Summary
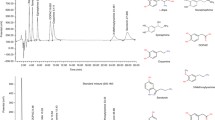
A validated reversed-phase high-performance liquid chromatographic procedure employing electrochemical detection (LCEC) for the analysis of carbidopa and levodopa in human plasma is reported. The method is sensitive and specific with amperometric detection at a glassy carbon working electrode with Eapp=0.75 V vs. Ag/AgCl. The retention times of levodopa, internal standard, and carbidopa are 3.3, 4.5, and 9.7 minutes, respectively, with an overall chromatographic run time of 12.0 minutes. The peak height ratio versus plasma concentration is linear over the range of 5.0 to 500 ng/mL for each analyte and exhibits correlation coefficients of 0.9957 or better (n=9). The mean absolute recovery of carbidopa and levodopa using the described assay is 36.6 and 66.0%, respectively. The inter- and intra-day accuracy and precision are within 11.8% of the actual values for all concentrations. Also, due to the demonstrated instability of carbidopa and levodopa in plasma a procedure is provided to circumvent this. Blood collected in pre-treated Vacutainer tubes can be stored in an ice bath for up to 4 hours without any significant degradation, thereby providing a practical means for processing several clinical samples simultaneously.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
R. M. Riggin, R. L. Alcorn, P. T. Kissinger, Clin. Chem.,22, 782 (1976).
I. Merits, D. J. Anderson, R. C. Sonders, Drug. Metab. Dispos.,1, 69 (1973).
R. L. Falck, Drug Intell. Clin. Pharm.,10, 84 (1976).
L. Rentzhog, Acta Physiol. Scand.,377, 1 (1972).
J. M. Holly, H. L. Makin, Anal. Biochem.,128, 257 (1983).
A. M. Krstulovic, Adv. Chromatogr.,17, 279 (1979).
L. A. Rihbany, M. F. Delaney, J. Chromatogr.,248, 125 (1982).
C. Lucarelli, P. Betto, G. Ricciarello, M. Giambenedetti, C. Corradini, F. Stocchi, F. Belliardo, J. Chromatogr.,511, 167 (1960).
D. C. Titus, T. F. August, K. C. Yeh, R. Eisenhandler, W. F. Bayne, D. G. Musson, J. Chromatogr.,534, 87 (1990).
T. Wikberg, J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal.9, 167 (1991).
Y. Michotte, M. Moors, D. Deleu, P. Herregodts, G. Ebinger, J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal.7, 659 (1987).
P. Y. T. Lin, M. C. Bulawa, P. Wong, L. Lin, J. Scott, C. L. Blank, J. Liq. Chromatogr.,7, 509 (1984).
P. T. Kissinger, J. Chromatogr.,488, 31 (1989).
S. Kaakkola, P. T. Männistö, E. Nissinen, A. Vuorela, R. Mäntylä, Acta Neurol. Scand.,72, 385 (1985).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Miller, R.B., Dehelean, L. & Bélanger, L. Determination of carbidopa and levodopa in human plasma by high-performance liquid chromatography with electrochemical detection. Chromatographia 35, 607–612 (1993). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02267924
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02267924