Summary
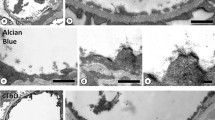
The distribution of mercury in the spleen, liver, lymph nodes, thymus and bone marrow was studied by autometallography in mice exposed to mercuric chloride intraperitoneally. Application of immunofluorescence histochemistry and an autometallographic silver amplification method was employed to the same tissue section. Mercury was not only detected in macrophages marked by the antibody M1/70 but also in macrophage-like cells, which were either autofluorescent or devoid of fluorescent signals. These two cell types were identified as macrophages at the electron microscopical level. Autometallographically stained macrophages were observed in the spleen, lymph nodes, thymus and in Kupffer cells of the liver. Furthermore, mercury was observed in endothelial cells. No obvious pathological disturbances were observed at light and electron microscopical level. At the subcellular level mercury was localized in lysosomes of macrophages and endothelial cells.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Austyn, J. M. &Gordon, S. (1981) F4/80, a monoclonal antibody directed specifically against the mouse macrophage.Eur. J. Immunol. 11, 805–15.
Baatrup, E., Thorlacius-Ussing, C., Nielsen, H. L. &Wilsky, K. (1989) Mercury selenium interactions in relation to histochemical staining of mercury in the rat liver.Histochem. J. 21, 89–98.
Basson, A. B., Terblanche, S. E. &Oelofsen, W. (1982) A comparative study on the effects of ageing and training on the levels of lipofuscin in various tissues of the rat.Comp. Biochem. Physiol. A. 71, 369–74.
Beregi, E. &Regius, O. (1983) Lipofuscin in lymphocytes and plasma cells in aging.Arch. Gerontol. Geriatr. 2, 229–35.
Carmichael, N. G. &Fowler, B. A. (1980) Effects of separate and combined chronic mercuric chloride and sodium selenate administration in rat: histological, ultrastructural, and x-ray microanalytic studies of liver and kidney.J. Environ. Pathol. Toxicol. 3, 399–412.
Christensen, M., Mogensen, S. C. &Rungby, J. (1988) Toxicity and ultrastructural localization of mercuric chloride in cultured murine macrophages.Arch. Toxicol. 62, 440–6.
Christensen, M., Rungby, J. &Mogensen, S. C. (1989) Effects of selenium on toxicity and ultrastructural localization of mercury in cultured murine macrophages.Toxicol. Lett. 47, 259–70.
Christensen, M., Ellermann Eriksen, S., Rungby, J., Mogensen, S. C. &Danscher, G. (1991) Histochemical and functional evaluation of mercuric chloride toxicity in cultured macrophages.Prog. Histochem. Cytochem. 23, 306–15.
Christensen, M. M., Ellermann Eriksen, S., Rungby, J. &Mogensen, S. C. (1993) Comparison of the interaction of methyl mercury and mercuric chloride with murine macrophages.Arch. Toxicol. 67, 205–11.
Crichton, D. N. &Shire, J. G. (1982) Genetic basis of susceptibility to splenic lipofuscinosis in mice.Genet. Res. 39, 275–85.
Danscher, G. (1981) Histochemical demonstration of heavy metals. A revised version of the sulphide silver method suitable for both light and electronmicroscopy.Histochemistry 71, 1–16.
Danscher, G. (1984) Autometallography. A new technique for light and electron microscopic visualization of metals in biological tissues (gold, silver, metal sulphides and metal selenides).Histochemistry 81, 331–5.
Danscher, G. (1991) Histochemical tracing of zinc, mercury, silver and gold.Prog. Histochem. Cytochem. 23, 273–85.
Danscher, G. &Møller-Madsen, B. (1985) Silver amplification of mercury sulfide and selenide: a histochemical method for light and electron microscopic localization of mercury in tissue.J. Histochem. Cytochem. 33, 219–28.
Ellerman Eriksen, S., Christensen, M. M. &Mogensen, S. C. (1994) Effect of mercuric chloride on macrophage-mediated resistance mechanisms against infection with herpes simplex virus type 2.Toxicology 93, 269–87.
Foulkes, E. C. (1991) Nature of Cd and Hg effects on epithelial amino acid transportin vivo and role of chelators.Toxicology 69, 177–85.
Fowler, B. A., Brown, H. W., Lucier, G. W. &Beard, M. E. (1974) Mercury uptake by renal lysosomes (+MetHg art) of rats ingesting methyl mercury hydroxide.Arch. Pathol. 98, 297–301.
Gainer, J. H. (1977) Effects of heavy metals and the deficiency of zinc on mortality rates in mice infected with encephalomyocarditis virus.Am. J. Vet. Res. 38, 669–72.
Graham, J. A., Gardner, D. E., Waters, M. D. &Coffin, D. L. (1975) Effect of trace metals on phagocytosis by alveolar macrophages.Infect. Immun. 11, 1278–83.
Hendriks, H. R. &Eestermans, I. L. (1986) Phagocytosis and lipofuscin accumulation in lymph node macrophages.Mechan. Ageing Dev. 35, 161–7.
Ikeda, H., Tauchi, H. &Sato, T. (1985) Fine structural analysis of lipofuscin in various tissues of rats of different ages.Mechan. Ageing Dev. 33, 77–93.
Klein, R., Herman, S. P., Brubaker, P. E., Lucier, G. W. &Krigman, M. R. (1972) A model of acute methyl mercury intoxication in rats.Arch. Pathol. 93, 408–18.
Koller, L. D. (1975) Methylmercury: effect on oncogenic and nononcogenic viruses in mice.Am. J. Vet. Res. 36, 1501–4.
Laschi-Loquerie, A., Eyraud, A., Morisset, D., Sanou, A., Tachon, P., Veysseyre, C. &Descotes, J. (1987) Influence of heavy metals on the resistance of mice toward infection.Immunopharmacol. Immunotoxicol. 9, 235–41.
Loose, L. D., Silkworth, J. B. &Warrington, D. (1977) Cadmium-induced depression of the respiratory burst in mouse pulmonary alveolar macrophages, pertioneal macrophages and polymorphonuclear neutrophils.Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 79(1), 326–32.
Madsen, K. M. &Christensen, E. I. (1978) Effects of mercury on lysosomal protein digestion in the kidney proximal tubule.Lab. Invest. 38(2), 165–74.
Mehra, M. &Kanwar, K. C. (1984) Clearance of parenterally administered 203Hg from the mouse tissues.Jepto 5–4/5, 127–30.
Mogensen, S. C. (1977) Role of macrophages in hepatitis induced by herpes simplex virus types 1 and 2 in mice.Infect. Immun. 15, 686–91.
Mogensen, S. C. &Virelizier, J.-L. (1987) The interferon-macrophage alliance.Interferon 8, 55–84.
Møller-Madsen, B. (1990) Localization of mercury in CNS of the rat. II Intraperitoneal injection of methylmercuric chloride and mercuric chloride.Toxicol. Appl. Pharmacol. 103, 303–23.
Møller-Madsen, B. (1992) Localization of mercury in CNS of the rat V. Inhalation exposure to metallic mercury.Arch. Toxicol. 66, 79–89.
Møller-Madsen, B. &Danscher, G. (1991) Localization of mercury in CNS of the rat.Toxicol. Appl. Pharmacol. 108, 457–73.
Nicholson, J. K., Osborn, D. &Kendall, M. D. (1984) Comparative distributions of zinc, cadmium and mercury in the tissues of experimental mice.Comp. Biochem. Physiol. B 77, 249–56.
Nielsen, J. B. &Andersen, O. (1990) Disposition and retention of mercuric chloride in mice after oral and parental administration.J. Trace Elem. Electrolytes Health Dis. 30, 167–80.
Norseth, T. &Brendeford, M. (1971) Intracellular distribution of inorganic and organic mercury in rat liver after exposure to methylmercury salts.Biochem. Pharmacol. 20, 1101–7.
Nørgaard, J. O., Ernst, E. &Juhl, S. (1994) Efficiency of autometallographic detection of mercury in the rat kidney.Histochem. J. 26, 100–2.
Nørgaard, J. O., Møller-Madsen, B., Hertel, N. &Danscher, G. (1989) Silver enhancement of tissue mercury: demonstration of mercury in autometallographic silver grains from rat kidneys.J. Histochem. Cytochem. 37, 1545–7.
Planas-Bohne, F., Taylor, D. M. &Walser, R. (1985) The influence of administered mass on the subcellular distribution and binding of mercury in rat liver and kidney.Arch. Toxicol. 56, 242–6.
Schiønning, J. &Møller-Madsen, B. (1991) Autometallographic mapping of mercury deposits in the spinal cord of rats treated with inorganic mercury.Acta Neuropathol. Berl. 81, 434–42.
Schiønning, J., Møller-Mädsen, B. &Danscher, G. (1991a) Mercury in the dorsal root ganglia of rats treated with inorganic or organic mercury.Environ. Res. 56, 48–56.
Schiønning, J. D., Poulsen, E. H., Møller-Madsen, B. &Danscher, G. (1991b) Ultrastructural localization of mercury in rat dorsal root ganglia after exposure to mercury vapor.Prog. Histochem. Cytochem. 23, 249–55.
Sin, Y. M., Lim, Y. F. &Wong, M. K. (1983) Uptake and distribution of mercury in mice from ingesting soluble and insoluble mercury compounds.Bull. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 31, 605–12.
Sin, Y. M., Wong, M. K. &Low, L. K. (1985) Effect of lead on tissue deposition of mercury in mice.Bull. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 34, 438–45.
Slaper-Cortenbach, I. C., Admiraal, L. G., Kerr, J. M., Vanleeuwen, E. F., Von-Dem-Borne, A. E. &Tetterroo, P. A. (1988) Flow-cytometric detection of terminal deoxynucleotidyl transferase and other intracellular antigens in combination with membrane antigens in acute lymphatic leukemias.Blood 72, 1639–44.
Springer, T., Galfre, G., Secher, D. S. &Milstein, C. (1979) Mac-1: a macrophage differentiation antigen identified by monoclonal antibody.Eur. J. Immunol. 9, 301–6.
Vallee, B. L. &Ulmer, D. D. (1972) Biochemical effects of mercury, cadmium and lead.Ann. Rev. Biochem. 41, 91–128.
Whittaker, S. G., Smith, D. G., Poster, J. R. &Rowland, I. R. (1990) Cytochemical localization of mercury inSaccharomyces cerevisiae treated with mercuric chloride.J. Histochem. Cytochem. 38, 823–7.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Christensen, M.M. Histochemical localization of autometallographically detectable mercury in tissues of the immune system from mice exposed to mercuric chloride. Histochem J 28, 217–225 (1996). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02331446
Received:
Revised:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02331446