Summary
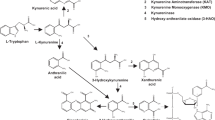
We studied changes in the concentrations of serotonin (5-HT), kynurenine, and other indoleamines in the cerebrospinal fluid of patients with Alzheimer type dementia (ATD) and those with Binswanger type vascular dementia (VDBT), and changes in these indoleamine concentrations 2 weeks after administration of citalopram, a 5-HT uptake inhibitor. The concentrations of total 5-HT (p<0.005) and kynurenine (p<0.005) were significantly decreased in ATD patients in comparison to those of the controls. After citalopram administration, there was a remarkable increase in 5-HT concentration (249%, p<0.0001) and a significant decrease in 5-HIAA concentration (22%, p<0.02). In the VDBT patients, only 5-HT showed a significant decrease (p<0.005) in comparison to the control values. It also increased significantly (214%) after citalopram administration. The 5-HT/tryptophan and kynurenine/tryptophan ratios were not correlated for the controls, but did significantly for the ATD and VDBT patients; after citalopram treatment, the increase in 5-HT/tryptophan was correlated significantly with that of kynurenine/tryptophan for ATD, but not for VDBT. These results suggest that both the serotonin and kynurenine pathways are impaired in ATD; whereas, the serotonin pathway alone is in VDBT, and that these impairments are ameliorated by the administration of citalopram.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
American Psychiatric Association (1987) Diagnostic and statistical manual of mental disorders, 3rd ed revised. APA, Washington DC, pp 21–23
Arai H, Kosaka K, Iizuka R (1984) Changes of biogenic, amines and their metabolites in postmortem brains from patients with Alzheimer-type dementia. J Neurochem 43: 388–393
Argentiero V, Tavolato B (1980) Dopamine (DA) and serotonin metabolic levels in the cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) in Alzheimer's presenile dementia under basic conditions and after stimulation with cerebral cortex phospholipids (BC-PL). J Neurol 224: 53–58
Bareggi SR, Franceschi M, Bonini L, Zecca L, Smirne S (1982) Decreased CSF concentrations of homovanillic acid and aminobutyric acid in Alzheimer's disease. Arch Neurol 39: 709–712
Baker PC, Goodrich CA (1982) The effects of the specific uptake inhibitor Lu 10-171 (citalopram) upon brain indoleamine stores in the maturing mouse. Gen Pharmacol 13: 59–61
Bulat M, Zivkovic B (1971) Origin of 5-hydroxyindoleacetic acid in the spinal fluid. Science 173: 738–740
Carlsson A, Lindqvist M (1978) Effects of antidepressant agents on the synthesis of brain monoamines. J Neural Transm 43: 73–91
Carlsson A, Adolfsson R, Aquilonius SM, Gottfries CG, Oreland L, Svennerholm L Winblad B (1980) Biogenic amines in human brain in normal aging, senile dementia, and chronic alcoholism. Adv Biochem Pharmacol 23: 295–304
Duncan GE, Little KY, Kirkman JA, Kaldas RS, Stumpf WE, Breese GR (1992) Autoradiographic characterization of [3H] imipramine and [3H] citalopram binding in rat and human brain: species differences and relationships to serotonin innervation patterns. Brain Res 591: 181–197
Fernstrom JD, Wurtman RJ (1971) Brain serotonin content: physiological dependence on plasma tryptophan levels. Science 173: 149–152
Folstein MF, Folstein SE, McHugh PR (1975) “Mini-Mental State”. A practical method of grading. The cognitive state of patients for the clinician. J Psychiatr Res 12: 189–198
Forsell LG, Eklöf R, Winblad B (1989) Early stages of late onset Alzheimer's disease. II. Derangements in protein metabolism with special reference to tryptophan, tyrosine and cystine. Acta Neurol Scand 79 [Suppl 121]: 27–42
Gottfries CG (1982) The metabolism of some neurotransmitters in ageing and dementia disorders. Gerontology 28 [Suppl 2]: 11–19
Gottfries CG (1990) Brain monoamines and their metabolites in dementia. Acta Neurol Scand [Suppl] 129: 8–11
Gottfries CG (1990) Disturbance of the 5-hydroxytryptamine metabolism in brains from patients with Alzheimer's dementia. J Neural Transm [Suppl] 30: 33–43
Hachinski VC, Iliff LD, Zilhka E, Du Boulay GH, McAllister VL, Marshall J, Ross Russell RW, Symon L (1975) Cerebral blood flow in dementia. Arch Neurol 32: 632–637
Hyttel J (1977) Effect of a selective 5-HT uptake inhibitor-Lu 10-171 — on rat brain 5-HT turnover. Acta Pharmacol Toxicol 40: 439–446
Hyttel J (1982) Citalopram-pharmacological profile of a specific serotonin uptake inhibitor with antidepressant activity. Prog Neuropsychopharmacol Biol Psychiatry 6: 277–295
Keshavan MJH, Gurbani NK, Dandiya PC (1980) Effect of citalopram (Lu 10-171) on tranylcypromine- and tryptophan-induced wet-dog shakes in rats. Psychopharmacology 70: 209–212
Mann DM, Yates PO (1983) Serotonin nerve cells in Alzheimer's disease [letter]. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry 46: 96–98
Matson WR, Gamache PG, Beal MF, Bird ED (1987) EC array sensor concepts and data. Life Sci 41: 905–908
McKhann G, Drachman D, Folstein M, Katzman R, Price D, Stadlan EM (1984) Clinical diagnosis of Alzheimer's disease: report of the NINCDS-ADRDA Work Group under the Auspices of the Department of Health and Human Services Task Force on Alzheimer's Disease. Neurology 34: 939–944
Moir ATB, Eccleston D (1968) The effects of precursor loading in the cerebral metabolism of 5-hydroxyindoles. J Neurochem 15: 1093–1108
Nyth AL, Gottfries CG (1990) The clinical efficacy of citalopram in treatment of emotional disturbances in dementia disorders. A Nordic multicentre study. Br J Psychiatry 157: 894–901
Román GC (1987) Senile dementia of the Binswanger type. A vascular form of dementia in the elderly. JAMA 258: 1782–1788
Sawada M, Hirata Y, Arai H, Iizuka R, Nagatsu T (1987) Tyrosine hydroxylase, tryptophan hydroxylase, biopterin, and neopterin in the brains of normal controls and patients with senile dementia of Alzheimer type. J Neurochem 48: 760–764
Sparks DL, Markesbery WR, Slevin JT (1986) Alzheimer's disease: monoamines and spiperone binding reduced in nucleus basalis. Ann Neurol 18: 562–565
Stone TW, Connick JH (1985) Quinolinic acid and other kynurenines in the central nervous system. Neuroscience 15: 597–617
Tohgi H, Abe T, Takahashi S, Kimura M, Takahashi J, Kikuchi T (1992) Concentrations of serotonin and its related substances in the cerebrospinal fluid in patients with Alzheimer type dementia. Neurosci Lett 141: 9–12
Tyce GM, Rorie DK, Byer DE, Danielson DR (1985) Free and conjugated amines in human lumbar cerebrospinal fluid. J Neurochem 44: 322–324
Volicer L, Langlais PJ, Matson WR, Mark KA, Gamache PH (1985) Serotoninergic system in dementia of the Alzheimer type: abnormal forms of 5-hydroxytryptophan and serotonin in cerebrospinal fluid. Arch Neurol 42: 1158–1161
Wallin A, Alafuzoff I, Carlsson A, Eckernäs SA, Gottfries CG, Karlsson I, Svennerholm L, Winblad B (1989) Neurotransmitter deficits in a non-multi-infarct category of vascular dementia. Acta Neurol Scand 79: 397–406
Watkins SE, Thomas DE, Clifford M, Tidmarsh SF, Sweeney AE, Ah Sing E, Dickerson JW, Cowie VA, Shaw DM (1989) Plasma amino acids in patients with senile dementia and in subjects with Down's syndrome at an age vulnerable to Alzheimer changes. J Ment Defic Res 33: 159–166
Yamamoto T, Hirano A (1985) Nucleus raphe dorsalis in Alzheimer's disease: neurofibrillary tangles and loss of large neurons. Ann Neurol 17: 573–577
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Tohgi, H., Abe, T., Takahashi, S. et al. Indoleamine concentrations in cerebrospinal fluid from patients with Alzheimer type and Binswanger type dementias before and after administration of citalopram, a synthetic serotonin uptake inhibitor. J Neural Transm Gen Sect 9, 121–131 (1995). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02259654
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02259654