Abstract
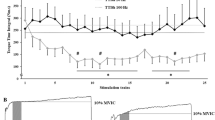
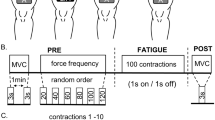
Pairs of intrafascicular electrodes were implanted within single fascicles of the nerve innervating the gastrocnemius muscle in cats. Measurements were made of fatigue induced in the muscle by single and dual channel tetanic stimulation. The level and rate of fatigue induced by concurrent dual channel stimulation (pulses presented simultaneously to the two electrodes) did not differ significantly from that induced by single channel stimulation. However, a significant reduction in the level and rate of muscle fatigue was found with interleaved dual channel stimulation. The extent of reduction in fatigue was found to be inversely related to the amount of overlap in the axonal populations activated by each of the two electrodes.
Similar content being viewed by others

References
Baratta, R.; Ichie, M.; Hwang, S.K.; Solomonow, M. Orderly stimulation of skeletal muscle motor units with tripolar nerve cuff electrode. IEEE Trans. Biomed. Eng. 36:836–843; 1989.
Burke, R.E.; Levine, D.N.; Salcman, M.; Tsairis, P., Motor units in cat soleus muscle: Physiological, histochemical and morphological characteristics. J. Physiol. 238:503–514; 1974.
Burke, R.E.; Levine, D.N.; Tsairis, P.; Zajac, F.E. Physiological types and histochemical profiles in motor units of the cat gastronemius. J. Physiol. 234:723–748; 1973.
Fang, Z.-P.; Mortimer, J.T. A method to effect physiological recruitment order in electrically activated muscle. IEEE Trans. Biomed. Eng. 38:175–179; 1991.
Goodall, E.V.; Lefurge, T.M.; Horch, K.W. Information contained in sensory nerve recordings made with intrafascicular electrodes. IEEE Trans. Biomed. Eng. 38:846–850; 1991.
Halbertsma, J.M. The stride cycle of the cat: The modelling of locomotion by computerized analysis of automatic recordings. Acta Physiol. Scand. Suppl. 521:1–75; 1983.
Happak, W.; Gruber, H.; Holle, J.; Mayr, W.; Schmutterer, C.; Windberger, U.; Losert, U.; Thoma, H. Multi-channel indirect stimulation reduces muscle fatigue. Proc. Ann. Intl. Cont. IEEE Eng. Med. Biol. Soc. 11:240–241; 1989.
Kraij, A.; Bajd, T.; Turk, R.; Benko, H. Posture switching for prolonging functional electrical stimulation standing in paraplegic patients. Paraplegia 24:221–230; 1986.
Kralj, A.; Bajd, T.; Turk, R.; Krajnik, J.; Benko, H. Gait restoration in paraplegic patients: a feasibility demonstration using multichannel surface electrode FES. J. Rehabil. R&D 20:3–20; 1983.
Kralj, A.R.; Bajd, T. Functional electrical stimulation: Standing and walking after spinal cord injury. Boca Raton, FL: CRC Press; 1989.
Lefurge, T.; Goodall, E.; Horch, K.; Stensaas, L.; Schoenberg, A. Chronically implanted intrafascicular recording electrodes. Ann. Biomed. Eng. 19:197–207; 1991.
McNeal, D.R.; Nakai, R.J.; Meadows, P.; Tu, W. Control of the freely-swinging paralyzed leg before and after exercise. IX International Symposium on External Control of Human Extremities. Belgrad, Yugoslavia: 1987:pp. 261–273.
McPhedran, A.M.; Wuerker, R.B.; Henneman, E. Properties of motor units in a homogeneous red muscle (soleus) of the cat. J. Neurophysiol. 28:71–84; 1965.
Meier, J.H.; Rutten, W.L.C.; Zoutman, A.E.; Boom, H.B.K.; Bergveld, P. Simulation of multipolar fiber selective neural stimulation using intrafascicular electrodes. IEEE Trans. Biomed. Eng. 39:122–134; 1992.
Mortimer, J.T. Motor prostheses. In: Brooks, V.B., ed. Handbook of physiology. Section 1: The nervous system. Bethesda, MD: American Physiological Society; 1981: pp. 155–187.
Nannini, N. Optimal stimulus parameters for muscle recruitment with intrafascicular electrodes. Salt Lake City, UT: Univ. Utah; 1989. M.S. Thesis.
Nannini, N.; Horch, K. Muscle recruitment with intrafascicular electrodes. IEEE Trans. Biomed. Eng. 38:769–776; 1991.
Peckham, P.H.; Van Der Meulen, J.P.; Reswick, J.B. Electrical activation of skeletal muscle by sequential stimulation. In: Wulfson, N.; Sances, A. Jr., eds. The nervous system and electrical currents. New York: Plenum; 1970: pp. 45–49.
Petrofsky, J.S. Sequential motor unit stimulation through peripheral motor nerves in the cat. Med. Biol. Eng. Comput. 17:87–93; 1979.
Powers, R.K.; Binder, M.D. Effects of low-frequency stimulation on the tension-frequency relations of fast-twitch motor units in the cat. J. Neurophysiol. 66:905–918; 1991.
Proske, U.; Waite, P.M.E. Properties of types of motor units in the medial gastrocnemius muscle of the cat. Brain Res. 67:89–101; 1974.
Rutten, W.L.C.; van Wier, H.J.; Put, J.H.M. Sensitivity and selectivity of intraneural stimulation using a silicon electrode array. IEEE Trans. Biomed. Eng. 38:192–198; 1991.
Sweeney, J.D., Ksienski, D.A.; Mortimer, J.T. A nerve cuff technique for selective excitation of peripheral nerve trunk regions. IEEE Trans. Biomed. Eng. 37:706–715; 1990.
Thoma, H.; Girsch, W., Holle, J.; Mayr, W. Technology and long-term application of an epineural electrode. Trans. Am. Soc. Artif. Intern. Organs 35:490–494; 1989.
Veltink, P.H.; van Alsté, J.A.; Boom, H.B.K. Simulation of intrafascicular and extraneural nerve stimulation. IEEE Trans. Biomed. Eng. 35:69–75; 1988.
Veltink, P.H.; van Alsté, J.A.; Boom, H.B.K. Influences of stimulation conditions on recruitment of myelinated nerve fibers: A model study. IEEE Trans. Biomed. Eng. 35:917–924; 1988.
Veltink, P.H.; van Alsté, J.A.; Boom, H.B.K. Multielectrode intrafascicular and extraneural stimulation. Med. Biol. Eng. Comput. 27:19–24; 1989.
Wuerker, R.B.; McPhedran, A.M.; Henneman, E. Properties of motor units in a heterogeneous pale muscle (M. gastrocnemius) of the cat. J. Neurophysiol. 28:85–99; 1965.
Yoshida, K.; Horch, K. Selective stimulation of peripheral nerve fibers using dual intrafascicular electrodes. IEEE Trans. Biomed. Eng. 40:492–494; 1993.
Zajac, F.E.; Faden, J.S. Relationship among recruitment order, axonal conduction velocity, and muscle-unit properties of type-identified motor units in cat plantaris muscle. J. Neurophysiol. 53:1303–1322; 1985.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yoshida, K., Horch, K. Reduced fatigue in electrically stimulated muscle using dual channel intrafascicular electrodes with interleaved stimulation. Ann Biomed Eng 21, 709–714 (1993). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02368649
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02368649