Summary
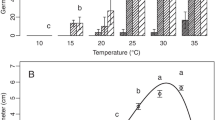
Potato seed pieces bearing one sprout were inoculated with cultures ofRhizoctonia solani, planted in pots of compost at 45, 60, 75 or 90% water holding capacity (whc) and incubated at 5, 10 or 15 °C. Shoots emerged after 2–3 wk at 15°C, 3–4 wk at 10 °C and after 9–11 wk at 5 °C and stem canker recorded after emergence, was severe at 10 and 15 °C but slight at 5 °C. Soil moisture had less effect on emergence but stem canker was more severe in dry (45 % whc) than moist soils (75 and 90 % whc). The relationship between time of shoot emergence and stem canker severity is discussed.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Adams, M. J., G. A. Hide & D. H. Lapwood, 1980. Relationships between disease levels on seed tubers, on crops during growth and in stored potatoes. 1. Introduction and black scurf.Potato Research 23: 201–214.
Adams, M. J. & G. A. Hide, 1980. Relationships between disease levels on seed tubers, on crops during growth and in stored potatoes. 5. Seed stocks grown at Rothamsted.Potato Research 23: 291–302.
Blair, I. D., 1943. Behaviour of the fungusRhizoctonia solani Kühn in the soil.Annals of Applied Biology 30: 118–127.
Bolkan, H. A., H. T. Wenham & K. S. Milne, 1974. Effect of soil temperature on severity ofRhizoctonia solani infection of potato shoots.Plant Disease Reporter 58: 646–649.
Brenchley, G. H. & H. J. Wilcox, 1979.Potato Diseases, London, HMSO. 106 pp.
Clarke, E. S. & W. H. Martin, 1935. Influence of depth of planting and soil moisture content onRhizoctonia. Annual Report, New Jersey Agricultural Experiment Station p. 61.
Frank, J. A., 1978. The Rhizoctonia disease of potatoes in Maine.American Potato Journal 55: 59.
Harrison, M. D., 1978. The Rhizoctonia disease of potatoes: importance and control. In:Control of important fungal diseases of potatoes, pp. 129–150. Lima, International Potato Center.
Hide, G. A., J. M. Hirst & O. J. Stedman, 1973. Effects of skin spot (Oospora pustulans) on potatoes.Annals of Applied Biology 73: 151–162.
Hide, G. A., P. J. Read & J. P. Sandison, 1985. Stem canker (Rhizoctonia solani) of maincrop potatoes. 1. Development of the disease.Annals of Applied Biology 106: 413–422.
Richards, B. L., 1921. Pathogenicity ofCorticium vagum on the potato as affected by soil temperature.Journal of Agricultural Research 21: 459–482.
Sanford, G. B., 1938. Studies onRhizoctonia solani Kühn. IV. Effect of soil temperature and moisture on virulence.Canadian Journal of Research, Series C 16: 203–213.
Van Emden, J. H., 1965.Rhizoctonia solani; results of recent experiments.European Potato Journal 8: 158–159.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hide, G.A., Firmager, J.P. Effects of soil temperature and moisture on stem canker (Rhizoctonia solani) disease of potatoes. Potato Res 32, 75–80 (1989). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02365819
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02365819