Abstract
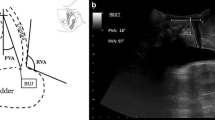
Using introital sonography as an alternative to lateral chain urethrocystography during urodynamic studies, a prospective investigation was carried out in 47 patients with lower urinary tract complaints, to determine the correlation of sonographic assessment with and without bladder catheterisation. The apparent location of the bladder neck in relation to the pubic symphysis and measurements of the posterior urethrovesical angle at rest and during straining during cystometry with and without intravesical urodynamic pressure transducers were determined. In 22 (46.8%) patients the bladder neck at rest was below the lower edge of the symphysis. This finding was not influenced by the presence of a catheter. Correlation coefficients (r) for posterior urethrovesical angles at rest and during straining measured with and without catheters were 0.95 (95% confidence limits 0.92–0.98;P<0.01) and 0.98 (95% confidence limits 0.96–0.99;P<0.01), respectively. The coefficients of determination (r 2) at rest and during straining were 0.92 and 0.95, respectively. Sonography with and without cystometry equipment in place gave similar results.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abrams PH, Blaivas JG, Stanton SL, Andersen JT (1990) The standardisation of terminology of lower urinary tract function recommended by the International Continence Society. Int Urogynecol J 1:45–58
Brown MC, Sutherst J, Murray A, Richmond DH (1985) Potential use of ultrasound in place of X-ray fluoroscopy in urodynamics. Br J Urol 57:88–90
Green TH Jr (1975) Urinary stress incontenence: differential diagnosis, pathophysiology, and management. Am J Obstet Gynecol 122:368–400
Koelbl H, Bernaschek G (1989) A new method for sonographic urethrocystography and simultaneous pressure-flow measurements. Obstet Gynecol 74:417–422
Koelbl H, Hanzal E, Bernaschek G (1991) Sonographic urethrocystography — methods and application in patients with genuine stress incontinence. Int Urogynecol J 2:25–31
Penttinen J, Lindholm EL, Kaar K, Kauppila A (1989) Successful colposuspension in stress urinary incontinence reduces bladder neck mobility and increases pressure transmission the urethra. Arch Gynecol Obstet 244:233–238
Ralph G, Tamussino K (1991) Die endoskopische Blasenhalsanhebung-klinische, urodynamische und radiologische Ergebnisse. Geburtshilfe Frauenheilk 51:830–833
Yamada T, Mizuo T, Kawakami S, Watanabe T, Negishi T, Oshima H (1991) Application of transrectal ultrasonography in modified Stamey procedure for stress urinary incontinence. J Urol 146:1555–1558
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hanzal, E., Joura, E.M., Haeusler, G. et al. Influence of catheterisation on the results of sonographic urethrocystography in patients with genuine stress incontinence. Arch Gynecol Obstet 255, 189–193 (1994). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02335084
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02335084