Summary
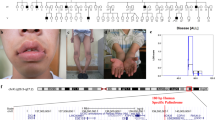
During a systematic chromosomal survey of 167 unrelated boys with the X-linked recessive Menkes disease (MIM 309400), a unique rearrangement of the X chromosome was detected, involving an insertion of the long arm segment Xq13.3-q21.2 into the short arm at band Xp11.4, giving the karyotype 46,XY,ins(X) (p11.4q13.3q21.2). The same rearranged X chromosome was present de novo in the subject's phenotypically normal mother, where it was preferentially inactivated. The restriction fragment length polymorphism and methylation patterns at DXS255 indicated that the rearrangement originated from the maternal grandfather. Together with a previously described X;autosomal translocation in a female Menkes patient, the present finding supports the localization of the Menkes locus (MNK) to Xq13, with a suggested fine mapping to sub-band Xq13.3. This localization is compatible with linkage data in both man and mouse. The chromosomal bend associated with the X-inactivation center (XIC) was present on the proximal long arm of the rearranged X chromosome, in line with a location of XIC proximal to MNK. Combined data suggest the following order: Xcen-XIST(XIC), DXS128-DXS171, DXS56-MNK-PGK1-Xqter.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bodrug SE, Roberson JR, Weiss L, Ray PN, Worton RG, Van Dyke DL (1990) Prenatal identification of a girl with a t(X;4) (p21;q35) translocation: molecular characterisation, paternal origin, and association with muscular dystrophy. J Med Genet 27:426–432
Boyd Y, Fraser NJ (1990) Methylation patterns at the hypervariable X-chromosome locus DXS255 (M27ß): correlation with X-inactivation status. Genomics 7:182–187
Brown CJ, Ballabio A, Rupert JL, Lafreniere RG, Grompe M, Tonlorenzi R, Willard HF (1991a) A gene from the region of the human X inactivation centre is expressed exclusively from the inactive X chromosome. Nature 349:38–44
Brown CJ, Lafreniere RG, Powers VE, Sebastio G, Ballabio A, Pettigrew AL, Ledbetter DH, Levy E, Craig I., Willard HF (1991b) Localization of the X inactivation center on the human X chromosome in Xq13. Nature 349:82–84
Chamberlin J, Magenis RE (1980) Parental origin of de novo chromosome rearrangements. Hum Genet 53:343–347
Couturier J, Dutrillaux B, Lejeune J (1973) Étude des fluorescences spécifiques des bandes R et des bandes Q des chromosomes humains. CR Acad Sci [Ser D] 276:339–342
Danks DM (1989) Hereditary disorders of copper metabolism in Wilson's disease and Menkes' disease. In: Scriver JR, Beaudet AL, Sly WS, Valle D (eds) The metabolic basis of inherited disease, 6th edn. McGraw-Hill, New-York, pp 1422–1431
Davisson MT (1987) Review: X-linked genetic homologies between mouse and man. Genomics 1:213–227
Flejter WL, Van Dyke DL, Weiss L (1984) Bends in human mitotic metaphase chromosomes, including a bend marking the X-inactivation center. Am J Hum Genet 36:218–226
Feinberg AP, Vogelstein B (1983) A technique for radiolabeling DNA restriction endonuclease fragments to high activity. Anal Biochem 132:6–13
Gerdes A-M, Tønnesen T, Pergament E, Sander C, Baerlocher KE, Wartha R, Güttler F, Horn N (1988) Variability in clinical expression of Menkes syndrome. Eur J Pediatr 148:132–135
Horn N (1984) Copper metabolism in Menkes' disease. In: Rennert OM, Chan W-Y (eds) Metabolism of trace metals in man. CRC Press, Boca Raton, Fla, pp 25–52
Horn N, Stene J, Mollekaer AM, Friedrich U (1984) Linkage studies in Menkes disease: the Xg blood group system and C-banding of the X chromosome. Ann Hum Genet 48:161–172
Huebner K, Isobe M, Gasson JI, Golde DW, Croce CM (1986) Localization of the gene encoding human erythroid-potentiating activity to chromosome region Xp11.1→Xp11.4. Am J Hum Genet 38:819–826
Ikeuchi T (1984) Inhibitory effect of ethidium bromide on mitotic chromosome condensation and its application to high-resolution chromosome banding. Cytogenet Cell Genet 38:56–61
Kapur S, Higgins JV, Delp K, Rogers B (1987) Menkes syndrome in a girl with X-autosome translocation. Am J Med Genet 26:503–510
Latt SA Willard HF, Gerald PS (1976) BrdU-33258 Hoechst analysis of DNA replication in human lymphocytes with supernumerary or structurally abnormal X chromosomes. Chromosome 57:135–153
Martin NJ, Cartwright DW, Harvey PJ (1985) Duplication 5q (5q22→5q33): from an intrachromosomal insertion. Am J Med Genet 20:57–62
Menkes JH, Alter M, Steigleder G, Weakley DR, Sung JH (1962) A sex-linked recessive disorder with retardation of growth, peculiar hair and focal cerebral and cerebellar degeneration. Pediatrics 29:764
Olson SB, Magenis RE (1988) Preferential paternal origin of de novo structural chromosome rearrangements. In: Daniels A (ed) The cytogenetics of mammalian autosomal rearrangements. Liss, New York, pp 583–599
Robinson D, Boyd Y, Collinson M, Jacobs P (1991) Determination of the parental origin of X;autosome translocations by M27ß methylation analysis. J Med Genet 28:63–64
Tønnesen T, Gerdes AM, Horn N, Friedrich U, Grisar T, Muller A (1986) Localization of the Menkes gene to the long arm of the X-chromosome (abstract). 7th Int Cong Hum Genet, Berlin 1986, p 627
Tønnesen T, Horn N (1989) Prenatal and postnatal diagnosis of Menkes disease, an inherited disorder of copper metabolism. J Inherited Metab Dis 12 [Suppl 1]:207–214
Verga V, Hall BK, Wang S, Johnson S, Higgins JV, Glover TW (1991) Localization of the translocation breakpoint in a female with Menkes syndrome to Xq13.2-q13.3 proximal to PGK-1. Am J Hum Genet 48:1133–1138
Wienker TF, Wieacker P, Cooke HJ, Horn N, Ropers H-H (1983) Evidence that Menkes locus maps on proximal Xp. Hum Genet 65:72–73
Willard HF, Goss SJ, Holmes MT, Munroe DL (1985) Regional localization of the phosphoglycerate kinase gene and pseudogene on the human X chromosome and assignment of a related DNA sequence to chromosome 19. Hum Genet 71:138–143
Willard HF, Durfy SJ, Mahtani MM, Dorkins H, Davies KE, Williams BRG (1989) Regional localization of the TIMP gene on the human X chromosome: extension of a conserved synteny and linkage group on proximal Xp. Hum Genet 81:234–238
Yang H-M, Lund T, Niebuhr E, Nørby S, Schwartz M, Shen L (1990) Exclusion mapping of 12 X-linked disease loci and 10 DNA probes from the long arm of the X-chromosome. Clin Genet 38:94–104
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Tümer, Z., Tommerup, N., Tønnesen, T. et al. Mapping of the Menkes locus to Xq13.3 distal to the X-inactivation center by an intrachromosomal insertion of the segment Xq13.3-q21.2. Hum Genet 88, 668–672 (1992). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02265295
Received:
Revised:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02265295