Abstract
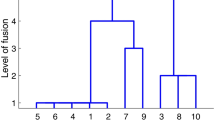
A major justification for the hierarchical clustering methods proposed by Johnson is based upon their invariance with respect to monotone increasing transformations of the original similarity measures. Several alternative procedures are presented in this paper that also share in the same property of invariance. One of these techniques constructs a hierarchy of partitions by sequentially minimizing a monotone invariant goodness-of-fit statistic; the other techniques construct a hierarchy of partitions by successively subdividing the complete set of objects until one partition class is defined for each individual member in the set. A numerical example comparing these alternative procedures with Johnson's two methods is duscussed in terms of a simplified computational scheme for obtaining the necessary hierarchies.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Cooley, W. W. and Lohnes, P. R.Multivariate data analysis. New York Wiley, 1971.
Hubert, L. Some extensions of Johnson's hierarchical clustering algorithms,Psychometrika, 1972,37, 261–274.
Johnson, S. C. Hierarchical clustering schemes,Psychometrika, 1967,32, 241–254.
Ward, J. H. Hierarchical grouping to optimize an objective function,Journal of the American Statistical Association, 1963,58, 236–244.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hubert, L. Monotone invariant clustering procedures. Psychometrika 38, 47–62 (1973). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02291173
Received:
Revised:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02291173