Abstract
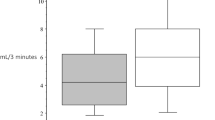
Cisapride improves reflux esophagitis and enhances esophageal acid clearance. To test the effect of cisapride on salivary production, we enrolled 14 healthy volunteers in a double-blind, randomized, placebo-controlled study. Subjects received cisapride, 10 mgper os four times a day, or placebo for three days. Saliva, collected during fasted and fed states, was analyzed for volume and buffer capacity. Buffer capacity was expressed as the volume of 0.01 N HCl needed to titrate 1 ml of saliva to pH 6.1. Both volume and buffer capacity significantly increased during the fed state as compared to the fasted on both cisapride and placebo. Cisapride significantly enhanced the postprandial salivary volume and buffer capacity compared to placebo: 29.6±11.3 ml vs 22.9±9.5 ml and 1.07±0.31 vs 0.89±0.28, respectively (P<0.0001). Cisapride's enhancement of salivary flow rate and buffer capacity in the fed state may be another mechanism by which it exerts its beneficial effect in patients with reflux esophagitis.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Corazziari E, Scopinaro F, Bontempo I, Gatti V, Liberatore M, Biliotti D, Delbuono G, Vignoni A, Torsoli A: Effect of R 51 619 on distal esophageal motor activity and gastric emptying. Gastroenterology 15:185–186, 1983
Cucchiara S, Stainano A, Boccieri A, De Stefano M, Capozzi C, Manzi G, Camberlingo F, Paone F: Effects of cisapride on parameters of oesophageal motility and on the prolonged intraoesophageal pH test in infants with gastro-oesophageal reflux disease. Gut 31:21–25, 1990
Gilbert RJ, Dodds WJ, Kahrilas PJ, Hogan WJ, Lipman S: Effect of cisapride, a new prokinetic agent, on esophageal motor function. Dig Dis Sci 33:1512–1519, 1987
McCallum RW: Cisapride: A new class of prokinetic agent. Am J Gastroenterol 36:135–149, 1991
Schuurkes JA, Van Nueten JM, Van Daele PGH, Reyntjens AJ, Janssen PA: Motor stimulating properties of cisapride on isolated gastrointestinal preparations of the guinea pig. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 234:775, 1985
Bucheit K, Buhl T: Prokinetic benzamides stimulate peristaltic activity in the isolated guinea pig ileum by activation of 5-HT4 receptors. Eur J Pharmacol 205:203–208, 1991
DeMicco M, Berenson M, Wu W, Castell D: Cisapride in the treatment of GERD: A double-blind placebo-controlled multicenter dose-response trial. Gastroenterology 102:A59, 1992
Lepoutre I, Van Der Spek P, Vanderlinden I, Bollen J, Laukens P: Healing of grade-II and III esophagitis through motility stimulation with cisapride. Digestion 45:109–114, 1990
Baldi F, Bianchi Porro G, Dobrilla G, Iascone C, Lobello R, Marzio L, Sabbatini F, Titobello A, Verme G: Cisapride versus placebo in reflux esophagitis. J Clin Gastroenterol 10:614–618, 1988
Cisapride for nocturnal heartburn. Med Lett 36:11–14, 1994
Richter JE, Long JF: Cisapride for gastroesophageal reflux disease: a placebo-controlled double blind study. Am J Gastroenterol 90:423–430, 1995
Helm JF, Dodds WJ, Riedel DR, Teeter BC, Hogan WJ, Arndorfer RC: Determinants of esophageal acid clearance in normal subjects. Gastroenterology 85:607–612, 1983
Helm JF, Dodds WJ, Pelc LR, Palmer DW, Hogan WJ, Teeter BC: Effect of esophageal emptying and saliva on clearance of acid from the esophagus. N Engl J Med 310:284–288, 1984
Sarosiek J, Feng T, McCallum RW: The interrelationship between salivary epidermal growth factor and functional integrity of the esophageal mucosal barrier in the rat. Am J Med Sci 302:359–363, 1991
Li L, Yu Z, Piascik R, Hetzel DP, Rourk RM, Namiot Z, Sarosiek J, McCallum RW: Effect of esophageal intraluminal mechanical and chemical stressors on salivary epidermal growth factor in humans. Am J Gastroenterol 88:1749–1755, 1993
Janish HD, Hutterman W, Bouzo MH: Cisapride versus ranitidine in the treatment of reflux esophagitis. Hepato-Gastroenterol 35:125–127, 1988
Galmiche JP, Fraitag B, Filocte B: A double-blind comparison of cisapride and cimetidine in the treatment of reflux esophagitis. Dig Dis Sci 35:649–655, 1990
Ceccatelli P, Janssens J, Vantrappen G, Cucchiara S: Cisapride restores the decreased lower esophageal sphincter pressure in reflux patients. Gut 29:631–635, 1988
Smout AJP, Bogaard JW, Grade AC, ten Thije OJ, Akkermans LM, Wittebol P: Effects of cisapride, a new gastrointestinal prokinetic substance, on interdigestive and postprandial motor activity of the distal esophagus in man. Gut 26:246–251, 1985
Holloway RH, Downton J, Mitchell B, Dent J: Effect of cisapride on postprandial gastro-oesophageal reflux. Gut 30:1187, 1989
Rode H, Stunden R, Millar JW, Cywes S: Esophageal pH assessment of gastroesophageal reflux in 18 patients and the effect of two prokinetic agents: Cisapride and metoclopramide. J Pediatr Surg 22:931–944, 1987
Baldi F, Ferrarini F, Longanesi A, Angeloni M, Ragazzini M, Barbara L: Effect of short-term cisapride treatment on gastroesophageal reflux disease. Prog Med 43(suppl 1):29–34, 1987
Collins BJ, Spence RAJ, Ferguson R, Laird J, Love AHG: Cisapride: Influence on oesophageal and gastric emptying and gastro-oesophageal reflux in patients with reflux oesophagitis. Hepato-Gastroenterol 34:113–116, 1987
Le Bell Y, Soderling E, Karjalainen S: Effect of repeated sampling and prestimulation on saliva buffer capacity and flow rate values in children. Scand J Dent Res 99:505–509, 1991
Kapila YV, Dodds WJ, Helm JF, Hogan WJ: Relationship between swallow rate and salivary flow. Dig Dis Sci 29:528–533, 1984
Namiot Z, Rourk RM, Piasik R, Hetzel DP, Sarosiek J, McCallum RW: Interrelationship between esophageal challenge with mechanical and chemical stimuli and salivary protective mechanisms. Am J Gastroenterol 89:581–587, 1994
Baum BJ: Principles of saliva secretion. Ann NY Acad Sci 694:17–23, 1993
Cook DI, Van Lennep EW, Roberts ML, Young JA: Secretion by the major salivary glands.In Physiology of the Gastrointestinal Tract, 3rd ed. LR Johnson (ed). New York, Raven Press, 1994, pp 1061–1117
Gifford AN, Nicholson RA, Pitman RM: The dopamine and 5-hydroxytryptamine content of locust and cockroach salivary neurones. J Exp Biol 161:405–414, 1991
Helm JF, Dodds WJ, Hogan WJ: Salivary response to esophageal acid in normal subjects and patients with reflux esophagitis. Gastroenterology 93:1393–1397, 1987
Kay RNB, Phillipson AT: Responses of the salivary glands to distension of the esophagus and rumen. J Physiol 148:507–523, 1959
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Supported by a grant from The Janssen Research Foundation.
Preliminary data from this paper have been presented at the 1994 meeting of the American Motility Society, Wintergreen, Virginia and published, in abstract form (Gastroenterology 107:1242, 1994).
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Patel, R., Launspach, J. & Soffer, E. Effects of cisapride on salivary production in normal subjects. Digest Dis Sci 41, 480–484 (1996). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02282322
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02282322