Abstract
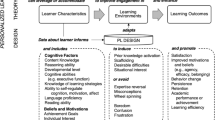
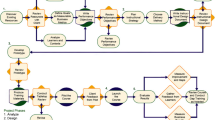
One way to better understand the difficult instructional issues associated with the integration of computer technology in classrooms is to analyze the implementation of computer technology. This study developed and validated a measure for examining the quality of implementation of an Integrated Learning System (ILS). The measure was used to analyze ILS implementation and determine if there were differences in the operational patterns of teachers implementing an ILS and identify implementation practices of teachers that indicated implementation fidelity. The measure indicated which teachers were high fidelity implementers and which implementation practices distinguished high fidelity implementers.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Albers, R. (1994). Effective change strategies: Implementation of computer-assisted instruction in elementary schools.Dissertation Abstracts Online, 55(12-A). (University Microfilms No. AAD95-14082)
Alifrangis, C. (1990, March).An integrated learning system in an elementary school: Implementation, attitudes, and results. Paper presented at the International Conference on Technology and Education, Brussels, Belgium. (ERIC Document Reproduction Service No. ED 325 100)
Alkin, M.C. (1969). Evaluation theory development.Evaluation Comment, 2(1), 2–7.
Bailey, G.D. (1993). Wanted: A road map for understanding integrated learning systems. In G.D. Bailey (Ed.),Computer-based integrated learning systems. Englewood Cliffs, NJ: Educational Technology Publications.
Bailey, G.D., & Lumley, D. (1991). Supervising teachers who use integrated learning systems: New roles for school administrators.Educational Technology.31(7), 21–24.
Becker, H.J. (1991). How computers are used in United States schools: Basic data from the 1989 I.E.A. computers in education survey.Journal of Educational Computing Research, 7(4), 385–406.
Becker, H.J. (1992). Computer-based integrated learning systems in the elementary and middle grades: A critical review and synthesis of evaluation reports.Journal of Educational Computing Research, 8(2), 1–41.
Becker, H.J. (1994). How exemplary computer-using teachers differ from other teachers: implications for realizing the potential of computers in schools.Journal of Research on Computing in Education, 26(3), 291–321.
Bender, P.V. (1991). The effectiveness of integrated computer learning systems in the elementary school.Contemporary Education, 63(1), 19–23.
Bloom, B.S. (1978). New views of the learner: Implications for instruction and curriculum.Educational Leadership, 37(7), 563–576.
Bond, E.A. (1988). Diversity of microcomputer implementations: A process perspective.Journal of Research on Computing in Education, 24(4), 321–330.
Bozeman, W.C., & House, J.E. (1988, February). Microcomputers in education: The second decade.T.H.E. Journal, 15(6), 82–86.
Bracey, G. (1991). ILS research isn't helpful.Electronic Learning, 11(1), 16.
Carroll, J.B. (1963). A model of school learning.Teachers College Record, 64, 723–733.
Cook, C.W. (1993). Factors affecting long-term implementation of integrated learning systems in elementary schools.Dissertation Abstracts Online, 54(07-A). (University Microfilms No. AAD93-35120)
Dockstader, J. (1999). Teachers of the 21st century know the what, why, and how of technology integration.T.H.E. Journal, 26(6), 73–74.
Dwyer, D., Ringstaff, C., & Sandholz, J.H. (1991). Changes in teachers' beliefs and practices in technology-rich classrooms.Educational Leadership, 48, 45–52.
Fullan, M., & Pomfret, A. (1977). Research on curriculum and instruction implementation.Review of Educational Research, 47(1), 335–397.
Gleghorn, S.R. (1993). A study of innovation configurations for integrated learning systems.Dissertation Abstracts International, 54(07-A). (University Microfilms No. AAD93-32907)
Hall, G.E., & Hord, S.M. (1984).A framework for analyzing what change facilitators do: The intervention taxonomy. Research and Development Report No. 3161. Research and Development Center for Teacher Education, University of Texas, Austin, TX.
Hall, G.E., George, A.A., & Rutherford, W.L. (1986).Measuring stages of concern about the innovation: A manual for use of the SoC questionnaire. Austin, TX: Southwest Educational Development Laboratory.
Hall, G.E., Loucks, S.F., Rutherford, W.L., & Newlove, B.W. (1975). Levels of use of the innovation: A framework for analyzing innovation adoption.Journal of Teacher Education, 26(1), 52–56.
Hall, G.E., Wallace, R.D., & Dossett, W.A. (1973).A developmental conceptualization of the adoption process within educational institutions. Austin, TX: Research and Development Center for Teacher Education, University of Texas.
Heck, S, Steigelbauer, S.M., Hall, G.E., & Loucks, S.F. (1981).Measuring innovation configurations: Procedures and applications. Austin, TX: Research and Development Center for Teacher Education, University of Texas.
Hord, S.M., & Huling-Austin, L. (1986). Effective curriculum implementation: Some promising new insights.Elementary School Journal, 87(1), 97–115.
Hord, S.M., Rutherford, W.L., Huling-Austin, L., & Hall, G.E. (1987).Taking charge of change. Alexandria, VA: ASCD Publications.
Instructional Management Handbook. (1993). Sunnyvale, CA: Computer Curriculum Corporation.
Kulik, J. (1994). Meta-analytic studies of findings on computer-based instruction. In E.L. Baker & H.F. O'Neil, Jr. (Eds.),Technology assessment in education and training. Hillsdale, NJ: Lawrence Erlbaum Associates.
Loucks, S.F. (1978).The adaptation of the Standford Research Institute Classroom Observation Instrument for use in studying teacher variations in innovation implementation. Austin, TX: Research and Development Center for Teacher Education, The University of Texas.
Loucks, S.F., Newlove, B.W., & Hall, G.E. (1976).Measuring levels of use of the innovation: A manual for trainers, interviewers, and raters. Austin, TX: Research and Development Center for Teacher Education, University of Texas.
Maddux, C.D., Johnson, L., & Harlow, S. (1993). The state of the art in computer education: Issues for discussion with teachers-in-training.Journal of Technology and Teacher Education, 1(3), 219–228.
Mageau, T. (1992). Integrating and ILS: Two teaching models that work.Electronic Learning, 11(4), 16–22.
Mills, S.C. (1994). Integrated learning systems: New technology for classrooms of the future.Tech Trends, 39(1), 27–31.
Niemiec, R.P., & Walberg, H.J. (1985). Computers and achievement in the elementary schools.Journal of Educational Computing Research, 1(4), 435–440.
Robertson, Stephens & Company (1993). Educational technology: A catalyst for change.Microcomputers for Information Management, 10(1), 3–28.
Robinson, S. (1992). Integrated learning systems: Staff development as the key to implementation.Educational Technology, 32(9), 40–43.
Sherry, M. (1990). Implementing an integrated instructional system: Critical issues.Phi Delta Kappan, 72(2), 118–120.
Shore, A., & Johnson, M.F. (1992). Integrated learning systems: A vision for the future.Educational Technology, 32(9), 36–39.
Skinner, M.E. (1990). The effects of computer-based instruction on the achievement of college students as a function of achievement status and mode of presentation.Computers in Human Behavior, 6(4), 351–360.
Smith, P.L., & Ragan, T.J. (1999).Instructional design, 2nd edition. Upper Saddle River, NJ: Prentice Hall.
Stallings, J.A. (1977, November).A study of implementation in seven follow through educational models and how instructional processes relate to child outcomes. Paper presented at the Conference on Research on Teacher Effect: An Examination by Policy-Makers and Researchers, Austin, TX.
Surry, D.W. (1997).Diffusion theory and instructional technology. Paper presented at the Annual Conference of the Association for Educational Communications and Technology, Albuquerque, NM.
Taylor, D.M. (1990).Computer based integrated learning systems in rural Alaska: An evaluation of the Jostens Learning System. Unpublished manuscript, University of Alaska, School of Education, Anchorage. (ERIC Document Reproduction Service No. ED 325 286)
Training Workbook. (1993). Sunnyvale, CA: Computer Curriculum Corporation.
Van Dusen, L.M., & Worthen, B.R. (1992). Factors that facilitate or impede implementation of integrated learning systems.Educational Technology, 32(9), 36–38.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Mills, S.C., Ragan, T.J. A tool for analyzing implementation fidelity of an integrated learning system. ETR&D 48, 21–41 (2000). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02300498
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02300498