Summary
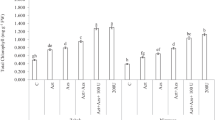
A greenhouse study was conducted to compare the growth of Lee and Bragg soybeans (Glycine max L. Merr.) on a calcareous soil at different soil temperatures (16 and 24°C) and FeEDDHA-Fe levels (0 and 2 μg Fe/g soil). Both varieties developed leaf chlorosis without the added chelate but Lee plants were more chlorotic. In addition, trifoliate leaves of Bragg without added FeEDDHA had crinkled leaf surfaces which were curled at the distal ends. This leaf distortion was worst on older leaves, was more pronounced at the lower temperature, and was completely absent in Bragg treated with FeEDDHA. In Bragg, some leaf distortion and associated cellular changes observed with scanning and transmission electron microscopy were not the same as the typical Fe deficiency syndrome found in Lee; these differences are believed to result from Mn toxicity in Bragg. High levels of Mn, 337 and 261 μg Mn/g in Bragg and Lee tops, respectively, accumulated without added FeEDDHA at 16°C; the corresponding values in the presence of FeEDDHA were 21 and 18 μg Mn/g, respectively. The visual symptoms and the Mn plant data support the hypothesis that the leaf distortion observed in Bragg without added FeEDDHA was due to Mn toxicity. The FeEDDHA x soil temperature interaction for plant Mn concentration was highly significant and reflected the fact that the lower soil temperature caused a decrease in plant Mn concentration only when FeEDDHA was applied. Bragg accumulated more Fe than Lee, especially when FeEDDHA was present.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Brown J C and Jones W E 1977 Manganese and iron toxicities dependent on soybean variety. Comm. Soil Sci. Plant Anal. 8, 1–15.
Brown J C and Jones W E 1977 Fitting plants nutritionally to soils. I. Soybeans. Agron. J. 69, 399–404.
Brown J C, Ambler J E, Chaney R L and Foy C D 1972In Micronutrients in Agriculture. Ed. J J Mortvedt et al. pp. 389–418, Soil Sci. Soc. Am., Madison, WI.
Carter O G, Rose I A and Reading P F 1975 Variation in susceptibility to manganese toxicity in 30 soybean genotypes. Crop Sci. 15, 730–732.
Hecht-Buchholz Ch 1983 Light and electron microscopic investigations of the reactions of various genotypes to nutritional disorders. Plant and Soil 72, 151–165.
Heenan D P and Campbell L C 1983 Manganese and iron interactions on their uptake and distribution in soybean (Glycine max (L.) Merr.). Plant and Soil 70, 317–326.
Heenan D P and Carter O G 1975 Response of two soya bean cultivars to manganese toxicity as affected by pH and calcium levels. Aust. J. Agric. Res. 26, 976–974.
Heenan D P and Carter O G 1976 Tolerance of soybean cultivars to manganese toxicity. Crop Sci. 16, 389–391.
Heenan D P and Carter O G 1977 Influence of temperature on the expression of manganese toxicity by two soybean varieties. Plant and Soil 47, 219–227.
Hewitt E J and Smith T A 1975 Plant Mineral Nutrition. John Wiley, New York.
Lindsay W L and Norvell W A 1978 Development of a DTPA soil test for zinc, iron, manganese and copper. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 42, 421–428.
Mederski H J and Wilson J H 1955 Effect of soil temperature and soil moisture on manganese absorption by soybean plants. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. Proc. 19, 461–464.
Moraghan J T 1978 Chlorotic dieback in flax. Agron. J. 70, 501–505.
Moraghan J T 1979 Manganese toxicity in flax growing on certain calcareous soils low in available iron. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 43, 1177–1180.
Moraghan J T 1985 Manganese deficiency in flax as affected by FeEDDHA and soil air drying. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 49, 668–671.
Parker M B, Harris H B, Morris H D and Perkins H F 1969 Manganese toxicity of soybeans as related to soil and fertility treatments. Agron. J. 61, 515–518.
Somers I I and Shive J W 1942 The iron-manganese relation in plant metabolism. Plant Physiol. 17, 582–602.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Professors in the Departments of Soil Science, Botany and Agronomy, respectively.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Moraghan, J.T., Freeman, T.P. & Whited, D. Influence of FeEDDHA and soil temperature on the growth of two soybean varieties. Plant Soil 95, 57–67 (1986). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02378852
Received:
Revised:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02378852