Abstract
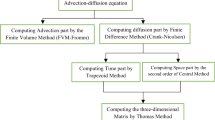
A cohesive sediment transport model considering the effects of flocculation, deposition and erosion is used in an attempt to simulate the suspended sediment distribution in a mesotidal estuary. The numerical model solves the three-dimensional (3D) advection-diffusion equation using a two-time level scheme, and a semi-implicit finite difference approach. The transport model is coupled to a 3D-barotropic hydrodynamic model for the simulation of the major tidal components reproducing the non-linear effects. An application of these models in the Western Scheldt estuary is described. The results of the different tests show that the adopted approach provides a useful basis for a good understanding of the physical processes involved in sediment transport and for the study of practical problems. The sensitivity of the model to key parameters controlling the simulation of bed sediment/water exchanges, shows the importance of a good definition of bottom sediment characteristics and the importance of further development of a consolidation algorithm.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
ARIATHURAI, R. and R.B. KRONE, 1976. Finite element model for cohesive sediment transport. J. Hydr. Div., ASCE, Vol. 102, No. HY3, p. 323–338.
AVOINE, J., 1986. Sediment exchanges between the Seine estuary and its adjacent shelf. J. Geol. Society, 144: 135–148.
BECKERS, J.M., 1991. Application of the GHER 3D general circulation model to the western Mediterranean. J. Marine Systems, Elsevier Science Publ. B.V., Amsterdam, 1: 315–332.
CANCINO, L. and R. NEVES, 1994. Numerical modelling of three-dimensional cohesive sediment transport in an estuarine environment. Proceedings of EUROMECH 310, Le Havre, France, 1993, World Scientific Publishing, 15 pp. (in press).
CLOERN, J.E., 1987. Turbidity as a control on phytoplankton biomass and productivity in estuaries In: R.J. Uncles, Ed., Dynamics of Turbid Coastal Environments. EBSA. 16th annual symposium. Cont. Shelf Res., 7: 1367–1381.
DELO, E.A., 1988. Estuarine muds manual. Report No. SR 164, Hydraulics Research, Wallingford, UK, 64 pp.
DYER, K.R., 1986. Coastal and estuarine sediment dynamics. Wiley-Interscience, New York, 342 pp.
DYER, K.R. and E.M. EVANS, 1989. Dynamics of turbidity maximum in a homogeneous tidal channel. J. Coastal Research, Special Issue No. 5, Fort Lauderdale, Florida, p. 23–30.
EINSTEIN, H. A., 1950. The bedload function for sediment transportation in open channel flows. Soil Cons. Serv. U. S. Dept. Agric. Tech. Bull., No. 1026, 78 pp.
FISHER, T.R., L.W. HARDING Jr., D.W. STANLEY and L.G. WARD. 1988 Phytoplankton, nutrients, and turbidity in the Chesapeake, Delaware, and Hudson estuaries. Estuar. Coast. Shelf Sci. 27: 61–93.
GIBBS, R.J., D.M. TSHUDY, L. KONWAR and J.M. MARTIN, 1989. Coagulation and transport of sediments in the Gironde estuary. Sedimentology, 36: 987–999.
HAYTER, E.J. and A.J. MEHTA, 1986. Modelling cohesive sediment transport in estuarine waters. Appl. Math. Modelling, 10: 294–303.
KIRBY, R. and W.R. PARKER, 1977. Ecological impact of cohesive sediment suspensions. In: 14th IAHR Conference, Ecological Aspects of Dredging, Baden-Baden, p. 854–857.
KRONE, R.B., 1962. Flume studies of the transport in estuarine shoaling processes. Hydr. Eng. Lab., Univ. of Berkeley, California, USA. 110 pp.
LARDNER, R.W. and Y. SONG, 1991. An algoritm for three-dimensional convection and diffusion with very different horizontal and vertical length scales. Int. J. Num. Meth. Eng., 32: 1303–1319.
LOOFF, D., 1978. Kaartering van de bodemsamenstelling van het oostelijk gedeelte van de Westerschelde. Methode en Resultaten. Rijkswaterstaat, Rep. WWKZ nr. 78.V013, 10 pp.
LOOFF, D., 1980. Kaartering van de bodemsamenstelling van het westelijk gedeelte van de Westerschelde. Methode en Resultaten. Rijkswaterstaat, Rep. WWKZ nr. 80.V009, 9 pp.
McLAREN, P. and D.I. LITTLE, 1987. The effects of sediment transport on contaminant dispersal: an example from Milford Haven. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 18: 586–594.
MEHTA, A.J., E.J. HAYTER, W.R. PARKER, R.B. KRONE and A.M. TEETER, 1986a. A cohesive sediment transport. I: Process description. J. Hydraul. Eng., 115: 1076–1093.
MEHTA, A.J., W.N. McANALLY, E.J. HAYTER, A.M. TEETER, D. SCHOELLHAMER, S.B. HELTZEL and W.P. CAREY, 1986b. A cohesive sediment transport. II: application. J. Hydraul. Eng., 115: 1094–1112.
MULDER, H.P.J. and C. UDINK, 1991. Modelling of cohesive sediment transport. A case study: The Western Scheldt Estuary. In: B.L. Edge, Ed., Proceed. 22nd Internat. Conf. Coast. Engin. Amer. Soc. Civ. Eng., New York, p. 3012–3023.
NICHOLSON, J.M.C., 1983. Three-dimensional models of particulate and cohesive suspended sediment transport. Ph.D. Thesis, Univ. of Manchester, England, p. 321.
NIHOUL, J.C.J., 1984. A three-dimensional general marine circulation model in a remote sensing perspective. Ann. Geophys., 2: 433–442.
O'CONNOR, B.A. and J.A. NICHOLSON, 1988. Three-dimensional model of suspended particulate sediment transport. Coastal Eng. 12: 157–174.
ODD, N.V.M. and M.W. OWEN, 1972. A two-layer model of mud transport in the Thames estuary. Proceedings, Institution of Civil Engineers, London, p. 195–202.
ODD, N.V.M., 1982. The feasibility of using mathematical models to predict sediment transport in the Severn estuary. The Severn Barrage, Thomas Telford Ltd, London, p. 195–202.
PARTHENIADES, E., 1965. Erosion and deposition of cohesive soils. J. Hydr. Div., ASCE, 91, No. HY1: 105–139.
PHILLIPS, N.A., 1957. A coordinate system having some spacial advantages for numerical forecasting. J. Meteorol., 14: 184–186.
PLUMMER, D.H., N.J.P. OWENS and R.A. HERBERT. 1987. Bacteria-particle interactions in turbid estuarine environments. In: R.J. Uncles, Ed., Dynamics of Turbid Coastal Environments (EBSA 16th annual symposium). Cont. Shelf Res. 7: 1492–1433.
ROBERT, J.L. and Y. OUELLET, 1987. A three-dimensional finite element model for the study of steady and non-steady natural flows. In: J.C.J. Nihoul and B.M. Jamart, Eds. Elsevier Oceanography Series, 45: 359–372.
RUCH, P., MIRMAND, M., JOUANNEAU, J.-M. and LATOUCHE, C., 1993. Sediment budget and transfer of suspended sediment from the Gironde estuary to Cap-Ferret Canyon. Mar. Geology, 111: 109–119.
SANTOS, A.J. and R. NEVES, 1991. Radiactive artificial boundaries in ocean barotropic models. In: A. S. Arcilla, Ed., Proceed. 2nd Int. Conf. on Computer Modelling in Ocean Engineering, Barcelona, p. 373–383.
SHENG, Y.P., 1986. Modelling bottom boundary layer and cohesive sediment dynamics in estuarine and coastal waters. In: A. J. Mehta, Ed., Estuarine cohesive sediment dynamics, Springer, Berlin, 14: 360–400.
SIMENSTAD, C.A., L.F. SMALL and C.D. McINTIRE, 1990. Consumption processes and food web structure in the Columbia river estuary. Prog. Oceanogr. 25: 271–297.
STEPHENS, J.A., R.J. UNCLES, M.L. BARTON and F. FITZPATRICK., 1992. Bulk properties of intertidal sediments in a muddy macrotidal estuary. Mar. Geol. 103: 15 pp.
STOLZENBACH, K.D., K.A. NEWMAN and C.S. WONG, 1992. Aggregation of fine particles at the sediment water interface. J. Geoph. Res., 97: 17,889–17,898.
THOMAS, L.H., 1994. Elliptic problems in linear difference equations over a network. Watson Sci. Comput. Lab. Rept., Columbia University, New York: 373–383.
VAN MALDEGEM, D.C., H.P.J. MULDER and A. LANGERAK, 1993. A cohesive sediment balance for the Scheldt Estuary. In: Proceed. ECSA-21 Symposium, Marine and Estuarine Gradients, Gent, Belgium, 1991. Neth. J. Aquat. Ecol., 27: 247–256.
VALE, C., 1990. Temporal variations of the particulate metals in the Tagus river estuary. The Sci. Total Environ., 97/98: 137–154.
VAN RIJN, L.C., 1989. State of the art in sediment transport modeling. In: Sam S. Y. Wang, Ed., Sediment Transport Modeling, ASCE, p. 13–32.
VINCX, M., G. DE SMET and A. VIERSTRAETE, 1993. Sediment grain size distribution in the Elbe, Schelde and Gironde around the maximum turbidity zone. EC-MATURE Report, Univ. of Gent, Belgium, 5 pp.
WELLERSHAUS, S. and A. SOLTANPOUR-GARGARI, 1991. Planktonic copepods in very low salinity mixing zone. Proceed 4th Internat. Conf. Copepoda. Bull. Plankton Soc. Japan, Spec. Vol.: 133–142.
WOLLAST, R., 1986. The Scheldt Estuary. In: W. Salomons, B.L. Bayne, E.K. Duursma and U. Förstner, Eds., Pollution of the North Sea. An Assessment. Springer-Verlag, p. 183–193.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Cancino, L., Neves, R. 3D-numerical modelling of cohesive suspended sediment in the Western Scheldt estuary (The Netherlands). Netherlands Journal of Aquatic Ecology 28, 337–345 (1994). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02334202
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02334202