Abstract
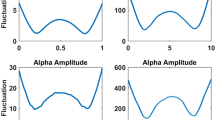
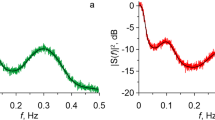
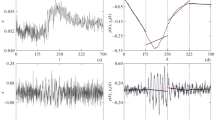
Recent studies were investigated that report spontaneous oscillations of cerebral perfusion in the very low-frequency range (0.01–0.04 Hz), emphasising details of spectral estimation. The effects of different spectral estimation procedures were compared, using simulated and clinical data. It was shown that data detrending, as used in many studies, can lead to an artifactual peak in the very low-frequency region of estimated power spectra, indicating that the peak cannot be taken as evidence of physiological oscillations. A quantitative, reliable method is described that can be used to assess very low-frequency oscillations. Using the method, very low-frequency oscillations were found in ten out of 17 healthy adults measured with transcranial Doppler (average frequency, 0.021±0.007 Hz, mean±SD), confirming earlier findings based on visual inspection of data.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Arnolds, B. J., andvon Reutern, G. M. (1986): ‘Transcranial doppler sonography. Examination technique and normal reference values’,Ultrasound Med. Biol.,12, pp. 115–123
Bäzner, H., Daffertshofer, M., Konietzko, M., andHennerici, M. G. (1995): ‘Modification of low-frequency spontaneous oscillations in blood flow velocity in large- and small-artery disease’,J. Neuroimag.,5, pp. 212–218
Brockwell, P. J., andDavis, R. A. (1991): ‘Time series: theory and methods’ (Springer, Berlin, 1991)
Diehl, R. R., andBerlit, P. (1996): ‘Funktionelle Dopplersonographie in der Neurologie’ (Springer, Berlin, 1996), p. 27
Dòra, E., andKovách, A. G. B. (1981): ‘Metabolic and vascular volume oscillations in the cat brain cortex’,Acta Physiol. Acad. Sci. Hung.,57, pp. 261–275
Droste, D. W., Krauss, J. K., Berger, W., Schuler, E., andBrown, M. M. (1994): ‘Rhythmic oscillations with a wavelength of 0.5–2 min in transcranial Doppler recordings’,Acta Neurol. Scand.,90, pp. 99–104
Elwell, C. E., Springett, R., Hillman, E., andDelpy, D. T. (1999): ‘Oscillations in cerebral haemodynamics. Implications for functional activation studies’,Adv. Exp. Med. Biol.,471, pp. 57–65
Giller, C. A., Hatab, M. R., andGiller, A. M. (1999): ‘Oscillations in cerebral blood flow detected with a transcranial doppler index’,J. Cereb. Blood Flow Metab.,19, pp. 452–459
Hamming, R. W. (1989): ‘Digital filters’, 3rd edn (Prentice Hall, Englewood Cliffs, 1989), p. 226
Hoshi, Y., Kosaka, S., Xie, Y., Kohri, S., andTamura, M. (1998): ‘Relationship between fluctuations in the cerebral hemoglobin oxygenation state and neuronal activity under resting conditions in man’,Neurosci. Lett.,245, pp. 147–150
Kuo, T. B., Chern, C. M., Sheng, W. Y., Wong, W. J., andHu, H. H. (1998): ‘Frequency domain analysis of cerebral blood flow velocity and its correlation with arterial blood pressure’,J. Cereb. Blood Flow Metab.,18, pp. 311–318
Li, S.-J., Biswal, B., Li, Z., Risinger, R., Rainey, C., Cho, J.-K., Salmeron, B. J., andStein, E. A. (2000): ‘Cocaine administration decreases functional connectivity in human primary visual and motor cortex as detected by functional MRI’,Magn. Reson. Med.,43, pp. 45–51
Lundberg, N. (1960): ‘Continuous recordings and control of ventricular fluid pressure in neurosurgical practice’,Acta Psychiatr. Neurol. Scand.,149, pp. 1–193
Malliani, A., Pagani, M., andLombardi, F. (1994): ‘Physiology and clinical implications of variability of cardiovascular parameters with focus on heart rate and blood pressure’,Am. J. Cardiol.,73, pp. 3C-9C
Mautner-Huppert, D., Haberl, R. L., Dirnagl, U., Villringer, A., Schmiedek, P., andEinhäupl, K. (1989): ‘B-waves in healthy persons’,Neurol. Res.,11, pp. 194–196
Mayer, S. (1876): ‘Studien zur Physiologie des Herzens und der Blutgefäße. V. Über spontane Blutdruckschwankungen’,Sächs. Akad. Wiss. Sitz. Math. Naturw.,74, pp. 281–307
Newell, D. W., Aaslid, R., Stoss, R., andReulen, H. J. (1992): ‘The relationship of blood flow velocity fluctuations to intracranial pressure B waves’,J. Neurosurg.,76, pp. 415–421
Obrig, H., Neufang, M., Wenzel, R., Kohl, M., Steinbrink, J., Einhäupl, K., andVillringer, A. (2000): ‘Spontaneous low frequency oscillations of cerebral hemodynamics and metabolism in human adults’,NeuroImage,12, pp. 623–639
Preiss, G., andPolosa, C. (1974): ‘Patterns of sympathetic neuron activity associated with Mayer waves’,Am. J. Physiol.,226, pp. 724–730
Press, W., Flannery, B., Saul, S., andVetterling, W. (1992): ‘Numerical recipes, 2nd edn’ (Cambridge University Press, 1992)
Rambaldi, S., andPinazza, O. (1994): ‘An accurate fractional Brownian motion generator’,Physica A,208, pp. 21–30
Timmer, J., andKönig, M. (1995): ‘On generating power law noise’,Astron. Astrophys.,300, pp. 707–710
Timmer, J., Lauk, M., andDeuschl, G. (1996): ‘Quantitative analysis of tremor time series’,Electroencephalogr. Clin. Neurophysiol.,101, pp. 461–468
Yang, M. W., Kuo, T. B., Llin, S. M., Chan, K. H., andChan, S. H. H. (1995): ‘Continuous, on-line, real-time spectral analysis of SAP signals during cardiopulmonary bypass’,Am. J. Physiol.,268, pp. H2329-H22335
Zhang, R., Zuckerman, J. H., Giller, C. A., andLevine, B. D. (1998): ‘Transfer function analysis of dynamic cerebral autoregulation in humans’,Am. J. Physiol.,274, pp. H233-H241
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Müller, T., Timmer, J., Reinhard, M. et al. Detection of very low-frequency oscillations of cerebral haemodynamics is influenced by data detrending. Med. Biol. Eng. Comput. 41, 69–74 (2003). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02343541
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02343541