Abstract
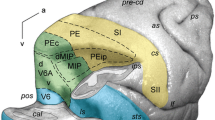
The cortical sensory projections of somatic, auditory, and visual origin have been mapped in the chloralosed potto. The pathways of the contralateral side of the body project in a classical somatotopic fashion to a large area SI, behind the motor cortex and the central sulcus. The latter constitutes the posterior boundary of the motor cortex only in its ventral part. In its middle zone the motor cortex extends to its posterior lip. Above the sulcus the motor zone is immediately adjacent to the preparietal area. Visual evoked potentials are recorded behind the transverse occipital sulcus with a maximal focus just caudal to an occipital dimple. The auditory area is situated between the sylvian and parallel sulci. No heterosensory potentials (visual or auditory) can be recorded from the somatomotor area, nor from any other part outside their primary projection area. An area of convergent somatic projection devoid of somatotopic organization is found between SI and the auditory zone and another one in front of the central sulcus. In view of the poor cortical heterosensory integration, the sensory projection system of the potto seems to be less developed than in the cat.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Albe-Fessard, D., 1967. Organization of somatic central projections. In:Contributions to Sensory Physiology, Vol. II,W. D. Neff (ed.), Academic Press, New York, pp. 101–167.
———— &J. M. Besson, 1973. Convergent thalamic and cortical properties: The non-specific system. In:Handbook of Sensory Physiology, Vol. II,A. Iggo (ed.), Springer Verlag, Berlin, pp. 489–560.
Beddard, F. E., 1895. On the brain in the Lemurs.Proc. zool. Soc. Lond., pp. 142–148.
————, 1904. Note on the brain of the Potto (Perodicticus potto) and the Slow Loris (Nycticebus tardigradus), with some observations upon the arteries of the brain in certain primates.Proc. zool. Soc. Lond., 1: 157–163.
Bosman, W., 1704.Nauwkeurige beschrijving van de guinese Goud, Tand- en Slavekust. Schouten, Utrecht.
Brodmann, K., 1908. Die cytoarchitektonische Cortex gliederung der Halbaffen (Lemuriden).J. Psychol. u. Neurol. (Leipzig), 10: 287–334.
Connolly, C. J., 1950.External Morphology of the Primate Brain. Springfield, Illinois.
Elliot Smith, G., 1903. On the morphology of the brain in the mammalia with special reference to that of the Lemurs, recent and extinct.Trans, Linn. Soc., 2nd Ser., Zool., 8: 319–432.
Heffner, H. &B. Masterton, 1970. Hearing in primitive primates: Slow Loris (Nycticebus coucang) and Potto (Perodicticus potto).J. comp. physiol. Psychol., 71: 175–182.
Haines, D. E., B. C. Albright, G. E. Goode, &H. M. Murray, 1974. The external morphology of the brain of some Lorisidae. In:Prosimian Biology,R. D. Martin,G. A. Doyle, &A. C. Walker (eds.), Duckworth, London, pp. 673–724.
Hildwein, G. &M. Goffart, 1975. Standard metabolism and thermoregulation in a ProsimianPerodicticus potto.Comp. Biochem. Physiol., 50(A): 201–213.
Hill, Osman W. C. 1953. GenusPerodicticticus. In:Primates, 1, Strepsirhini, The University Press, Edinburgh, pp. 175–194.
Krishnamurti, A., 1966. The external morphology of the brain of the Slow LorisNycticebus coucang coucang.Folia primat., 4: 361–380.
Le Gros Clark, W.E., 1945. Deformation patterns in the cerebral cortex. In:Essays on Growth and Form,W. E. Le Gros Clark &P. B. Medawar (eds.), Clarendon Press, Oxford, pp. 1–22.
Radinsky, L. B., 1968. A new approach to mammalian cranial analysis, illustrated by examples of prosimian primates.J. Morphol., 24: 167–179.
————, 1974. Prosimian brain morphology: functional and phylogenetic implications. In:Prosimian Biology,R. D. Martin,G.A. Doyle, &A. C. Walker (eds.), Duckworth, London, pp. 781–798.
Roucoux-Hanus, M., N. Boisacq-Schepens, &M. Crommelinck, 1974. Organisation d’afférences périphériques et interhémisphériques et relation avec l’efférence pyramidale au niveau du cortex moteur du Chat.Arch. ital. Biol., 112: 199–226.
Sanides, F., 1970. Functional architecture of motor and sensory cortices in Primates in the light of a new concept of neocortex evolution. In:The Primate Brain,C.R. Noback &W. Montagna (eds.), Appleton-Century-Crofts, New York, pp. 137–208.
———— &A. Krishnamurti, 1967. Cytoarchitectonic subdivisions of sensorimotor and prefrontal regions and of bordering insular and limbic fields in Slow Loris (Nycticebus coucang concang).J. Hirnforsch., 9: 225–252.
Stephan, H., 1969. Quantitative investigations on visual structures in primate brains.Proc. 2nd Congr. Primat., 3: 34–42.
Stephan, H. &O. J. Andy, 1970. The allocortex in primates. In:The Primate Brain,C. R. Noback &W. Montagna (eds.), Appleton-Century-Crofts, New York, pp. 109–135.
van der Hoeven, 1851. Bijdrage tot de Kennis van den Potto van Bosman. Met 2 Platen.Verhandelingen der Eerste Klasse van het Koninklijke Nederlandsche Instituut, 3e Reeks, 4e deel., Amsterdam, pp. 1–12.
Vogt, O., 1906, Ueber strukturelle Hirncentra mit besonderer Berücksichtigung der strukturellen Felder des Cortex pallii.Anat. Anzeiger, 29, (Ergänz): 74–114.
Vogt, G. &O. Vogt, 1907. Zur Kenntnis der elektrisch erregbaren Hirnrindengebiete bei den Saügetieren.J. Psychol. u. Neurol. (Leipzig), 8: 277–454.
Weber, M., 1896. Vorstudien über das Hirngewicht der Saügetiere., Leipzig. Quoted byElliot Smith (1903).
Woolsey, C. N., 1958. Organization of somatic sensory and motor areas of the cerebral cortex. In:Biological and Biochemical Basis of Behavior,H. F. Harlow &C. N. Woosley (eds.), University of Wisconsin Press, Madison.
Ziehen, Th., 1896. Über die Grosshirnfurchung der Halbaffen und die Deutung einer Furchen des menschlichen Gehirns.Arch. f. Psychiatrie, 28: 898–930.
Zuckerman, S. &J.F. Fulton, 1941. The motor cortex inGalago andPerodicticus.J. Anat., 75: 447–456.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
About this article
Cite this article
Boisacq-Schepens, N., Gerebtzoff, M.A. & Goffart, M. Sensory projections to the cerebral cortex inPerodicticus potto edwarsi Bouvier . Primates 18, 401–416 (1977). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02383118
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02383118