Abstract
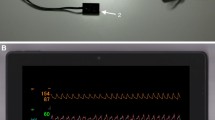
Photoplethysmography (PPG) can be used to measure systolic blood pressure at the brachial artery. With a specially designed probe, positioned in the most distal position beneath a pressure cuff on the upper arm, this is possible. The distance between the light source (880 nm) and the photodetector was 20 mm. A test was performed on neuro-intensive care patients by determining blood pressure from the PPG curves, and, when it was compared with systolic blood pressure obtained from inserted indwelling arterial catheters, a correlation factor of r=0.95 was achieved. The difference between blood pressure obtained using PPG and invasive blood pressure measurement was 3.9±9.1 mmHg (mean±SD), n=19. The depth to the brachial artery was 13.9±4.1 mm (mean±SD), n=18. A digital PPG system utilising pulsating light was also developed.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bukhari, A. R. S. (1993): ‘Skin blood flow measurements—a review of noninvasive methods’,J. Clin. Eng.,18, pp. 53–65
Cederholm, I., Sørensen, J., andCarlsson, C. (1986): ‘Thrombosis following percutaneous radial artery cannulation’,Acta Anaesthesiol. Scand.,30, pp. 227–230
Chawla, R., Kumarvel, V., Girdhar, K. K., Sethi, A. K., Indrayan, A., andBhattacharya, A. (1992): ‘Can pulse oximetry be used to measure systolic blood pressure?’,Anesth. Analg.,74, pp. 196–200
Frezza, E. E., andMezghebe, H. (1998): ‘Indications and complications of arterial catheter use in surgical or medical intensive care units: Analysis of 4932 patients’,Am. Surgeon,64, pp. 127–131
Fronek, A., Blazek, V., andCurran, B. (1994): ‘Toe pressure determination by audiophotoplethysmography’,J. Vasc. Surg.,20, pp. 267–270
Guelen, I., Westerhof, B. E., Van Der Sar, G. L., Van Montfrans, G. A., Kiemeneij, F., Wesseling, K. H., andBos, W. J. (2003): ‘Finometer, finger pressure measurements with the possibility to reconstruct brachial pressure’,Blood Press. Monit.,8, pp. 27–30
Hertzman, A. B., andSpealman, C. R. (1937): ‘Observations on the finger volume pulse recorded photo-electrically’,Am. J. Physiol.,119, pp. 334–335
Hunyor, S. N. (1991): ‘Blood pressure in clinical practice’, inO'Brien, E., andO'Malley, K. (Eds.) ‘Blood pressure measurement, vol. 14’, in ‘Handbook of hypertension’ (Elsevier, Amsterdam, New York, 1991), chap. 4, pp. 95–111
Johansson, A., Öberg, P. Å., andSedin, G. (1999): ‘Monitoring of heart and respiratory rates in newborn infants using a new photoplethysmographic technique’,J. Clin. Monit. Comput.,15, pp. 461–467
Jönsson, B., Lindberg, L. G., Skau, T., andThulesius, O. (2001): ‘Is oscillometric ankle pressure reliable in leg vascular disease?’,Clin. Physiol.,21, pp. 155–163
Kamal, A. A. R., Harness, J. B., Irving, G., andMearns, A. J. (1989): ‘Skin photoplethysmography—a review’,Comput. Methods Programs Biomed.,28, pp. 257–269
Langbaum, M., andEyall, F. G. (1994): ‘A practical and reliable method of measuring blood pressure in the neonate by pulse oximetry’,J. Pediatr. 125, pp. 591–595
Lindberg, L.-G., Ugnell, H., andÖberg, P. Å. (1992): ‘Monitoring of respiratory and heart rates using a fibre-optic sensor’,Med. Biol. Eng. Comput.,30, pp. 533–537
O'Brien, E., Waeber, B., Parati, G., Staessen, J., andMyers, M. G. (2001): ‘Blood pressure measuring devices: recommendations of the European Society of Hypertension (Clinical review)’,Br. Med. J.,322, pp. 531–536
Sapinski, A. (1996): ‘Standard algorithm for blood pressure measurement by sphygmo-oscillographic method’,Med. Biol. Eng. Comput.,34, pp. 82–83
Tremper, K. K., andBarker, S. J. (1989): ‘Pulse oximetry’,Anesthesiology,70, pp. 98–108
Weinman, J. (1967): ‘Photoplethysmography’, inVenables, P., andMartin, I. (Eds.): ‘A manual of psychophysiological methods’ (Wiley, New York, 1967), pp. 185–217
Yamakoshi, K.-I., andKamiya, A. (1987): ‘Noninvasive measurement of arterial blood pressure and elastic properties using photoelectric plethysmography technique’,Med. Progr. Technol.,12, pp. 123–143
Yamakoshi, K.-I. (1991): ‘Non-invasive techniques for ambulatory blood pressure monitoring and simultaneous cardiovascular measurements’,J. Ambulat. Monit.,4, pp. 123–143
Yao, S. T. (1993): ‘Pressure measurements in the extremity’, inBernstein, E. F. (Ed.): ‘Vascular diagnosis’ (Mosby, St. Louis, 1993), pp. 169–175
Zhang, Q. (2002): ‘Non-invasive measurement of skeletal muscle blood using photoplethysmography—Experimental studies on the human leg’. Medical dissertation, Dept of Orthopaedics, Institute of Surgical Sciences, Göteborgs University, Sweden, p. 17
Zourabian, A., Siegel, A., Chance, B., Ramanujan, N., Rode, M., andBoas, D. A. (2000): ‘Trans-abdominal monitoring of fetal arterial blood oxygenation using pulse oximetry’,J. Biomed. Opt.,5, pp. 391–405
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Laurent, C., Jönsson, B., Vegfors, M. et al. Non-invasive measurement of systolic blood pressure on the arm utilising photoplethysmography: development of the methodology. Med. Biol. Eng. Comput. 43, 131–135 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02345134
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02345134