Summary
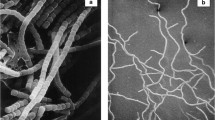
Most of theFrankia strains isolated fromAlnus andMyrica species are morphologically almost indistinguishable, when grown under standard culture conditions. They form similar vegetative hyphae while sporangia are produced in variable amounts from strain to strain.
Physiological reactions were assessed in order to compare 20 strains isolated from various species ofAlnus and one species ofMyrica in Europe and North America. Among invariant negative or positive characteristics, differences in urease, protease and β-glucosidase activities appeared to be of significant value.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Baker D 1982 A cumulative listing of isolated frankiae, the symbiotic nitrogen-fixing actinomycetes. The Actinomycetes 17, 35–42.
Baker D 1982 Serologic and host compatibility relationships among the isolated frankiae. Can. J. Bot. Unpublished manuscript.
Baker D, Pengelly W L and Torrey J G 1981 Immunochemical analysis of relationships among isolated frankiae (Actinomycetales). Int. J. Syst. Bacteriol. 31, 148–151.
Chaloupka J, Severin A I, Sastry K J, Kucerova H and Strnadova M 1982 Differences in the regulation of exocellular proteinase synthesis during growth and sporogenesis ofBacillus megaterium. Can. J. Microbiol. 28, 1214–1218.
Goodfellow M and Pirouz T 1982 Numerical classification of sporoactinomycetes containing meso-diaminopimelic acid in the cell wall. J. Gen. Microbiol. 128, 503–527.
Lalonde M and Calvert H E 1979 Production ofFrankia hyphae and spores as infective inoculant forAlnus species.In Symbiotic Nitrogen Fixation in the Management of temperate Forests. Eds. J C Gordon et al. Oregon State university, Corvallis, pp 95–110.
Lechevalier M P, Baker D and Horrière F 1983 Physiology, chemistry, serology and infectivity of two Frankia isolates fromAlnus incana subsp.rugosa. Can. J. Bot. 61, 2826–2833.
Lechevalier M P, Horrière F and Lechevalier H 1982 The biology of Frankia and related organisms. Develop. Indust. Microbiol. 23, 51–60.
Lechevalier M P and Lechevalier H A 1979 The taxonomic position of the actinomycetic endophytes.In Symbiotic Nitrogen Fixation in the Management of temperate Forests. Ed. J C Gordon et al. Oregon State University, Corvallis, pp 111–122.
Le Minor L and Piéchaud M 1963 Une méthode rapide de recherche de la proteolyse de la gélatine. Ann. Inst. Pasteur 105, 792–794.
Scharfen J 1973 Urease as a useful criterion in the classification of microaerophilic actinomycetes. Zbl. Bakt. Hyg., 1. Abt. Orig. A 225, 89–94.
Schofield G M and Schaal K P 1980 Rapid micromethods for detecting deamination and decarboxylation of aminoacids, indole production, and reduction of nitrate and nitrite by facultatively anaerobic actinomycetes. Zbl. Bakt. Hyg., 1. Abt. Orig. A 247, 383–391.
Schofield G M and Schaal K P 1981 A numerical taxonomic study of members of the Actinomycetaceae and related taxa. J. Gen. Microbiol. 127, 237–259.
Stuart C A, van Stratum E and Rustignan R 1945 Further studies on urease production by Proteus and related organisms. J. Bacteriol. 49, 437–444.
Wikström M B 1983 Detection of microbial proteolytic activity by a cultivation plate assay in which different proteins absorbed to a hydrophobic surface are used as substrates. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 45, 393–400.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Horrière, F. In vitro physiological approach to classification ofFrankia isolates of ‘the Alnus group’, based on urease, protease and β-glucosidase activities. Plant Soil 78, 7–13 (1984). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02277835
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02277835