Abstract
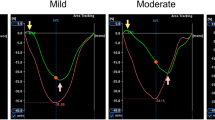
Several indexes have been reported to improve the accuracy of exercise test electrocardiogram (ECG) analysis in the diagnosis of coronary artery disease (CAD), compared with the classical ST depression criterion. Some of them combine repolarisation measurements with heart rate (HR) information (such as the so-called ST/HR hysteresis); others are obtained from the depolarisation period (such as the Athens QRS score); finally, there are heart rate variability (HRV) indexes that account for the nervous system activity. The aim of this study was to identify the best exercise ECG indexes for CAD diagnosis. First, a method to automatically estimate repolarisation and depolarisation indexes in the presence of noise during a stress test was developed. The method is divided into three stages: first, a preprocessing step, where QRS detection, filtering and baseline beat rejection are applied to the raw ECG, prior to a weighted averaging secondly, a post-processing step in which potentially noisy averaged beats are identified and discarded based on their noise variance; finally, the measurement step, in which ECG indexes are computed from the averaged beats. Then, a multivariate discriminant analysis was applied to classify patients referred for the exercise test into two groups: ischaemic (positive coronary angiography) and low-risk (Framingham risk index<5%). HR-corrected repolarisation indexes improved the sensitivity (SE) and specificity (SP) of the classical exercise test (SE=90%, SP-79% against SE=65%, SP=66%). Depolarisation indexes also achieved an improvement over ST depression measurements (SE=78%, SP=81%). HRV indexes obtained the best classification results in our study population (SE=94%, SP=92%) by means of the very high-frequency power (VHF) (0.4–1 Hz) at stress peak.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Badilini, F., Zareba, W., Titlebaum, E., andMoss, A. (1996): ‘Analysis of ST segment variability in Holter recordings’, in ‘Noninvasive electrocardiology: clinical aspects of Holter monitoring. Frontiers in cardiology’ (W.B. Saunders Company Ltd, UK, 1996) pp. 357–372
Bailón, R., Olmos, S., Serrano, P., García, J., andLaguna, P. (2002): ‘Robust measure of ST/HR hysteresis in stress test ECG recordings’, in ‘Computers in cardiology’, vol. 29 (IEEE Computer Society Press 2002), pp. 329–332
Bayés, A. (1992): ‘Tratado de electrocardiografía clínica’ (Ed.) (Científico-Técnica, Barcelona, Spain, 1992)
Bilchick, K., Fetics, B., Djoukeng, R., Fisher, S., Fletcher, R., Singh, S., Nevo, E., andBerger, R. (2002): ‘Prognostic value of heart rate variability in chronic congestive heart failure (Veterans Affairs' Survival Trial of Antiarrhythmic Therapy in Congestive Heart Failure)’,Am. J. Cardiol.,90, pp. 24–28
Bruce, R., Kusumi, F., andHosmer, D. (1973): ‘Maximal oxygen intake and nomographic assessment of functional aerobic impairment in cardiovascular disease’,Am. Heart. J.,85, pp. 546–562
D'Agostino, R., Russell, M., Huse, D., Ellison, C., Silbershatz, H., Wilson, P.,et al. (2000): ‘Primary and subsequent coronary risk appraisal: new results from the Framingham study’,Am. Heart J.,139, pp. 272–281
Detrano, R., Salcedo, E., Passalcqa, M., andFriis, R. (1986): ‘Exercise electrocardiographic variables: a critical appraisal’,J. Am. Coll. Cardiol.,8, pp. 836–847
Dilaveris, P., Zervopoulos, G., Michaelides, A., Sideris, S., Psomadaki, Z., Gialafos, E., Gialafos, J., andToutouzas, P. (1988): ‘Ischemia-induced reflex sympathoexcitation during the recovery period after maximal treadmill exercise testing’,Clin. Cardiol.,21, pp. 585–590
García, J., Serrano, P. Bailón, R., Gutiérrez, E., Del Rio, A., Casasnovas, J., Ferreira, I., andLaguna, P. (2000). ‘Comparison of ECG-based clinical indexes during exercise test’, in ‘Computers in cardiology’, vol. 27 (IEEE Computer Society Press, 2000), pp. 833–836
Gianrossi, R., Detrano, R., Mulvihill, D., Lehmann, K., Dubach, P., Colombo, A., McArthur, D., andFroelicher, V. (1989): ‘Exercise-induced ST depression in the diagnosis of coronary artery disease: A meta-analysis’,Circulation,80, pp. 87–98
Hampel, F., Ronchetti, E., Rousseeuw, P., andStahel, W. (1986): ‘Robust statistics’ (John Wiley & Sons, New York, USA)
Herpin, D., Ferrandis, J., Borderon, P., Gaudeau, B., Ragot, S., andDemange, J. (1995): ‘Comparison of the diagnostic accuracy of different methods of measurement of heart rate-adjusted ST-segment depression during exercise testing for identification of coronary artery disease’,Am. J. Cardiol. 76, pp. 1147–1151
Hoke, M., Ross, B., Wickesberg, R., andLütkenhöner, B. (1984): ‘Weighted averaging: theory and application to electric response audiometry’,Electroencephal. Clin. Neurophysiol.,57, pp. 579–584
Iskandrian, A., Decker, W. V., Gupta-Bala, S., Heo, J., Acio, E., andNallamothu, N. (1997): ‘Nuclear cardiac imaging’ (Medical Monograph Series, Office of Continuing Medical Education, Drexel University College of Medicine), 7
Jager, F., Moody, G., Antolic, G., Masic, D., andMark, R. (1997): ‘Sympatho-vagal correlates of transient ischemia in ambulatory patients’, in ‘Computers in cardiology’ (IEEE Computer Society Press, 1997), pp. 387–390
Kligfield, P., andOkin, P. (1999): ‘Heart rate adjustment of ST depression in patients with coronary disease and negative standard exercise test’,J. Electrocardiol.,32, pp. 193–197
Laguna, P., Jané, R., andCaminal, P. (1994): ‘Automatic detection of wave boundaries in multilead ECG signals: validation with the CSE database’,Comput. Biomed. Res.,27, pp. 45–60
Lehtinen, R., Sievänen, H., Viik, J., Turjanmaa, V., Niemelä, K., andMalmivuo, J. (1996): ‘Accurate detection of coronary artery disease by integrated analysis of the ST-segment depression/heart rate patterns/during the exercise and recovery phases of the exercise ECG test’,Am. J. Cardiol.,78, pp. 1002–1006
Lehtinen, R. (1999): ‘ST/HR hysteresis. Exercise and recovery phase ST depression/heart rate analysis of the exercise ECG’,J. Electrocardiol.,32, pp. 198–203
Mateo, J., andLaguna, P. (2000): ‘Improved heart rate variability time-domain signal construction from the beat occurrence times according to the IPFM model’,IEEE Trans. Biomed. Eng.,47, pp. 985–996
Mateo, J., Serrano, P., Bailón, R., García, J., Ferreira, A., Del Rio, A., Ferreira, I., andLaguna, P. (2001a): ‘Heart rate variability measurements during exercise test may improve the diagnosis of ischemic heart disease’. Proc. 23rd Int. Conf., IEEE-EMBS Society, Istanbul (CD-ROM)
Mateo, J., Serrano, P., Bailón, R., Olmos, S., García, J., Del Río, A., Ferreira, I., andLaguna, P. (2001b): ‘ECG-based clinical indexes during exercise test including repolarization, depolarization and HRV’, in ‘Computers in cardiology’, vol. 28 (IEEE Computer Society Press, 2001), pp. 309–312
Mateo, J., andLaguna, P. (2003): ‘Analysis of heart rate variability in the presence of ectopic beast using the heart timing signal’,IEEE Trans. Biomed. Eng. 50, pp. 334–343
Michaelides, A., Triposkiadis, F., Boudoulas, H., Spanos, A., Papadopoulos, P., Kourouklis, K., andToutouzas, P. (1990): ‘New coronary artery disease index based on exercise-induced QRS changes’,Am. Heart J.,120, pp. 292–302
Michaelddes, A., Ryan, J., Fossen, D. V., Pozderac, R., andBoudoulas, H. (1993). ‘Exercise-induced QRS prolongation in patients with coronary artery disease: a marker of myocardial ischemia’,Am. Heart J.,126 pp. 1320–1325
Michaelides, A., Psomadaki, Z., Aggeli, K., Georgiades, G., Pitsavos, C., Seferlis, C., andToutouzas, P. (1996). ‘Best detection of coronary artery and identification of the significantly narrowed coronary artery (ies), using a new technique in exercise testing’,J. Am. Coll. Cardiol.,27, p. 129A (932)
Moody, G., andMark, R. (1982): ‘Development and evaluation of a 2-lead ECG analysis program’ in ‘Computers in cardiology’ (IEEE Computer Society Press, 1982), pp. 39–44
Morise, A. (1997): ‘Accuracy of heart rate-adjusted ST segments in populations with and without posttest referral bias’,Am. Heart J.,134 pp. 647–655
Morise, A., andDuval, R. (1995): ‘Diagnostic accuracy of heart rate-adjusted ST segments compared with standard ST-segment criteria’,Am. J. Cardiol.,75, pp. 118–121
Morshedi-Meibodi, A., Larson, M., Levy, D., O'Donnell, C., andVasan, R. (2002): ‘Heart rate recovery after treadmill exercise testing and risk of cardiovascular disease events (The Framingham Heart Study)’,Am. J. Cardiol. 90, pp. 848–852
Okin, P., Ameisen, O., andKligfield, P. (1989): ‘Recovery-phase patterns of ST segment depression in the heart rate domain. Identification of coronary artery disease by the rate-recovery loop’,Circulation,80, pp. 533–541
Okin, P., Bergman, G., andKligfield, P. (1991a): ‘Effect of ST segment measurement point on performance of standard and heart rate-adjusted ST segment criteria for the identification of coronary artery disease’,Circulation,84, pp. 57–66
Okin, P., Bergman, G., andKligfield, P. (1991b): ‘Heart rate adjustment of the time-voltage ST segment integral: identification of coronary disease and relation to standard and heart rate-adjusted ST segment depression criteria’,J. Am. Coll. Cardiol.,18, pp. 1487–1492
Okin, P., andKligfield, P. (1995a): ‘Gender-specific criteria and performance of the exercise electrocardiogram’,Circulation,92, pp. 1209–1216
Okin, P., andKligfield, P. (1995b): ‘Heart rate adjustment of ST segment depression and performance of the exercise electrocardiogram: a critical evaluation’,J. Am. Coll. Cardiol.,25, pp. 1726–1735
Task Force of ESC and Naspe, T. (1996): ‘Heart rate variability. Standards of measurment, physiological interpretation, and clinical use’,Eur. Heart J.,17, pp. 354–381
Toth, A., Marton, Z., Czopf, L., Kesmarky, G., Halmosi, R., Juricskay, I., Habon, T., andToth, K. (2001): ‘QRS score: a composite index of exercise-induced changes in the Q, R, and S waves during exercise stress testing in patients with ischemic heart disease’,Ann. Noninvas. Electrocardiol.,6, pp. 310–318
Tsuji, H., Venditti, F., Manders, E., Evans, J., Larson, M., Feldman, C., andLevy, D. (1994): ‘Reduced heart rate variability and mortality risk in an elderly cohort. The Framingham Heart Study’,Circulation,90, pp. 878–883
Tsuji, H., Larson, M., Venditti, F., Manders, E., Evans, J., Feldman, C., andLevy, D. (1996): ‘Impact of reduced heart rate variability on risk for cardiac events. The Framingham Heart Study’,Circulation,94, pp. 2850–2855
VanCampen, C., Visser, F., andVisser, C. (1996): ‘The QRS score: a promising new exercise score for detecting coronary artery disease based on exercise-induced changes of Q-, R-and S-waves: a relationship with myocardial ischaemia’,Eur. Heart J.,17, pp. 699–708
Warnik, W., Ross, J., andKaralis, D. (1996): ‘Stress echocardiography in clinical practice’ (Medical Monograph Series, Office of Continuing Medical Education, Drexel University College of Medicine),6
Watanabe, J., Thamilarasan, M., Blackstone, E., Thomas, J., andLauer, M. (2001): ‘Heart rate recovery immediately after treadmill exercise and left ventricular systolic dysfunction as predictors of mortality. The case of stress echocardiography’,Circulation,104, pp. 1911–1916
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Bailón, R., Mateo, J., Olmos, S. et al. Coronary artery disease diagnosis based on exercise electrocardiogram indexes from repolarisation, depolarisation and heart rate variability. Med. Biol. Eng. Comput. 41, 561–571 (2003). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02345319
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02345319