Summary
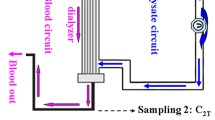
We developed a new adsorbent utilizing hydrophobic amino acids in order to treat severe rheumatoid arthritis patients with extracorporeal adsorption therapy. In in vitro experiment, the new adsorbent selectively removed immune complexes and rheumatoid factors from RA plasma presumably due to hydrophobic adsorption. Six out of elevent patients markedly improved in clinical as well as laboratory parameters of disease activities, particularly in their extra-articular manifestations. We recommend preferential use of this treatment since it can spare the replacement protein solution and is expected to give similar efficacy to simple plasma exchange therapy.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Jaffe, I.A. Comparison of the effect of plasmapheresis and penicillamine on the level of circulating rheumatoid factor. Ann Rheum Dis 1963, 22, 71–76.
Wallace, J.D., Goldfinger, D., Gatti, R., et al. Plasmapheresis and lymphoplasmapheresis in the management of rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Rheum 1979, 22, 703–710.
Jones, J.V., Bucknell, R.C., Cumming, R.M., et al. The role of therapeutic plasmapheresis in the rheumatic diseases. J Lab Clin Med 1981, 97, 589–597.
Scott, G.I.D. Baron, P.A., Bothanmley, J.E., et al. Plasma exchange in rheumatoid vasculitis. J Rheumatol 1981, 8, 433–439.
Brubaker, B.D., Winkelstein, A. Plasma exchange in rheumatoid vasculitis. Vox Sang 1981, 41, 295–301.
Wallace, J.D., Goldfinger, D., Lowe, C., et al. A double-blind, controlled study of lymphoplasmapheresis vs sham apheresis in rheumatoid arthritis. N Engl J Med 1982, 307, 1406–1410.
Shumak, K.H., Rock, G.A. Therapeutic plasma exchange. N Engl J Med 1984, 310, 762–770.
Rothwell, R.S., Davis, P., Gordon, P.A., et al. A controlled study of plasma exchange in the treatment of severe rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Rheum 1980, 23, 785–790.
Dwosh, I.L., Giles, A.R., Ford, P.M., et al. Plasmapheresis therapy in the treatment of rheumatoid arthritis, a controlled, a double-blind, crossover trial. N Engl J Med 1983, 308, 1124–1129.
Nozaki, Y., Tanford, C. The solubility of amino acids and two glycine peptides in aqueous ethanol and dioxane solutions. J Bio Chem 1971, 246, 2211–2217.
Yoshinoya, S., McDuffy, S., Alarcon-Segovia, D., et al. Detection and partial characterization of immune complexes in patients with RA plus Sjögren's syndrome and with Sjögren syndrome alone. Clin Exp Immunol 1982, 48 (2), 339–347.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Takahashi, K., Yoshinoya, S., Yoshizawa, H. et al. Extracorporeal hydrophobic amino acid adsorbent therapy in rheumatoid arthritis. Clin Rheumatol 6, 553–563 (1987). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02330593
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02330593