Abstract
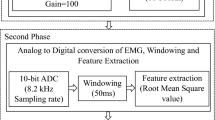
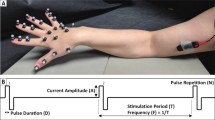
Recent commercially available miniature sensors have the potential to improve the functions of functional electrical stimulation (FES) systems in terms of control, reliability and robustness. A new control approach using a miniature gyroscope and an accelerometer was studied. These sensors were used to detect the linear acceleration and angular velocity of residual voluntary movements on upper limbs and were small and easy to put on. Five healthy subjects and three cervical spinal cord injured subjects were recruited to evaluate this controller. Sensors were placed on four locations: the shoulder, upper arm, wrist and hand. A quick forward-and-backward movement was employed to produce a distinctive waveform that was different from general movements. A detection algorithm was developed to generate a command signal by identifying this distinctive waveform through the detection of peaks and valleys in the sensor's signals. This command signal was used to control different FES hand grasp patterns. With a specificity of 0.9, the sensors had a success rate of 85–100% on healthy subjects and 82–97% on spinal cord injured subjects. In terms of sensor placement, the gyroscope was better as a control source than the accelerometer for wrist and hand positions, but the reverse was true for the shoulder.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Adamczky, M. M., andCrago, P. E. (1997): ‘Integrated hand/wrist control in a neuroprosthesis for individuals with tetraplegia’. Proc. Ann. Conf. IEEE Eng Med. Biol. Soc., pp. 1924–1927
Bhadra, N., Kilgore, K. L., andPeckham, P. H. (2001): ‘Implanted stimulators for restoration of function in spinal cord injury’,Med. Eng. Phys.,23, pp. 19–28
Burelbach, J. C., andCrago, P. E. (1994). Instrumented assessment of FNS hand control during specific manipulation tasks’,IEEE Trans. Rehab. Eng.,2, pp. 165–176
Graupe, D. (1989): ‘EMG pattern analysis for patient-responsive control of FES in paraplegics for walker-supported walking’,IEEE Trans. Biomed. Eng.,36, pp. 711–719
Hart, R. L., Kilgore, K. L., andPeckham, P. H. (1998): ‘A comparison between control methods for implanted FES hand grasp systems’,IEEE Trans. Rehab. Eng.,6, pp. 208–218
Johnson, M. W., andPeckham, P. H. (1990) ‘Evaluation of shoulder movement as a command control source’,IEEE Trans. Biomed. Eng.,37, pp. 876–885
Johnson, M. W., Peckham, P. H., Bhadra, N. et al. (1999): ‘Implantable transducer for two-degree of freedom joint angle sensing’,IEEE Trans. Rehab. Eng.,7, pp. 349–359
Liberson, W. T., Holmquest, H. J., Scott, D., andDow, A. (1961): ‘Functional electrotherapy: stimulation of the peroneal nerve synchronized with the swing phase of gait in hemiplegic patients’,Arch. Phys. Med. Rehab.,42, pp. 101–105
Mulcahey, M. J., Betz, R. R., Smith, B. T. et al. (1997): ‘Implanted functional electrical stimulation hand system in adolescents with spinal injuries: an evaluation’,Arch. Phys. Med. Rehab.,78, pp. 597–607
Nathan, R. H. (1990): ‘FNS of the upper limb: targeting the forearm muscles for surface stimulation’,Med. Biol. Eng. Comput.,28, pp. 249–256
Pappas, I. P. I., Popovic, M. R., Keller, T. et al. (2001): ‘A reliable gait phase detection system’,IEEE Trans. Neur. Syst. Rehab.,9, pp. 113–125
Popovic, D., Stojanovic, A., Pjanovic, A., et al. (1999): ‘Clinical evaluation of the bionic glove’,Arch. Phys. Med. Rehabil.,80, pp. 299–304
Prochazka, A., Gauthier, M., Wieler, M. et al. (1997): ‘The bionic glove: an electrical stimulator garment that provides controlled grasp and hand opening in quadriplegia’,Arch. Phys. Med. Rehab.,78, pp. 608–613
Sarver, J. J., Smith, B. T., Seliktar, R. et al. (1999): ‘A study of shoulder motions as a control source for adolescents with C4 level SCI’,IEEE Trans. Rehab. Eng.,7, pp. 27–34
Scott, T. R. D., Peckham, P. H., andKilgore, K. L. (1996): ‘Tristate myoelectric control of bilateral upper extremity neuroprostheses for tetraplegic individuals’,IEEE Trans. Rehab. Eng.,4, pp. 251–263
Scott, T. R. D., Heasman, J. M., Vare, V. A., et al. (2000): ‘Quantitative evaluation of two methods of control of bilateral stimulated hand grasps in persons with tetraplegia’,IEEE Trans. Rehab. Eng.,8, pp. 259–267
Teeter, J. O., Kantor, C., andBrown, D. (1995): ‘Functional electrical stimulation(FES) resource guide for persons with spinal cord injury or multiple sclerosis’.Cleveland FES Center, Cleveland, USA
Tong, K. Y., andGranat, M. H. (1998): ‘The use of neural networks and virtual sensors for the control of FES assisted walking’,Med. Biol. Eng. Comput.,22, pp. 458–468
Tong, K. Y., andGranat, M. H. (1999): ‘A practical gait analysis system using gyroscopes’,Med. Eng. Phys.,21, pp. 87–94
Tong, K. Y., andGranat, M. H. (2000): ‘Artificial neural network control on functional electrical stimulation assisted gait with spinal cord injury persons’ inLisboa, P. J. G., Ifeachor, E. C., andSzczepaniak, P. S. (Eds): ‘Artificial neural networks in biomedicine’ (Springer-Verlag, 2000), chap. 14
Tong, K. Y., andMak, A. F. T. (2001): ‘A computer-based environment for simulating the voluntary upper limb movements of persons with disability’,Med. Biol. Eng. Comput.,39, pp. 414–421
Triolo, R., Nathan, R., Handa, Y. et al. (1996): ‘Challenges to clinical deployment of upper limb neuroprostheses’,J. Rehab. Res. Dev. 33, pp. 111–122
Williamson, R., andAndrews, B. J. (2000): ‘Sensor systems for lower limb functional electrical stimulation (FES) control’,Med. Eng. Phys.,22, pp. 313–325
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Tong, K.Y., Mak, A.F.T. & Ip, W.Y. Command control for functional electrical stimulation hand grasp systems using miniature accelerometers and gyroscopes. Med. Biol. Eng. Comput. 41, 710–717 (2003). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02349979
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02349979