Abstract
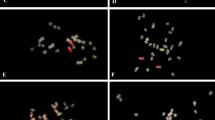
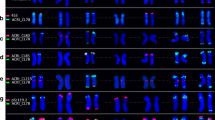
The genetic relationships between several wild species and subspecies of the genusHordeum were assessed using fluorescencein situ hybridization (FISH). Plant material included natural populations of wild barley growing in Spain of the annual species,H. marinum ssp.marinum (2n=14) andgussoneanum (2n=14), andH. murinum ssp.murinum (2n=28), andleporinum (2n=28) and the perennial speciesH. bulbosum (2n=14) andH. secalinum (2n=28), plus the South American perennial speciesH. chilense (2n=14). FISH was used to locate the chromosomal sites of two rDNA multigene families 5S and 18S–26S (pTa71 and pTa794) and three repetitive DNA sequences (pSc119.2, pAs1 and pHch950) isolated from different species and genera. The seven chromosomes of the diploid species were readily distinguished by their external morphology and hybridization patterns to pTa71, pTa794, pSc119.2 and pAs1. These DNA probes were also useful for the identification of homologous chromosomes and in differentiating these from unidentified chromosomes in the tetraploid taxa. The use of the probe pHch950 permitted intergenomic differentiation in tetraploids and supports the diphyletic origin ofH. murinum andH. secalinum. Thein situ experiments yielded the following conclusions: (1) differences between the subspeciesmarinum andgussoneanum; (2) close relationships between the subspeciesmurinum andLeporinum; and (3) major differences in physical mapping betweenH. bulbosum and the remaining taxa. The genomic and phylogenetic relationships between taxa, as inferred from the results, are discussed.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Anamthwat-Jónsson K, Heslop-Harrison JS (1993) Isolation and characterization of genome-specific DNA sequences in Triticeae species.Mol Gen Genet 240: 151–158.
Bedbrook JR, Jones J, O'Neill M, Thompson RD, Flavell RB (1980) A molecular description of telomeric heterochromatin inSecale species.Cell,19: 545–560.
Bernardo A, Montero M, Cuadrado A, Jouve N (1992). Image analysis of C-banded chromosomes and pairing regionalization in wheat.Genome 35: 1062–1067.
Bothmer R, Jacobsen N (1985) Origin, taxonomy and related species. In: Rasmusson, D, ed.Barley. Agronomy Monograph No. 26, ASA, pp 19–26.
Bothmer R, Flink J, Landström T (1986) Meiosis inHordeum interspecific hybrids. I. Diploid combinations.Can J Genet Cytol 28: 525–535.
Bothmer R, Flink J, Landström T (1987) Meiosis inHordeum interspecific hybrids. II. Triploid combinations.Evol Trend Plants 1: 41–50.
Bothmer R, Flink J, Landström T (1988) Meiosis in interspecificHordeum hybrids. IV. Tetraploid (4x 4x) hybrids.Genome 30: 47–485.
Bothmer R, Flink J, Jacobsen N, Jorgensen RB (1989) Variation and differentiation inHordeum marinum (Poaceae).Nord J Bot 9: 1–10.
Bothmer R, Jacobsen N, Baden C, Jorgensen RB, Linde-Laursen I (1991). AnEcogeographical Study of the Genus Hordeum. Systematic and Ecogeographic Studies on Crop Genepools. IBPGR: Rome.
Cabrera A, Friebe B, Jiang J, Gill BS (1995) Characterization ofHordeum chilense chromosomes by C-banding andin situ hybridization using highly repeated DNA probes.Genome 38: 435–442.
Castilho A, Heslop-Harrison JS (1995) Physical mapping of 5S and 18S26S rDNA and repetitive DNA sequences inAegilops umbellulata.Genome 38: 91–96.
Covas G (1949) Taxonomic observations on the North American species ofHordeum.Madroño 10: 1–21.
Cuadrado A, Jouve N (1994) Mapping and organization of highly-repeated DNA sequences by means of simultaneous and sequential FISH and C-banding in 6x-Triticale.Chrom Res 2: 231–338.
Cuadrado A, Jouve N (1995) Fluorescencein situ hybridization and C-banding analyses of highly repetitive DNA sequences in the heterochromatin of rye (Secale montanum Guss) and wheat incorporatingS. montanum chromosome segments.Genome 38: 795–802
Cuadrado A, Ceoloni C, Jouve N (1995) Variation in highly repetitive DNA composition of heterochromatin in rye studied by FISH.Genome 38: 1061–1069.
Doebley, J, Bothmer R von, Larson S (1992) Chloroplast DNA variation and the phylogeny ofHordeum (Poaceae).Am J Bot 79: 576–584.
Fernández JA, Jouve N (1984) Giemsa C-banding of the chromosomes ofHordeum chilense and its amphiploid ×Triticum turgidum conv.durum.Z. Pflanzenzüchtg 93: 212–221.
Ferrer E, Loarce Y, Hueros G (1995) Molecular characterization and chromosome location of repeated DNA sequences inHordeum species and in the amphiploid tritordeum (×Tritodeum Ascherson et Graebner).Genome 38: 850–857.
Gerlach WL, Bedbrook JR (1979) Cloning and characterization of ribosomal RNA genes from wheat and barley.Nucleic Acid Res 7: 1869–1885.
Gerlach WL, Dyer TA (1980) Sequence organization of the repeating units in the nucleus of wheat which contain 5S rRNA genes.Nucleic Acid Res 8: 4851–4865.
Gupta PK, Fedak G, Molnar SJ, Wheatcroft R (1989) Distribution of aSecale cereale sequence among 25Hordeum species.Genome 32: 383–388.
Heslop-Harrison JS, Schwarzacher T, Anamthwat-Jónsson K, Leitch AR, Shi M, Leitch IJ. (1991)In situ hybridization with automated chromosome denaturation.J Methods Cell Mol Biol 3: 109–116.
Hueros G, Loarce Y, Ferrer E (1993) A structural and evolutionary analysis of a dispersed repetitive sequence.Plant Mol Genet 22: 635–643.
Jaaska V, Jaaska V (1986) Isozyme variation in the barley genus Hordeum L. 1. Alcohol dehydrogenase and superoxide dismutase.Biochem Physiol Pflanzen 181: 301–320.
Jacobsen N, Bothmer R (1992) Supraspecific groups in the genusHordeum.Hereditas 116: 21–24.
Jones JDG, Flavell, RB (1982) The structure, amount and chromosomal location of defined repeated sequences in species of the genusSecale.Chromosoma 86: 613–641.
Jorgensen RB (1986) Relationships in the barley genus (Hordeum): and electrophoretic examination of proteins.Hereditas 104: 273–291.
Kasha KJ, Sadasivaiah RS (1971) Genome relationships betweenHordeum vulgare L. andH. bulbosum L.Chromosoma 35: 264–287.
Lapitan NLV, Gill BS, Sears RG (1987) Genomic and phylogenetic relationships among rye and perennial speices in the Triticeae.Crop Sci 27: 682–687.
Leitch IJ, Heslop-Harrison JS (1992) Physical mapping of the 18S-5.8S-26S rRNA genes in barley byin situ hybridization.Genome 35: 1013–1018.
Leitch IJ, Heslop-Harrison JS (1993) Physical mapping of four sites of 5S rDNA sequences and one site of theamylase-2 gene in barley (Hordeum vulgare).Genome 36: 517–523.
Leitch, IJ, Leitch AR, Heslop-Harrison JS (1991) Physical mapping of plant DNA sequences by simultaneousin situ hybridization of two differently labelled fluorescent probes.Genome 34: 329–333.
Linde-Laursen I, Bothmer R, Jacobsen N (1986) Giemsa C-banded karyotypes ofHordeum secalinum, H. capense and their interspecific hybrids withH. vulgare.Hereditas 105: 179–185.
Linde-Laursen I, Bothmer R, Jacobsen N (1989) Giemsa C-banded karyotypes ofHordeum marinum, andH. murinum.Genome 32: 629–639.
Linde-Laursen I, Bothmer R, Jacobsen N (1990) Giemsa C-banded karyotypes of diploid and tetraploidHordeum bulbosum (Poaceae).Plant Syst Evol 172: 141–150
Linde-Laursen I, Ibsen E, Bothmer R von, Giese H (1992a) Physical localization of active and inactive rRNA gene loci inHordeum marinum ssp.gussoneanum (4x) by in situ hybridization.Genome 35: 1032–1036.
Linde-Laursen I, Bothmer R von, Jacobsen N (1992b). Relationships in the genusHordeum: Giemsa C-banded karyotypes.Hereditas 116: 111–116.
McIntyre CL, Clarke BC, Apples R (1988) Amplification and dispersion of repeated DNA sequences in the Triticeae.Plant Syst Evol 160: 39–59.
McIntyre CL, Pereira S, Moran LB, Appels R (1990) NewSecale cereale (rye) DNA derivatives for the detection of rye chromosome segments in wheat.Genome 33: 635–640.
Molnar SJ, Gupta PK, Fedak G, Wheatcroft R (1989) Ribosomal DNA repeat unit polymorphism in 25 Hordeum species.Theor Appl Genet 78: 387–392.
Molnar SJ, Wheatcroft R, Fedak G (1992) RFLP analysis ofHordeum species relationships.Hereditas 116: 87–91.
Monte JV, McIntyre CL, Gustafson JP (1993) Analysis of phylogenetic relationships in the Triticeae tribe using RFLPs.Theor Appl Genet 86: 649–655.
Morrison JW (1958) Hordeum murinum in Holland.Acta Bot Neerl 3: 654–664.
Mukai Y, Endo TR, Gill BS (1990) Physical mapping of the 5S rRNA multigene family in common wheat.J Hered 81: 290–295.
Mukai Y, Endo TR, Gill BS. (1991) Physical mapping of the 18S.26S rRNA multigene family in common wheat: identification of a new locus.Chromosoma 100: 71–78.
Mukai Y, Nakahara Y, Yamamoto M (1993) Simultaneous discrimination of the three genomes in hexaploid wheat by multicolor fluorescencein situ hybridization using total genomic and highly repeated DNA probes.Genome 36: 489–494.
Nevski SA (1941) Beiträge zur Kenntnis der wildwachsenden Gersten in Zusammenhang mit der Frage über den Ursprung vonHordeum vulgare 1. (Versuch einer Monographie der GattungHordeum) (in Russian).Acta Inst Botnum V L. Komarovii Acad Sci USSR Sec 1, Fasc5: 64–255.
Orgaard M, Heslop-Harrison JS (1994) Relationships between species of Leymus, Psathyrostachys andHordeum (Poaceae, Tritidceae) inferred from Southern hybridization of genomic DNA and cloned DNA probes.Plant Syst Evol 189: 217–231.
Pedersen C, Linde-Laursen I (1994) Chromosomal locations of four minor rDNA loci and a marker microsatellite sequence in barley.Chrom Res 2: 65–71.
Rajhathy T, Morrison JW (1962) Cytogenetic studies in the genus Hordeum. VI. Themurinum complex.Can J Genet Cytol 4: 240–247.
Rayburn AL, Gill BS (1985) Use of biotin-labelled probes to map specific DNA sequences on wheat chromosomes.J Hered 76: 78–81.
Shcherban AB, Vershinin AV (1992) The stretched BamHI-fragment of barley genome containing richly repetitive DNA sequences.Genetika 28: 15–21
Svitashev S, Bryngelsson T, Vershinin A, Pedersen C, Säll T, von Bothmer R (1994) Phylogenetic analysis of the genusHordeum using repetitive DNA sequences.Theor Appl Genet 89: 801–810.
Symeonidis L, Moustakas M (1986) Biosystematic study of the Hordeum murinum group in Greece.Flora 178: 177–182.
Tercero JA, Bernardo A, Jouve N (1991) Encoding genes for endosperm proteins inHordeum chilense.Theor Appl Genet 81: 127–132.
Vershinin AV, Salina EA, Solovyov VV, Timofeeva LL (1990) Genomic organization, evolution, and structural peculiarities of highly repetitive DNA ofHordeum vulgare.Genome 33: 441–449
Vershinin AV, Svitashev SK, Gummesson PO, Salomon B, von Bothmer R, Bryngelsson T (1994) Characterization of a family of tandemly repeated DNA sequences in Triticeae.Theor Appl Genet 89: 217–225
Vosa CG (1976) Chromosome banding patterns in cultivated and wild barleys (Hordeum spp).Heredity 37: 395–403.
Xu J, Procunier JD, Kasha KJ (1990) Species-specificin situ hybridization ofHordeum bulbosum chromosomes.Genome 33: 628–634.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
accepted by J.S. (Pat) Heslop-Harrison
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
de Bustos, A., Cuadrado, A., Soler, C. et al. Physical mapping of repetitive DNA sequences and 5S and 18S–26S rDNA in five wild species of the genusHordeum . Chromosome Res 4, 491–499 (1996). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02261776
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02261776