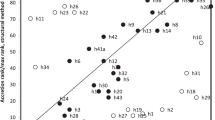
Abstract
We report a detailed evolutionary study of the RNase P- and RNase MRP- associated RNAs. The analyses were performed on all the available complete sequences of RNase MRP (vertebrates, yeast, plant), nuclear RNase P (vertebrates, yeast), and mitochondrial RNase P (yeast) RNAs. For the first time the phylogenetic distance between these sequences and the nucleotide substitution rates have been quantitatively measured.
The analyses were performed by considering the optimal multiple alignments obtained mostly by maximizing similarity between primary sequences. RNase P RNA and MRP RNA display evolutionary dynamics following the molecular clock. Both have similar rates and evolve about one order of magnitude faster than the corresponding small rRNA sequences which have been, so far, the most common gene markers used for phylogeny. However, small rRNAs evolve too slowly to solve close phylogenetic relationships such as those between mammals. The quicker rate of RNase P and MRP RNA allowed us to assess phylogenetic relationships between mammals and other vertebrate species and yeast strains. The phylogenetic data obtained with yeasts perfectly agree with those obtained by functional assays, thus demonstrating the potential offered by this approach for laboratory experiments.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Altman S, Kirsebom L, Talbot S (1993a) Recent studies of ribonuclease P. FASEB J 7:7–14
Altman S, Wesolowski D, Puranam R (1993b) Nucleotide sequences of the RNA subunit of RNase P from several mammals. Genomics 18:418–422
Baer M, Nilsen T, Costigan C, Altman S (1990) Structure and transcription of a human gene for H1 RNA, the RNA component of human RNase P. Nucleic Acids Res 18:97–103
Bartkiewicz M, Gold H, Altman S (1989) Identification and characterization of an RNA molecule that copurifies with RNase P activity from HeLa cells. Genes Dev 3:488–499
Bennett J, Jeong-Yu S, Clayton D (1992) Characterization of aXenopus laevis ribonucleoprotein endoribonuclease. J Biol Chem 267: 21765–21772
Benton M (1990) Phylogeny of the major tetrapod groups: morphological data and divergence data. J Mol Evol 30:409–424
Brown J, Haas E, Gilbert D, Pace N (1994) The ribonuclease P database. Nucleic Acids Res 22:3660–3662
Chang D, Clayton D (1987) A novel endoribonuclease cleaves at a priming site of mouse mitochondrial DNA replication. EMBO J 6:409–417
Chang D, Clayton D (1989) Mouse RNase MRP RNA is encoded by a nuclear gene and contains a decamer sequence complementary to a conserved region of mitochondrial RNA substrate. Cell 56:131–139
Dairaghi D, Clayton D (1993) Bovine RNase MRP cleaves the divergent bovine mitochondrial RNA sequence at the displacement-loop region. J Mol Evol 37:338–346
Darr S, Brown J, Pace N (1992) The varieties of ribonuclease P. Trends Biochem Sci 17:178–182
Doersen CJ, Guerrier-Takada C, Altman S, Attardi G (1985) Characterization of RNase P activity from HeLa cell mitochondria. J Biol Chem 260:5942–5949
Doria M, Carrara G, Calandra P, Tocchini-Valentini G (1991) An RNA molecule copurifies with RNase P activity fromXenopus laevis oocytes. Nucleic Acids Res 19:2315–2320
Felsenstein J (1993) PHYLIP (Phylogeny Inference Package). Department of Genetics, University of Washington, Seattle
Forster A, Altman S (1990) Similar cage-shaped structures for the RNA components of all ribonuclease P and Ribonuclease MRP enzymes. Cell 62:407–409
GCG (1993) Program manual for the GCG package. 575 Science Drive, Madison, Wisconsin, USA 53711, Genetic Computer Group GCG
Gold H, Topper J, Clayton D, Craft J (1989) The RNA processing enzyme RNase MRP is identical to the Th RNP and related to RNase P. Science 245:1377–1380
Gopolan V, Talbot SJ, Altman S (1995) RNA-protein interactions. Oxford University Press, Nagai K, Mattaj IW, eds.
Gouy M, Gautier C, Attimonelli M, Lanave C, Di Paola G (1985) ACNUC—a portable retrieval system for nucleic acid sequence databases: logical and physical designs and usage. Comput Appl Biosci 1(3):167–172
Hannon G, Chubb A, Maroney P, Hannon G, Altman S, Nilsen T (1991) Multiple cis-acting elements are required for RNA polymerase III transcription of the gene encoding H1 RNA, the RNA component of human RNase P. J Biol Chem 266:22796–22799
Janke A, Feldmaier-Fuchs G, Thomas W, von Haeseler A, Paabo S (1994) The marsupial mitochondrial genome and the evolution of placental mammals. Genetics 137:243–256
Kiss T, Marshallsay C, Filipowicz W (1992) 7-2/MRP RNAs in plant and mammalian cells: association with higher order structures in the nucleolus. EMBO J 11:3737–3746
Krupp G, Cherayil B, Frendeway D, Nishikawa S, Soll D (1986) Two RNA species co-purify with RNase P from the fission yeastSchizosaccharomyces pombe. EMBO J 15:1697–1703
Lee J-Y, Rohlman C, Molony L, Engelke D (1991) Characterization of RPR1, an essential gene encoding the RNA component ofSaccharomyces cerevisiae nuclear RNase P. Mol Cell Biol 11:721–730
Lygerou Z, Mitchell P, Petfalski E, Seraphin B, Tollervey D (1994) The POP1 gene encodes a protein component common to the RNase MRP and RNase P ribonucleoprotein. Genes Dev 8:1423–1433
Manam S, Van Tuyle G (1987) Separation and characterization of 5′-and 3′-tRNA processing nucleases from rat liver mitochondria. J Biol Chem 262:10272–10279
Marchfelder A, Brennicke A (1994) Characterization and partial purification of tRNA processing activities from potato mitochondria. Plant Physiol 105:1247–1254
Miller D, Martin N (1983) Characterization of the yeast mitochondrial locus necessary for tRNA biosynthesis: DNA sequence analysis and identification of a new transcript. Cell 34:911–917
Morrissey J, Tollervey D (1995) Birth of the snoRNPs: the evolution of RNase MRP and the eukaryotic pre-RNA-processing system. Trends Biochem Sci 20:78–82
Muse SV, Weir BS (1992) Testing for equality of evolutionary rates. Genetics 132:269–276
Olsen G, Woese C (1993) Ribosomal RNA: a key to phylogeny FASEB J 7:113–123
Pagàn-Ramos E, Tranguch A, Kindelberger D, Engelke D (1994) Replacement of theSaccharomyces cerevisiae RPR1 gene with heterologous RNase P RNA gene. Nucleic Acids Res 22:200–207
Potuschak T, Rossmanith W, Karwan R (1993) RNase MRP and RNase P share a common substrate. Nucleic Acids Res 21:3239–3243
Ragnini A, Grisanti P, Rinaldi T, Frontali L, Palleschi C (1991) Mitochondrial genome ofSaccharomyces douglasii: genes coding for components of the protein synthetic apparatus. Curr Genet 19:169–174
Rossmanith W, Karwan R (1993) Definition of the Th/To ribonucleoprotein by RNase P and RNase MRP. Mol Biol Rep 18:29–35
Rossmanith W, Tullo A, Potuschak T, Karwan R, Sbisà E (1995) Human mitochondrial tRNA processing. J Biol Chem 270:12885–12891
Saccone C, Lanave C, Pesole G, Preparata G (1990) Influence of base composition on quantitative estimates of gene evolution. Methods Enzymol 183:570–583
Schmitt M, Bennett J, Dairaghi D, Clayton D (1993) Secondary structure of RNase MRP as predicted by phylogenetic comparison. FASEB J 7:208–213
Schmitt M, Clayton D (1992) Yeast site-specific ribonucleoprotein endoribonuclease MRP contains an RNA component homologous to mammalian RNase MRP RNA and essential for cell viability. Genes Dev 6:1975–1985
Shu H-H, Wise C, Clark-Walker G, Martin N (1991) A gene required for RNase P activity inCandida (Torulopsis)glabrata mitochondria codes for a 227-nucleotide RNA with homology to bacterial RNase P RNA. Mol Cell Biol 11:1662–1667
Topper J, Clayton D (1990) Characterization of human MRP/Th RNA and its nuclear gene: full length MRP/Th RNA is an active endoribonuclease when assembled as an RNP. Nucleic Acids Res 18:793–799
Tranguch A, Engelke D (1993) Comparative structural analysis of nuclear RNase P RNAs from yeast. J Biol Chem 268:15045–15055
Tullo A, Rossmanith W, Imre E-M, Sbisà E, Saccone C, Karwan R (1995) RNase mitochondrial RNA processing cleaves RNA from the rat mitochondrial displacement loop at the origin of heavy-strand replication. Eur J Biochem 227:657–662
Wang JW, Davis NW, Gegenheimer P (1988) Novel mechanisms for maturation of chloroplast transfer RNA precursor. EMBO J 7(6): 1567–1574
Wise C, Martin N (1991) Dramatic size variation of yeast mitochondrial RNAs suggests that RNase P RNAs can be quite small. J Biol Chem 266:19154–19157
Yuan Y, Singh R, Reddy R (1989) Rat nucleolar 7-2 RNA is homologous to mouse mitochondrial RNase mitochondrial RNA-processing RNA. J Biol Chem 264:1435–14839
Zimmerly S, Gamulin V, Burkard U, Soll D (1990) The RNA component of RNase P inSchizosaccaromyces species. FEBS lett 271: 189–193
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Correspondence to: E. Sbisà
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sbisà, E., Pesole, G., Tullo, A. et al. The evolution of the RNase P- and RNase MRP-associated RNAs: Phylogenetic analysis and nucleotide substitution rate. J Mol Evol 43, 46–57 (1996). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02352299
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02352299