Abstract
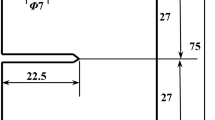
An antisymmetric test fixture is employed to investigate interlaminar fracture behavior in graphite/epoxy composite material under mixed-mode deformations. Finite correction factors for the graphite/epoxy fracture specimen with various crack lengths are used to determine the interlaminar fracture toughness by finite-element stress analysis. Interlaminar fracture characteristics of graphite/epoxy composite material under mode-I, mode-II and mixed-mode deformations are evaluated experimentally. A mixed-mode fracture criterion is also investigated to obtain information on mixedmode interlaminar fracture behavior of graphite/epoxy composite material.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Whitney, J.M., Browning, C.E. andHoogsteden, W., “A Double Cantilever Beam Test for Characterizing Mode I Delamination of Composite Materials,”J. Reinforced Composites,1,297–330 (1982).
Wilkins, D.J., Eisenmann, J.R., Camin, R.A., Margolis, W.S. and Benson, R.A., “Characterizing Delamination Growth in Graphite-Epoxy,” Damage in Composite Materials, ASTM STP 775, 168–183 (1982).
Devitt, D.F., Schapery, R.A. andBradley, W.L., “A Method for Determining the Mode I Delamination Fracture Toughness of Elastic and Viscoelastic Composite Materials,”J. Comp. Mat.,14,270–285 (1980).
Russell, A.J. and Street, K.N., “Factors Affecting the Interlaminar Fracture Energy of Graphite/Epoxy Laminates,” Progress in Science and Engineering of Composite (ICCM-IV), 279–286 (1982).
Murri, G.B. and O'Brien, T.K., “Interlaminar G IIC Evaluation of Toughened-Resin Matrix Composites using the End-Notched Flexure Test,” 26th AIAA/ASME/ASCE/AHS Structures, Structural Dynamics and Materials Conf. (1985).
Carlsson, L.A., Gillespie, J.W. Jr. andPipes, R.B., “On the Analysis and Design of the End Notched Flexure (ENF) Specimen for Mode II Testing,”J. Comp. Mat.,20,594–604 (1986).
Donaldson, S.L., “Fracture Toughness Testing of Graphite/Epoxy and Graphite/PEEK Composites,”Composites,16,103–112 (1985).
Wang, A.S.D., Kishore, N.N. and Feng, W.W., “On Mixed Mode Fracture in Off-axis Unidirectional Graphite-Epoxy Composites,” Progress in Science and Engineering of Composite (ICCM-IV), 599–606 (1982).
Banks-Sills, L., Arcan, M. andBortman, Y., “A Mixed Mode Fracture Specimen for Mode II Dominant Deformation,”Eng. Fract. Mech.,20,145–157 (1984).
Ramkumar, R.L. and Witcomb, J.D., “Characterization of Mode I and Mixed-Mode Delamination Growth in T300/5208 Graphite/Epoxy,” Delamination and Debonding of Materials, ASTM STP 876, 315–335 (1985).
Russell, A.J. and Street, K.N., “Moisture and Temperature Effects on the Mixed-Mode Delamination Fracture of Unidirectional Graphite/Epoxy,” Delamination and Debonding of Materials, ASTM STP 876, 349–370 (1985).
Banks-Sills, L., Arcan, M. andBui, H.D., “Toward a Pure Shear Specimen for K IIC Determination,”Int. J. Fract.,22,R9-R14 (1983).
Arcan, M., Hashin, Z. andVoloshin, A., “A Method to Produce Plane-Stress States with Applications to Fiber-Reinforced Materials,”Experimental Mechanics,18,141–146 (1978).
Jurf, R.A. andPipes, R.B., “Interlaminar Fracture of Composite Materials,”J. Comp. Mat.,16,386–394 (1982).
Hong, C.S. and Yoon, S.H., “Interlaminar Fracture Toughness of Graphite/Epoxy Composite under Mixed Mode Deformations,” Proc. VI Int. Cong. on Exp. Mech., Oregon (1988).
Arcan, L., Arcan, M. and Daniel, I.M., “SEM Fractography of Pure and Mixed-Mode Interlaminar Fractures in Graphite/Epoxy Composites,” Fractography of Modern Engineering Materials: Composites and Metals, ASTM STP 948, 41–67 (1987).
Sih, G.C. and Liebowitz, H., “Mathematical Theories of Brittle Fracture,” Fracture — an Advanced Treatise,II,Academic Press (1968).
Chan, S.K., Tuba, I.S. andWilson, W.K., “On the Finite Element Method in Linear Fracture Mechanics,”Eng. Fract. Mech.,2,1–17 (1970).
Hahn, H.T., “A Mixed-Mode Fracture Criterion for Composite Materials,”Comp. Tech. and Rev.,5,26–29 (1983).
Spencer, B. andBarnby, J.T., “The Effects of Notch and Fiber Angles on Crack Propagation in Fiber Reinforced Polymers,”J. Mat. Sci.,11,83–88 (1976).
Wu, E.M., “Application of Fracture Mechanics to Anisotropic Plates,”J. Appl. Mech.,34,967–974 (1967).
McKinney, J.M., “Mixed-Mode Fracture of Unidirectional Graphite/Epoxy Composites,”J. Comp. Mat.,6,164–166 (1972).
Banks-Sills, L., Arcan, M. andGabay, H., “A Mode II Fracture Specimen—Finite Element Analysis,”Eng. Fract. Mech.,19,739–750 (1984).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yoon, S.H., Hong, C.S. Interlaminar fracture toughness of graphite/epoxy composite under mixed-mode deformations. Experimental Mechanics 30, 234–239 (1990). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02322816
Received:
Revised:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02322816