiss, V. L. Spate, C. K. Baskett, E. R. Greenberg, Cancer Epidemiol., Biomarkers Prevention, 5 (1996) 849.
H. Y. Chiou, Y. M. Hsueh, K. F. Liaw, S. F. Horng, M. H. Chiang, Y. S. Pu, J. S. N. Lin, C. H. Huang, C. J. Chen, Cancer Res., 55 (1995) 1296.
C. J. Chen, Y. C. Chuang, T. M. Lin, H. Y. Wu, Cancer Res., 45 (1985) 5895.
K. P. Chen, H. Y. Wu, J. Formosan Med. Assoc., 61 (1962) 611.
Y. M. Hsueh, G. S. Cheng, M. M. Wu, H. S. Yu, T. L. Kuo, C. J. Chen, Br. J. Cancer, 71 (1995) 109.
W. P. Tseng, Environ. Health Perspect., 19 (1977) 9.
C. J. Chen, Y. C. Chuang, S. L. You, T. M. Lin, H. Y. Wu, Br. J. Cancer., 53 (1986) 399.
J. R. Goldsmith, M. Deane, J. Thom, G. Gentry, Water Res., 6 (1972) 1133.
W. Morton, G. Starr, D. Pohl, J. Stoner, S. Wagner, D. Weswig, Cancer, 37 (1976) 2523.
J. M. Harrington, J. P. Middaugh, D. L. Morse, J. Housworth, Am. J. Epidemiol., 108 (1978) 377.
New Hampshire Water Supply and Pollution Control Commission (NHWSPCC), 1986. (unpublished).
H. A. Schroeder, J. J. Balassa, J. Chron. Dis., 19 (1966) 85.
G. Henke, A. Nucci, L. S. Queiroz, Arch. Toxicol., 50 (1982) 125.
C. K. Baskett, M. S. Thesis, University of Missouri-Columbia, 1995.
M. Garland, J. S. Morris, B. A. Rosner, M. J. Stampfer, V. L. Spate, C. K. Baskett, W. C. Willett, D. J. Hunter, Cancer Epidemiol., Biomarkers Prevention, 2 (1993) 493.
T. P. Cheng, Ph. D. Dissertation, University of Missouri-Columbia, 1994.
C. K. Baskett, V. L. Spate, J. S. Morris, H. D. Anderson, M. M. Mason, C. L. Reams, T. P. Cheng, K. R. Zinn, G. M. Hill, R. P. Dowdy, J. Radioanal. Nucl. Chem., 195 (1995) 97.
T. P. Cheng, J. S. Morris, S. R. Koirtyohann, V. L. Spate, C. K. Baskett J. Radioanal. Nucl. Chem., 195 (1995) 31.
L. Wetter, M.S. Thesis, University of Missouri-Columbia, 1990.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Nichols, T.A., Morris, J.S., Mason, M.M. et al. The study of human nails as an intake monitor for arsenic using neutron activation analysis. J Radioanal Nucl Chem 236, 51–57 (1998). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02386317
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02386317