Abstract
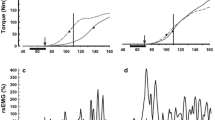
The mechanical performance, repeatability and comfort of the Quadrisotester, which assesses isometric knee extensor muscle strength, were examined. Twenty healthy subjects and 20 patients treated for unilateral anteriorligamenta cruciata insufficiency were tested. Intra-rater repeatability was determined by the testing and retesting of subjects and calculation of the intra-class correlation coefficient and the mean difference between test and retest values. The comfort level was determined a questionnaire. Measuring time was recorded, and the relationship between knee angle and extension moment was plotted. Strength and stiffness were determined using the finite element method. Intra-rater repeatability was high; the intra-class correlation coefficient of the right and left leg was 0.90 and 0.91, respectively; the coefficient of variation was 6.4 and 6.0%, respectively. The median comfort score of the healthy subjects was 7, and that of the patients was 9. Measuring time remained within 30 min. Misalignment of the knee and sidebar axis disturbed the relationship between knee angle and extension moment. Strength and stiffness were higher than required. In conclusion, the Quadriso-tester is a comfortable and fast device to determine quadriceps force with a high repeatability. The knee and sidebar axis should be well aligned.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Agre, J. C., Magness, J. L., Hull, S. Z.,et al. (1987): ‘Strength testing with a portable dynamometer: reliability for upper and lower extremities’,Arch. Phys. Med. Rehabil.,68, pp. 454–458
Andrews, W. A., Thomas, M. W., andBohannon, R. W. (1996): ‘Normative values for isometric muscle force measurements obtained with hand-held dynamometers’,Phys. Therapy,76, pp. 248–259
Baaij, J., Beijer, J., Beukers, A.,et al. (2000): ‘Engineering dossiers, technical materials (in Dutch)’ (Ten Hagen Stam, The Hague, 2000)
Baumgartner, T. A., andJackson, A. S. (1991): ‘Measurement for evaluation in physical education and exercise science’, (Wm C. Brown Publ, Dubuque, 1991)
Brooks, S. V., andFaulkner, J. A. (1994): ‘Skeletal muscle weakness in old age: underlying mechanisms’,Med. Sci. Sports Exerc.,26, pp. 432–439
Enoka, R. M. (1994): ‘Neuromechanical basis of kinesioloy’, 2nd edn (Human Kinetics, Champaign, IL, 1994)
Frontera, W. R., Meredith, C. N., O'Reilly, K. P.,et al. (1988): ‘Strength conditioning in older men: skeletal muscle hypertrophy and improved function’,J. Appl. Physiol.,64, pp. 1038–1044
Grimby, G., Aniansson, A., Hedberg, M.,et al. (1992): ‘Training can improve muscle strength and endurance in 78-to 84-yr-old men.J. Appl. Physiol.,73, pp. 2517–2523
Guralnik, J. M., Simonsick, E. M., Ferrucci, L.,et al. (1994): A short physical performance battery assessing lower extremity function: association with self-reported disability and prediction of mortality and nursing home admission.J. Gerontology.,49, pp. 85–94
Harlaar, J., Roebroeck, M. E., andLankhorst, G. J. (1996): Computer-assisted hand-held dynamometer: low cost instrument for muscle function assessment in rehabilitation medicine.Med. Biol. Eng. Comput.,34, pp. 329–335
Jenson, R. H., Smidt, G. L., andJohnston, R. C. (1971): A technique for obtaining measurements of force generated by hip muscles.Arch. Phys. Med. Rehabil.,52, pp. 207–215
Larsson, L., Grimby, G., andKarlsson, J. (1979): ‘Muscle strength and speed of movement in relation to age and muscle morphology’.J. Appl. Physiol.,46, pp. 451–456
Lemmink, K. (1996): ‘De Groninger Fitheidstest voor ouderen: ontwikkeling van een meetinstrument’. dissertation, Univ. of Groningen, Groningen, The Netherlands
Lemmink, K. A. P. M., Kemper, H. C. G., De Greef, M. H. G.,et al. (2001): ‘The reliability of the Groningen fitness test for the elderly’,J. Aging Phys. Activity,9, pp. 194–212
Mikesky, A. E., Topp, R., Wigglesworth, J. K.,et al. (1994): ‘Efficacy of a home-based training program for older adults using elastic tubing’,Eur. J. Appl. Physiol.,69, pp. 316–320
Molenbroek, J. F. M., andDirken, J. M. (1986):Dined table with Dutch antropometric data. Available from: http://www.io.tudelft.nl/research/ergonomics/frame_research.htm
Nadler, S. F., DePrince, M. L., Hauesien, N.,et al. (2000): ‘Portable dynamometer anchoring station for measuring strength of the hip extensors and abductors’,Arch. Phys. Med. Rehabil.,81, pp. 1072–1076
Nichols, J. F., Omizo, D. K., Peterson, K. K., andNelson, N. P. (1993): ‘Efficacy of heavy resistance training for active women over sixty: muscular strength, body composition, and program adherence’,J. Am. Geriatrics Soc.,41, pp. 205–210
Ralston, H. J., andTodd, F. (1981): ‘Human walking’ (Williams & Wilkens, Baltimore, 1981)
Roebroeck, M. E., Harlaar, J., andLankhorst, G. J. (1998): ‘Reliability assessment of isometric knee extension measurement with a computer-assisted hand-held dynamometer’,Arch. Phys. Med. Rehabil.,79, pp. 442–448
Skelton, D. A., Young, A., Greig, C. A., andMalbut, K. E. (1995): ‘Effects of resistance training on strength, power, and selected functional abilities of women aged 75 and older’,J. Am. Geriatrics Soc.,43, pp. 1081–1087
Skelton, D. A., andMcLaughlin, A. W. (1996): ‘Training functional ability in old age’,Physiotherapy,82, pp. 159–167
Stulen, F. B., andDe Luca, C. J. (1982): ‘Muscle fatigue monitor: a noninvasive device for observing localized muscle fatigue’,IEEE Trans. Biomed. Eng.,29, pp. 760–768
Verbrugge, L. M., andJette, A. M. (1994): ‘The disablement process’,Social Sci. and Med. 38, pp. 1–14
Westhoff, M. H., Stemmerik, L., andBoshuizen, H. C. (2000): ‘Effects of a low intensity strength-training program on knee-extensor strength and functional ability of frail older people’,J. Aging Physic. Activity,8, pp. 325–342
Winter, D. A. (1979): ‘Biomechanics of human movement’ (John Wiley, New York, 1979)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Verkerke, G.J., Lemmink, K.A.P.M., Slagers, A.J. et al. Precision, comfort and mechanical performance of the Quadriso-tester, a quadriceps force measuring device. Med. Biol. Eng. Comput. 41, 283–289 (2003). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02348432
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02348432