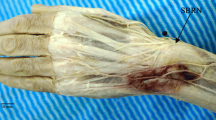
Abstract
A case with a median nerve lesion at the wrist without thenar atrophy and another with an ulnar nerve lesion at the elbow sparing the first dorsal interosseous are reported. Simultaneous multiple channel recording demonstrated in the first case a dual innervation of the abductor pollicis brevis by median and ulnar fibers via a Martin-Gruber anastomosis. In the second case, the cross over of the median fibers innervating the first dorsal interosseous was very proximal in the antecubital fossa. Stimulation at discrete points documented that the communicating fibers from the median joined the ulnar nerve 3 cm below the medial epicondyle.
Sommario
Vengono descritti due casi: il primo con una lesione del nervo mediano al polso senza atrofia della eminenza thenar, il secondo con una lesione del nervo ulnare al gomito che risparmiava il muscolo primo interosseo dorsale. La tecnica di registrazione simultanea con canali multipli ha consentito di dimostrare nel primo caso una innervazione duplice (mediano ed ulnare) del muscolo adbuttore breve del pollice tramite una anastomosi di Martin-Gruber. Nel secondo caso, l'incrocio verso il nervo ulnare delle fibre a partenza dal mediano e destinate ad innervare il muscolo primo interosseo dorsale, era molto prossimale nella fossa antecubitale. La stimolazione nervosa in punti discreti permetteva di dimostrare che le fibre anastomotiche provenienti dal nervo mediano si univano all'ulnare 3 cm al di sotto dell'epicondilo mediale.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Cannieu J.M.A.:Note sur une anostomose entre la branche profonde du cubital et le median. Bull. Soc. d'Anat. Physio. Bordeaux 18: 339–340, 1897.
Cliffton E.E.:Unusual innervation of the intrinsic muscles of the hand by median and ulnar nerve. Surgery 23: 12–31, 1948.
Dyro M.:Ulnar innervation of opponens pollicis. Electromyograph. clin. Neurophysiol. 23: 257–260, 1983.
Foerster O.:Spezielle Anatomie and Physiologie der peripheren Nerven. In M. Lewandowsky Handbuch der Neurologie. Julius Springer, Berlin, 2: 786–838, 1929.
Gruber W.:Uber die Verbindung des Nervus medianus mit dem Nervus ulnaris am Unterarme des Menschen und der Saugethiere. Arch. Anat. Physiol. Med. Leipzig, 37: 501–522, 1870.
Gutmann L.:Median-ulnar communications and carpal tunnel syndrome. J. Neurol. Neurosurg. Psychiatry 40: 982–986, 1977.
Hepburn D.:The comparative anatomy of the muscles and nerves of superior and inferior extremities of the antropoid apes. J. Anat. and Physiol, 26:149–186, 1892.
Highet W.B.:Innervation and function of the thenar muscles. Lancet 1: 227, 1897.
Hollyday M.:Motoneuron histogenesis and the development of limb innervation. Current topics in development biology 15, 181–213, 1980.
Kimura J., Murphy M.J., Varda D.J.:Electrophysiological study of anomalous innervation of intrinsic hand muscles. Arch. Neurol. 33: 842–844, 1976.
Mannerfelt L.:Studies on the hand in ulnar nerve paralysis. Acta Orthopaedica Scandinavica Suppl. 87:23–142, 1966.
Marinacci A.A.:Anomalous innervation of the small muscles of the hand “all median” or “all ulnar hand”. Applied Electromyography, Lea and Fehiger, Philadelphia, 23–30, 1968.
Martin R.:Tal om Nervus allmauna Egenskaper i Mannsikans Kropp. L. Salvius, Stockholm, 1763.
Murphey F., Kizklin J.W., Finlayson A.I.:Anomalous innervation of the intrinsic muscles of the hand. Surgery Ginec Obstet 83: 15–23, 1946.
Richie P.:Le nerf cubital et les muscles de l'éminence thénar. Bull. mem. Soc. anat. Paris 5: 251–252, 1897.
Rowntree T.:Anomalus innervation of the hand muscles. J. Bone Jt. Surgery 31 B, 505, 1949.
Spinner M.:Kaplan's functional and surgical anatomy of the hand. Lippincot Co. Philadelphia, 1984.
Stookey B.:Surgical and mechanical treatment of peripheral nerves. Saunders Philadelphia, 325, 1922.
Sunderland S.:Voluntary movements and the deceptive action of muscles in peripheral nerve lesions. Aust. N.Z. J. Surg 13: 160, 1944.
Sunderland S.:Nerves and nerve injuries. 2nd Edition. Churchill Livingston, Edinburgh 1978.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Uncini, A., Lange, D.J. & Lovelace, R.E. Anomalous intrinsic hand muscle innervation in median and ulnar nerve lesions: An electrophysiological study. Ital J Neuro Sci 9, 497–503 (1988). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02337169
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02337169