Abstract
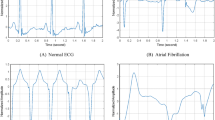
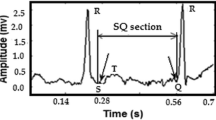
The distribution of atrial electrogram types has been proposed to characterise human atrial fibrillation. The aim of this study was to provide computer procedures for evaluating the local organisation of intracardiac recordings during AF as an alternative to off-line manual classification. Principal component analysis (PCA) reduced the data set to a few representative activations, and cluster analysis (CA) measured the average dissimilarity between consecutive activations of an intracardiac signal. The data set consisted of 106 bipolar signals recorded on 11 patients during electrophysiological studies for catheter ablation. Performances of PCA and CA in distinguishing between organised (type I) and disorganised (type II/III, Wells criteria) were assessed, in comparison with manual reading, by evaluating the predictive parameters of the classification analysis. Both methods gave high accuracy (92% for PCA and 89% for CA), confirming the feasibility of on-line characterisation of AF. Sensitivity was lower than specificity (81% against 98% for PCA, and 77% against 97% for CA), with seven out of eight misclassifications of PCA in common with CA. Differences between manual and computer analysis may be related to the higher resolution of PCA and CA in the measurement of the organisation of atrial activations. These procedures are suitable for providing automatic (by CA) or semi-automatic (by PCA) measures of the extent of local organisation of AF in the pre-ablation treatment phase.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Allessie, M. A., Lammers, W. J. E. P., Bonke, F. I. M., andHollen, J. (1985): ‘Experimental evaluation of Moe's multiple wavelet hypothesis of atrial fibrillation’ inZipes, D. P., andJalife, J. (Eds.): ‘Cardiac electrophysiology and arrhythmias’ (Grune and Straton, New York, 1985) pp. 265–275
Barbaro, V., Bartolini, P., Calcagnini, G., Morelli, S., Michelucci, A., andGensini, G. (2000): ‘Automated classification of human atrial fibrillation from intraatrial electrograms’,PACE,23, pp. 192–202
Bishop, C. M. (1995): ‘Neural networks for pattern recognition’ (University Press, Oxford, 1995)
Botteron, G. W., andSmith, J. M. (1995): ‘A technique for measurement of the extent of spatial organization of atrial activation during atrial fibrillation in the intact human heart’,IEEE Trans. Biomed. Eng. 42, pp. 579–586
Capucci, A., Biffi, M., Boriani, G., Ravelli, F., Nollo, G., Sabbatani, P., Orsi, C., andMagnani, B. (1995): ‘Dynamic electrophysiological behavior of human atria during paroxysmal atrial fibrilation’,Circulation,92, pp. 1193–1202
Censi, F., Barbaro, V., Bartolini, P., Calcagnini, G., Michelucci, A., Gensini, G. F., andCerutti, S. (2000): ‘Recurrent patterns of atrial depolarization during atrial fibrillation assessed by recurrence plot quantification’,Ann. Biomed. Eng.,28, pp. 61–70
Duda, R. O., andHart, P. E. (1973): ‘Pattern classification and scene analysis’ (John Wiley & Sons, New York, 1973) pp. 73–78
Dugad, R., andAhuja, N. (1998): ‘Unsupervised multidimensional hierarchical clustering’. Proc. Conf. Acoust. Speech and Signal Processing, Seattle, USA, pp. 2761–2764
Fisher, L. D., andVan Belle, G. (1993): ‘Biostatistics. A methodology for the health sciences’ (John Wiley & Sons, New York, 1993), pp. 692–762
Gaita, F., Riccardi, R., Calò, L., Scaglione, M., Garberoglio, L., Antolini, R., Kirchner, M., Lamberti, F., andRichiardi, E. (1998): ‘Atrial mapping and radiofrequency catheter ablation in patients with idiopathic atrial fibrillation’,Circulation,97, pp. 2136–2145
Gaita, F., Calò, L., Riccardi, R., Garberoglio, L., Scaglione, M., Licciardello, G., Coda, L., Di Donna, P., Bocchiardo, M., Caponi, D., Antolini, R., Orzan, F., andTrevi, G. P. (2001): ‘Different pattern of atrial activation in idiopathic atrial fibrillation: simultaneous multisite atrial mapping in patients with paroxysmal and chronic atrial fibrillation’,J. Am. Coll. Cardiol.,37, pp. 534–541
Gerstenfeld, E. P., Sahakian, A. V., andSwiryn, S. (1992): ‘Evidence for transient linking of atrial excitation during atrial fibrillation in humans’,Circulation,86, pp. 375–382
Hafner, B. J., Zachariah, S. G., andSanders, J. E. (2000): ‘Characterisation of three-dimensional anatomic shapes using principal components: application to the proximal tibia’,Med. Biol. Eng. Comput.,38, pp. 9–16
Holm, M., Johansson, R., Olsson, S. B., Brandt, J., andLuhrs, C. (1996): ‘A new method for analysis of atrial activation during chronic atrial fibrillation in man’,IEEE Trans. Biomed. Eng.,43, pp. 198–210
Jackson, J. E. (1981): ‘Principal components and factor analysis: Part 1—principal components’,J. Qual. Tech.,13, pp. 55–63
Jain, A. K., andDubes, R. C. (1988): ‘Algorithms for clustering data’ (Englewood Cliffs, Prentice Hall, New Jersey, 1988)
Kaufman, L., andRousseeuw, P. J. (1990): ‘Finding groups in data: an introduction to cluster analysis’ (John Wiley & Sons, New York, 1990)
Konings, K. T. S., Kirchhof, C. J. H. J., Smeets, J. L. R. M., Wellens, H. J. J., Penn, O. C., andAllessie, M. A. (1994): ‘High-density mapping of electrically induced atrial fibrillation in humans’,Circulation,89, pp. 1665–1680
Langley, P., Bourke, J. P. andMurray, A. (2000): ‘Frequency analysis of atrial fibirllation’,Comput. Cardiol.,27, pp. 65–68
Li, H., Hare, J., Mughal, K., Krum, D., Biehl, M., Deshpande, S., Dhala, A., Blanck, Z., Sra, J., Jazayeri, M., andAkhtar, M. (1996): ‘Distribution of atrial electrogram types during atrial fibrillation: effect of rapid atrial pacing and intercaval junction ablation’,J. Am. Coll. Cardiol.,27, pp. 1713–1721
Levy, S., Breithardt, G., Campbell, R. W. F., Camm, A. J., Daubert, J. C., Allessie, M. A., Aliot, E., Capucci, A., Cosio, F., Crijns, H., Jordaens, L., Hauer, R. N. W., Lombardi, F., andLüderitz, B. (1998): ‘Atrial fibrillation: current knowledge and recommendations for management,Europ. Heart J.,19, pp. 1294–1320
Moe, G. K. (1962): ‘On the multiple wavelet hypothesis of atrial fibrillation’,Arch. Int. Pharmacodyn. Ther.,140, pp. 183–188
Natale, A., Leonelli, F., Beheiry S., Newby, K., Pisano, E., Potenza, D., Rajkovich, K., Wides, B., Cromwell, L., andTomassoni, G. (2000): ‘Catheter ablation approach on the right side only for paroxysmal atrial fibrillation therapy: long term results’,PACE,23, pp. 224–233
Pieper, C. F., Blue, R., andPacifico, A. (1991): ‘Influence of time of sampling onset on parameters used for activation time determination in computerized intraoperative mapping’,Pacing Clin. Electrophysiol.,14, pp. 214–226
Ropella, K. M., Sahakian, A. V., Baerman, J. M., andSwiryn, S. (1989): ‘The coherence spectrum: a quantitative discriminator of fibrillatory and nonfibrillatory rhythms’,Circulation,80, pp. 112–119
Sih, H. J., Zipes, D. P., Berbari, E. J., andOlgin, J. E. (1999): ‘A high-temporal resolution algorithm for quantifying organization during atrial fibrillation,’,IEEE Trans. Biomed. Eng.,46, pp. 440–450
Slocum, J., Byrom, E., McCarthy, L., Sahakian, A., andSwiryn, S. (1985): ‘Computer detection of atrioventricular dissociation from surface electrocardiograms during wide QRS complex tachycardias’,Circulation,72, pp. 1028–1036
Smeets, J. L. R. M., Allessie, M. A., Lammers, W. J. E. P., Bonke, F. I. M., andHollen, J. (1986): ‘The wavelength of the cardiac impulse and reentrant arrhythmias in isolated rabbit atrium: the role of heart rate, autonomic transmitters, temperature, and potassium’,Circ. Res.,58, pp. 96–108
Wells, J. L., Karp, R. B., Kouchoukos, N. T., Maclean, W. A. H., James, T. N., andWaldo, A. L. (1978): ‘Characterization of atrial fibrillation in man: studies following open heart surgery’,PACE,1, pp. 426–438
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Faes, L., Nollo, G., Kirchner, M. et al. Principal component analysis and cluster analysis for measuring the local organisation of human atrial fibrillation. Med. Biol. Eng. Comput. 39, 656–663 (2001). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02345438
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02345438